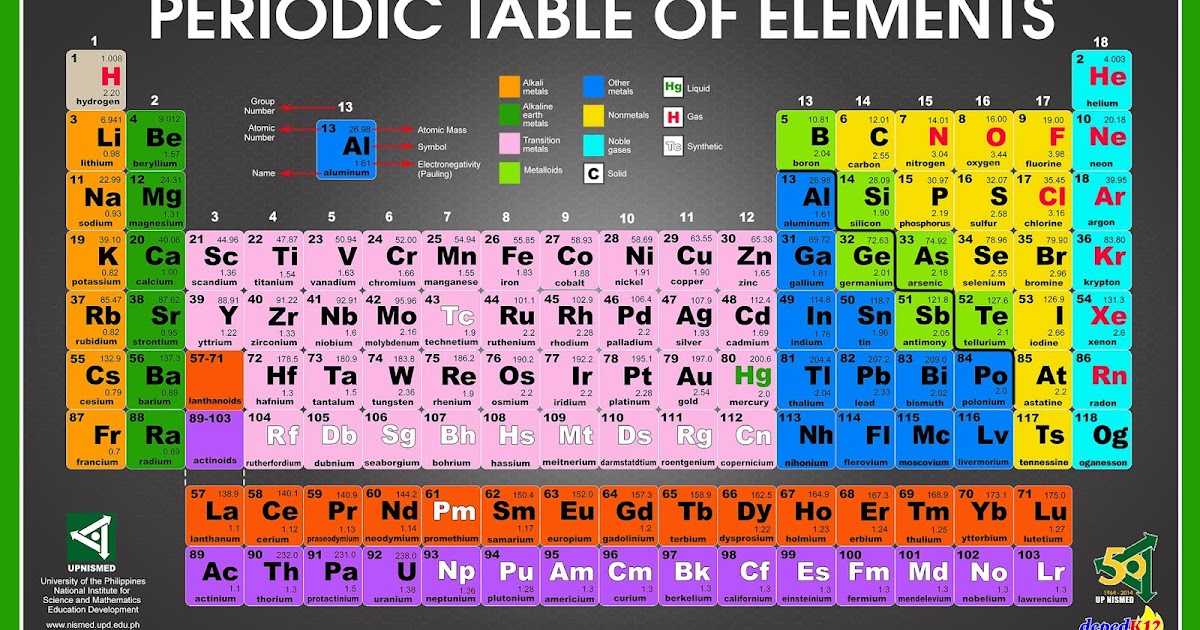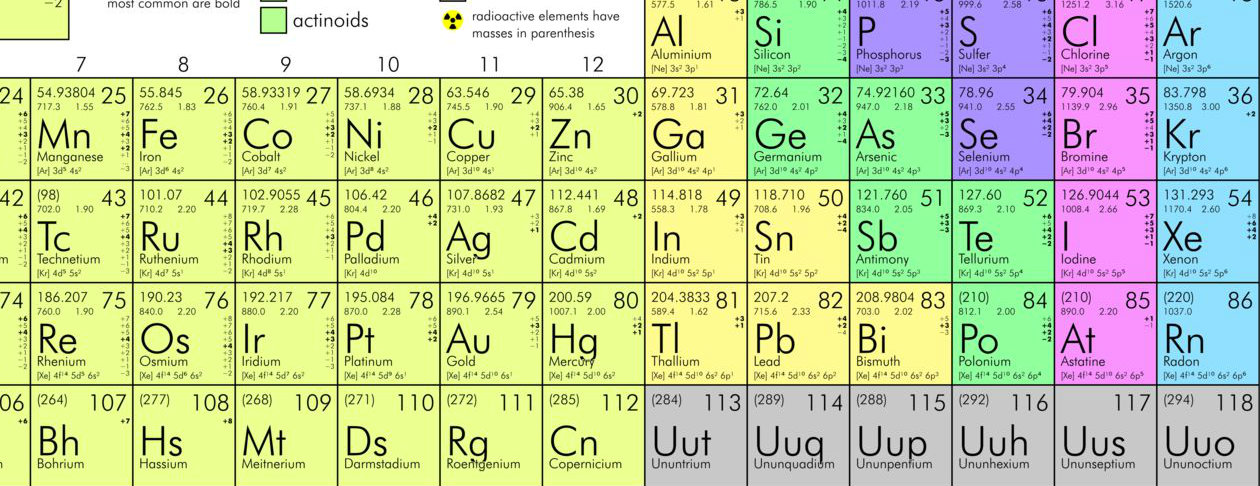
What are the steps of the periodic table in order?
- H - hydrogen
- He - helium
- Li - lithium
- Be - beryllium
- B - boron
- C - carbon
- N - nitrogen
- O - oxygen
- F - fluorine
How are elements put in order in the periodic table?
- The groups are not divided into sub-groups.
- The elements present in a group have the same number of valence electrons and valency.
- The number of shells increases as we go down the group.
- The elements present in a group have identical chemical properties and their physical properties like density, melting point vary gradually.
How are periods and groups arranged on the periodic table?
Summary
- The periodic table is arranged in order of atomic number
- A period is a horizontal row of the periodic table.
- A group is a vertical row of the periodic table.
How many groups are defined in the periodic table?
There are 18 groups or columns in periodic table. They are also called families. The elements with same properties are grouped together. The horizontal rows of the periodic table are periods. The vertical columns are groups.There are 18 groups and 7 periods.
