So, as you move down a group on the periodic table, the electronegativity of an element decreases because the increased number of energy levels puts the outer electrons very far away from the pull of the nucleus. Electronegativity
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside fro…
Why does electronegativity increase as you go across a period?
In general, Electronegativity increases across a period because the number of charges on the nucleus increases. That attracts the bonding pair of electrons more strongly. As you go down a group, electronegativity decreases because the bonding pair of electrons is increasingly distant from the attraction of the nucleus.
What are the trends in electronegativity?
This trend is seen as you move across the periodic table from left to right: the electronegativity increases while it decreases as you move down a group of elements. While this is the basic definition of the electronegativity trend, to truly understand it, it would be helpful to put it in perspective and look at some specific examples of the trend.
Why does electronegativity decrease downward?
In basic terms, electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons. Electronegativity decreases as one goes from top to bottom within a group because added energy levels and the shielding of nuclear pull by electrons in lower energy levels weaken the ability of the nucleus to attract electrons.
Why does electronegativity decrease down a group?
Moving down in a group, the electronegativity decreases due to the longer distance between the nucleus and the valence electron shell, thereby decreasing the attraction, making the atom have less of an attraction for electrons or protons.” The electronegativity of hydrogen is 2.1 and for chlorine it’s 3.2.
How does electronegativity increase and decrease on the periodic table?
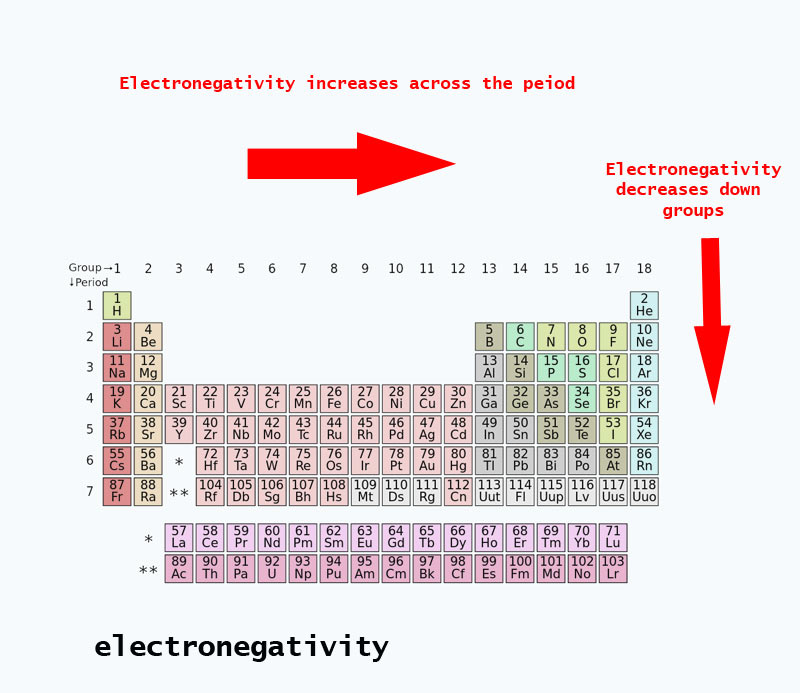
On the periodic table, electronegativity generally increases as you move from left to right across a period and decreases as you move down a group. As a result, the most electronegative elements are found on the top right of the periodic table, while the least electronegative elements are found on the bottom left.
Why does electronegativity increase going across the periodic table?
Electronegativity increases across a period because the number of charges on the nucleus increases. That attracts the bonding pair of electrons more strongly.
Does electronegativity increase or decrease across a period on the periodic table?
The higher the electronegativity, the more desperate for an electron the atom is. o Electronegativity increases from left to right across a period. o The closer the valence shell is to full, the stronger the pull of that atom on the electrons in a bonding pair. Electronegativity decreases down a group.
Why does electronegativity decrease going down the periodic table?
From top to bottom down a group, electronegativity decreases. This is because atomic number increases down a group, and thus there is an increased distance between the valence electrons and nucleus, or a greater atomic radius.
Why does electronegativity increase across the period and decrease down the group?
Electronegativity increases as we move left to the right in the period because as we move across the period, the effective nuclear charge increases and the atomic size decreases. Therefore, the tendency to attract shared pairs of electrons increases, thereby increasing electronegativity.
Why does electronegativity decrease from right to left within a period?
