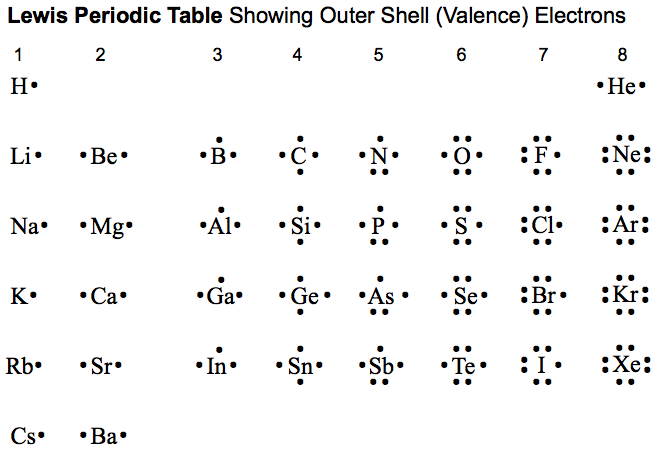
How are the elements grouped in the periodic table?
- Group 1 contains elements containing only 1 valence electron in their atoms, these are called alkali metals such as lithium, sodium, potassium, etc. ...
- Group 2 contains alkaline earth metals like beryllium, magnesium, calcium, and so on have 2 valence electrons. ...
- Group 17 contains halogens like fluorine, chlorine, bromine, etc. ...
How many elements are arranged on the periodic table?
How Many Elements Are There?
- There are 118 elements on periodic table
- The number of protons in an element gives the atomic number of the element
- In 2016 four more elements were added into the periodic table
How do you find elements in the periodic table?
How do you find elements in the periodic table? To find the number of electrons an element has, locate it on the periodic table of elements, find the atomic number, and note the number of protons; because atoms are naturally electrically neutral, the protons and electrons are usually equal. Look at the oxidation number for further information.
How are families of elements arranged in a periodic table?
Three systems have been used to number families and groups:
- The older IUPAC system used Roman numerals together with letters to distinguish between the left (A) and right (B) side of the periodic table.
- The CAS system used letters to differentiate main group (A) and transition (B) elements.
- The modern IUPAC system uses Arabic numbers 1-18, simply numbering the columns of the periodic table from left to right.

How the periodic table is Organised?
The periodic table is arranged by atomic weight and valence electrons. These variables allowed Mendeleev to place each element in a certain row (called a period) and column (called a group).
What are the 3 ways the periodic table is organized?
The periodic table is organized into groups (vertical columns), periods (horizontal rows), and families (groups of elements that are similar).
Why is periodic table arranged the way it is?
Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing weight and broke them into rows such that elements in each column shared valence, the number of other atoms they combined with, as well as other properties.
Why is the periodic table organized by atomic number?
In the modern periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons define the identity of an element (i.e., an element with 6 protons is a carbon atom, no matter how many neutrons may be present).
How is the periodic table organized by reactivity?
Reactivity: The reactivity of the elements increases going from left to right on the periodic table. Each element going from left to right tends to be more reactive.
What are the different groups and periods in the periodic table?
The horizontal rows in the periodic table are called periods. The elements in same period have same no of orbitals and electrons are added in the same valence shell. The vertical columns in the periodic table are called groups. An extra shell is added as we go down the group.
How many groups are in the periodic table?
18The s-, p-, and d-block elements of the periodic table are arranged into 18 numbered columns, or groups. The elements in each group have the same number of valence electrons.
Which statement best explains how periods on the periodic table are organized?
Which statement best explains how periods on the Periodic Table are organized? Increasing atomic number from left to right.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular array of the chemical elements organized by atomic number, from the element with the lowest atomic number, hydrogen...
What do periodic table groups have in common?
The groups of the periodic table are displayed as vertical columns numbered from 1 to 18. The elements in a group have very similar chemical proper...
Where does the periodic table come from?
The arrangement of the elements in the periodic table comes from the electronic configuration of the elements. Because of the Pauli exclusion princ...
Why does the periodic table split?
The periodic table has two rows at the bottom that are usually split out from the main body of the table. These rows contain elements in the lantha...
Why the periodic table was developed
In 1869, Russian chemist Dimitri Mendeleev wanted to see if there was a pattern to the chemical properties of the elements he knew. He found a pattern, listing elements by their increasing atomic number and arranging them in a chart—creating the first periodic table.
How elements are organized on the periodic table
Elements are organized in horizontal rows by increasing atomic number. 4 The atomic number, located at the top left of the element symbol, signifies the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus.
What are periods?
The horizontal rows across the periodic table are called periods. The periodic table contains seven periods 5 (nine if you count the lanthanides and actinide series). In each period, the elements’ atomic numbers increase from left to right.
How are elements added to the table?
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) maintains the periodic table and sets criteria for new additions. 9 IUPAC last updated the periodic table in 2016, adding four new elements: Nihonium (Nh), Moscovium (Mc), Tennessine (Ts) and Oganesson (Og). 10
How to read and interpret the periodic table
The periodic table helps chemists classify elements by properties and similarities. One way to sort the elements is to divide them into three categories: metals, nonmetals and metalloids:
What is the periodic table?
periodic table, in full periodic table of the elements, in chemistry, the organized array of all the chemical elements in order of increasing atomic number —i.e., the total number of protons in the atomic nucleus. When the chemical elements are thus arranged, there is a recurring pattern called the “periodic law” in their properties, ...
Why do the elements in the periodic table have different orbits?
The arrangement of the elements in the periodic table comes from the electronic configuration of the elements. Because of the Pauli exclusion principle, no more than two electrons can fill the same orbital. The first row of the periodic table consists of just two elements, hydrogen and helium. As atoms have more electrons, they have more orbits available to fill, and thus the rows contain more elements farther down in the table.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element . Hydrogen has 1 proton, and oganesson has ...
What elements are triads?
Döbereiner in 1817 showed that the combining weight, meaning atomic weight, of strontium lies midway between those of calcium and barium, and some years later he showed that other such “ triads ” exist (chlorine, bromine, and iodine [halogens] and lithium, sodium, and potassium [alkali metals]). J.-B.-A. Dumas, L. Gmelin, E. Lenssen, Max von Pettenkofer, and J.P. Cooke expanded Döbereiner’s suggestions between 1827 and 1858 by showing that similar relationships extended further than the triads of elements, fluorine being added to the halogens and magnesium to the alkaline-earth metals, while oxygen, sulfur, selenium, and tellurium were classed as one family and nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth as another family of elements.
What are the elements that are related to the first seven?
Newlands proposed classifying the elements in the order of increasing atomic weights, the elements being assigned ordinal numbers from unity upward and divided into seven groups having properties closely related to the first seven of the elements then known: hydrogen, lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen . This relationship was termed the law of octaves, by analogy with the seven intervals of the musical scale.
Who proposed the periodic law?
Then in 1869, as a result of an extensive correlation of the properties and the atomic weights of the elements, with special attention to valency (that is, the number of single bonds the element can form), Mendeleyev proposed the periodic law, by which “the elements arranged according to the magnitude of atomic weights show a periodic change of properties.” Lothar Meyer had independently reached a similar conclusion, published after the appearance of Mendeleyev ’s paper.
Who proposed the atomic weights of the elements?
Attempts were later made to show that the atomic weights of the elements could be expressed by an arithmetic function, and in 1862 A.-E.-B. de Chancourtois proposed a classification of the elements based on the new values of atomic weights given by Stanislao Cannizzaro’s system of 1858.
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).
How does the periodic table organize the elements?
The classic Periodic Table organizes the chemical elements according to the number of protons that each has in its atomic nucleus. (Image credit: Karl Tate, Livescience.com contributor)
How is the Periodic Table arranged?
Hydrogen shares its single valence electron with one of the valence electrons of oxygen; when two hydrogen atoms form these covalent bonds with a single oxygen atom, the result is H2O or water. (Image credit: Encyclopaedia Britannica/UIG Via Getty Images)
What did Mendeleev do to the periodic system?
Mendeleev arranged the elements according to both atomic weight and valence. Not only did he leave space for elements not yet discovered, but he predicted the properties of five of these elements and their compounds. In 1869, he presented the findings to the Russian Chemical Society. His new periodic system was published in the German chemistry periodical Zeitschrift fϋr Chemie (Journal of Chemistry).
Why is the atomic mass of an atom a decimal number?
Individual atoms always have an integer number of atomic mass units; however, the atomic mass on the periodic table is stated as a decimal number because it is an average of the various isotopes of an element. The average number of neutrons for an element can be found by subtracting the number of protons (atomic number) from the atomic mass.
What are superheavy elements?
As such, these outsized elements are fleeting, lasting mere milliseconds before decaying into lighter elements, according to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). For instance, superheavy elements 113, 115, 117 and 118 were verified by the IUPAC in December 2015, completing the seventh row, or period, on the table. Several different labs produced the superheavy elements. The atomic numbers, temporary names and official names are:
What is the atomic symbol for gold?
Also, the atomic symbol for gold if "Au" because the word for gold in Latin is aurum . Atomic weight: The standard atomic weight of an element is the average mass of the element in atomic mass units (amu). Individual atoms always have an integer number of atomic mass units; however, the atomic mass on the periodic table is stated as ...
How are elements arranged in the periodic table?
Elements are arranged from left to right and top to bottom in order of increasing atomic number . Order generally coincides with increasing atomic mass.
What does the periodic table provide?
The periodic table provides the atomic number, atomic mass, symbol and name. Also provides if the elements are metal,non-metal and the state of matter.
What do periods tell you about Bohr?
Periods tell you the number of energy levels in the Bohr model.
Which group does not react easily?
Groups 1,2 and 17 are highly reactive which means they combine chemically with other elements easily. Group 18 does not react easily.
Do metals lose electrons?
Metals have a high density, high melting point, malleable, ductile and good conductors. They lose electrons when combining chemically with nonmetals. The nonmetals are the opposite and are also brittle. They tend to gain electrons when combining chemically with metals. The metalloids are semi-conductors and share the properties of metals and nonmetals.