Electronegativity increases on moving along a period from left to right. This is due to the increase in nuclear charge and decrease in atomic size, as a result of which shared electron pair can be attracted more towards itself.
Does electronegativity increases down the group?
Electronegativity generally increases down the group.
Does electronegativity increase from left to right?
Thus, we find that electronegativity increases from left to right across the periodic table. Electronegativity values increase in period 2 in the order C < N < O < F. Electronegativity values decrease from top to bottom within a group of elements.
Why does electronegativity increase as atomic radius decreases?
A relationship is intuitively expected between electronegativity and radius: the size of an atom is determined by the distribution of electrons around its nucleus. The closer the electrons are to the nucleus, the more tightly they are bound, thus increasing the electronegativity of the atom.
How does electronegativity change going down and across the periodic table apex?
1 Answer. Down a group, the electronegativity decreases. Across a period, it increases.
How does the electronegativity change as you move down a group Brainly?
Answer. ❄️As you move down a group on the periodic table, the electronegativity of an element decreases because the increased number of energy levels puts the outer electrons very far away from the pull of the nucleus.
Why does electronegativity decrease down group 7?
As the halogen atoms get bigger, any bonding pair gets further and further away from the halogen nucleus, and so is less strongly attracted towards it. In other words, as you go down the Group, the elements become less electronegative.
Why does electronegativity increase as atomic radius decreases?
A relationship is intuitively expected between electronegativity and radius: the size of an atom is determined by the distribution of electrons around its nucleus. The closer the electrons are to the nucleus, the more tightly they are bound, thus increasing the electronegativity of the atom.
Why does electron affinity increase across a period?
Electron affinity increases going left to right across a period because of increased nuclear attraction.
Why is electronegativity higher at the top of a group?
Group and Period Trends in Electronegativity This is because as you go from top to bottom down a group, the atoms of each element have an increasing number of energy levels. The electrons in a bond are thus farther away from the nucleus and are held less tightly.
Why does it make sense for the valence electrons to increase going across a period?
Across a period, the distance between the nucleus and the valence electrons remains constant but the effective core charge increases. As a result the force of attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons increases across a period.
Which is the best definition of electronegativity?
Electronegativity is a function of an atom’s ability to attract an electrons binding pair. The most frequently used is the Pauling scale. Fluorine...
What is high electronegativity?
Electronegativity decrease as it moves from top to bottom and increases over time from left to right. The most electronegative element is, therefor...
What is the electronegativity difference?
The degree to which an atom attracts electrons in a chemical bond is described by electronegativity. If the difference in electronegativity is grea...
What is the difference between electron affinity and electronegativity?
The difference between the two is that electronegativity is a chemical property that shows how well an atom can attract electrons to itself as the...
Is electronegativity a relative quantity?
Electronegativity is an example of an atom’s ability to attract electrons. It is proportional to the difference between the potential for ionizatio...
How does electronegative vary along the period?
Electronegativity increases as we move left to the right in the period because as we move across the period, the effective nuclear charge increases...
How does electronegative vary in a group?
Electronegativity decreases as we move down the group because as we move down the group, the atomic size increases and the effective nuclear charge...
Name the most electronegative element and least electronegative element in the periodic table?
Fluorine is the most electronegative element, and caesium is the least electronegative element in the periodic table.
How does the electronegativity of an element affect its bonding?
The electronegativity of an element affects the bonding of an element. Elements with high electronegativity tend to form ionic bonds with other ele...
Why does atomic size decrease electronegativity?
A greater atomic size will result in less value of electronegativity, this happens because electrons being far away from the nucleus will experience a lesser force of attraction.
What happens to electronegativity as we move from left to right?
As we move across a period from left to right the nuclear charge increases and the atomic size decreases, therefore the value of electronegativity increases across a period in the modern periodic table. For example, the electronegativity trend across period 3 in the periodic table is depicted below.
What is Electronegativity?
The tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself is known as electronegativity.
What is the power of an atom to attract electrons to itself?
Electronegativity is a chemical property that describes the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. There is a large difference in electronegativity for atoms from the left- and right-hand sides of the periodic table. Electronegativity is an important quantity in determining the nature of bonds between elements ...
What happens when a covalent bond is more electronegative?
In the covalent bonds featuring a large difference in the electronegativities of the bonded atoms, it is not uncommon for the more electronegative atom to gain complete control over the bond pair of electrons , resulting in the formation of two ions. Here, the more electronegative atom forms an anion and the more electropositive atom becomes ...
Why do covalent bonds become polarized?
This occurs because the more electronegative atom pulls the bond pair of electrons closer to itself, developing a partially negative charge in the process (which is usually denoted by the symbol -𝛿). At the same time, the more electropositive atom develops a partial positive charge (denoted by +𝛿). These partial charges are responsible for the polarity of the chemical bond.
How does electronegativity affect covalent bonds?
Impact of Electronegativity on Covalent Bonding. The strength of a covalent bond is highly dependent on the electronegativities of the two bonded atoms (especially the difference in the electronegativities of the bonded atoms). Homonuclear diatomic molecules feature relatively ‘pure’ covalent bonds since the electronegativities ...
Which element is the most electronegative?
And it is no surprise that oxygen, and fluorine are the most electronegative elements.
What is the polarization of an electron?
The polarization is a contest between (i) nuclear charge, and (ii) shielding by other electrons. Incomplete electronic shells shield the nucular charge VERY INEFFECTIVELY, and this is physically manifested in the well-known decrease in atomic radii, from left to right across the Period.
Does electronegativity increase or decrease as we face the periodic table?
As we face the Periodic Table, electronegativity increases ACROSS the Period from LEFT to RIGHT, BUT DECREASES down a Group, a column of the the Periodic Table.
Why does the periodic table increase electronegativity?
Because as you move to the right of the periodic table, each element gets a proton added to it’s nuclei, an what this does (not its only use, obviously)is it increases the attraction between the nuclei and it’s electrons which shrinks the atom, and due to there being greater attraction and a smaller radii, this increases the attraction between the nucleus of an atom, and the valence electrons (electrons that will be participating in reaction)of a different atom which increases the potential of a reaction occurring and therefore increases electronegativity, also as you move from the metals to the non-metals, the ionic charge will start to be negative, which mean that atom will prefer to gain electrons, rather than lose them, this also increases electronegativity. This is what electronegativity is.
What is electronegativity in chemistry?
First, what is electronegativity? Broadly, electronegativity (hereafter, EN) is a measure of an atom’s tendency to attract bonding pairs of electrons. As a general rule, the EN values of elements tends to increase as you move from left to right across the periodic table (with the exception of the noble gases, which do not have EN values).
Why does the size of an atom matter?
Why does that matter? Well, atoms only form bonds with their valence (outermost) electrons, so the size of the atom determines how closely the bonding electrons are held to the atom’s positively charged nucleus. The smaller the atom, the closer the bonding electrons are to the nucleus, and the more tightly they’re held.
How many electrons does a neutral atom of lithium have?
A neutral lithium atom has 3 electrons, a neutral beryllium atom has 4 electrons, and so on. With each extra electron, the negative charge of the electron cloud increases.
Why do elements get proton added to their nuclei?
Because as you move to the right of the periodic table , each element gets a proton added to it’s nuclei, an what this does (not its only use, obviously)is it increases the attraction between the nuclei and it’s electrons which shrinks the atom , and due to there being greater attraction and a smaller radii, this increases the attraction between the nucleus of an atom, and the valence electrons (electrons that will be participating in reaction)of a different atom which increases the potential of a reaction occurring and therefore increases electronegativity, also as you move from the metals to the
How many protons does lithium have?
Consider the second row of the table: lithium has 3 protons, beryllium has 4 protons, boron has 5 protons, etc. With each proton, the positive charge of the nucleus increases.
Why do chlorine-35 and chlorine-37 have the same atomic number?
Chlorine-35 and Chlorine-37 both have the same atomic number because the latter is the number of protons in the nucleus.
What is the measure of the electronegativity of an atom?
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s attraction for the electrons in a bond. Across a period from left to right the electronegativity of atoms increases. As you move from left to right across the periodic table, atoms have a greater nuclear charge and a smaller covalent radius. This allows the nucleus to attract the bonding electrons more ...
What is the screening effect of atoms further down the group?
This screening effect is caused by the extra energy levels and means that atoms further down groups have less attraction for the bonding electrons.
What happens when you move down a group?
Going down a group, the electronegativity of atoms decreases. As you move down a group in the periodic table, atoms increase in size, with a greater number of energy levels. The extra energy levels and increased covalent radius keep the bonding electrons further away from the nucleus.