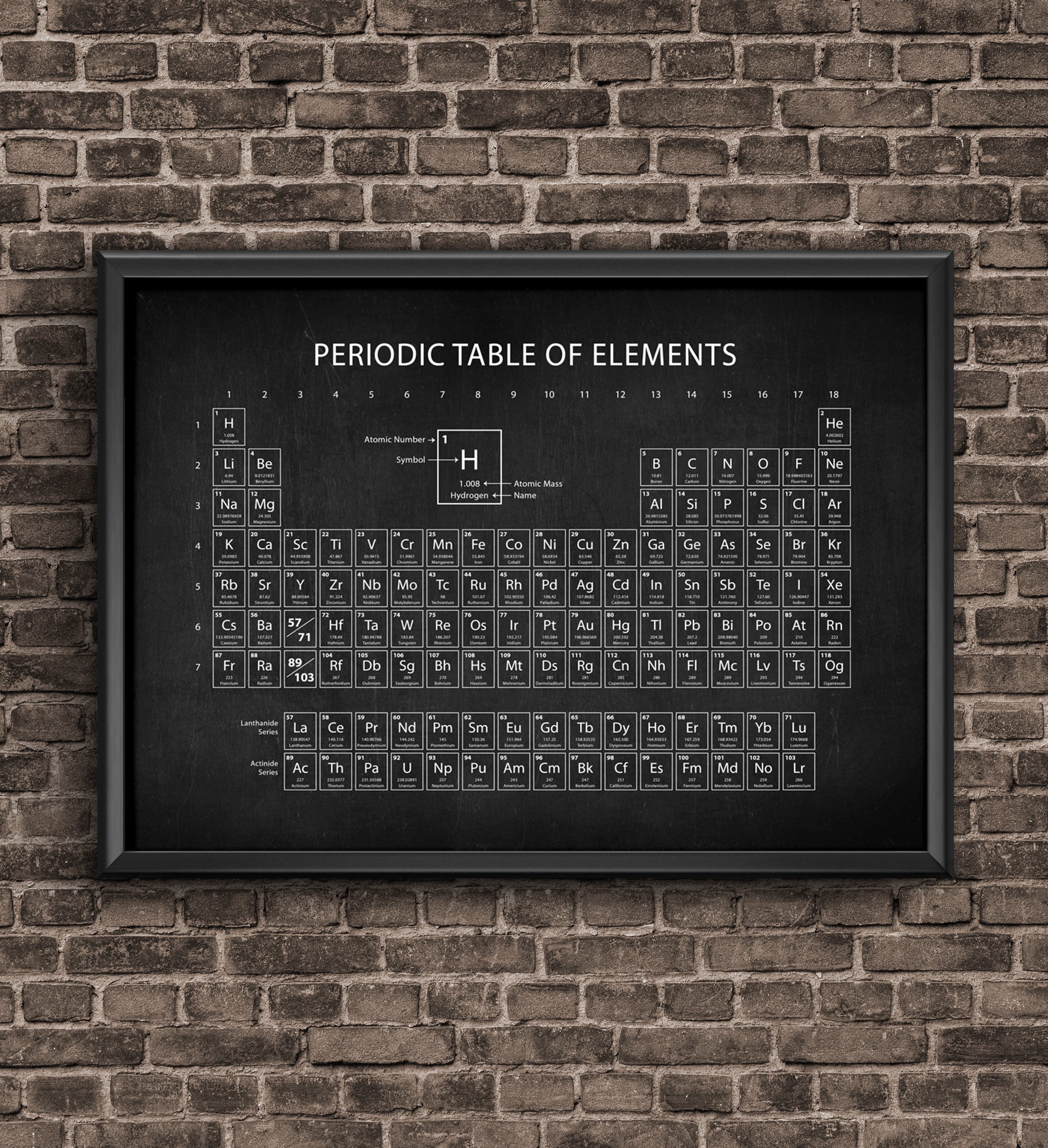
How is the periodic table organizer?
The table is organized by atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus. We can organize the periodic table this way because all atoms of a specific element have the same number of protons.
How the periodic table originated and how it is organized?
In 1869, Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev created the framework that became the modern periodic table, leaving gaps for elements that were yet to be discovered. While arranging the elements according to their atomic weight, if he found that they did not fit into the group he would rearrange them.
How is the periodic table arranged worksheet?
Elements in the periodic table are arranged in periods (rows) and groups (columns). Atomic number increases as you move across a period. Metals are located on the left side of the periodic staircase on the periodic table.
How is the periodic table organized by reactivity?
Reactivity: The reactivity of the elements increases going from left to right on the periodic table. Each element going from left to right tends to be more reactive.
Why is the organization of the periodic table important?
To summarize, the periodic table is important because it is organized to provide a great deal of information about elements and how they relate to one another in one easy-to-use reference. The table can be used to predict the properties of elements, even those that have not yet been discovered.
Why is the periodic table shaped that way?
Why does the periodic table have the structure it does? The answer is rather simple, if you understand electron configurations: the shape of the periodic table mimics the filling of the subshells with electrons. The shape of the periodic table mimics the filling of the subshells with electrons.
How is the periodic table arranged horizontally?
In the periodic table, the elements are arranged in horizontal rows called periods (numbered in blue) and vertically into columns called groups.
Why are elements in the periodic table arranged by atomic numbers?
In the modern periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons define the identity of an element (i.e., an element with 6 protons is a carbon atom, no matter how many neutrons may be present).
What is a periodic table for grade 7?
The periodic table is an organized arrangement of the chemical elements, in order of their atomic number (number of protons), electron configurations, and their chemical properties. This ordering segregates elements according to their periodic trends that are elements with similar behavior in the same column.
What determines the order of elements on today's periodic table?
The elements in the modern periodic table are arranged in order of their atomic numbers, which is the number of protons in the nuclei of the atoms of an element. Each element has a unique atomic number.
What is the periodic table for dummies?
The periodic table arranges the elements in rows and columns. In the rows, the elements are placed in order of their atomic number. The columns form groups of elements that have similar chemical properties. For example, certain gases are in one column and metals are in another.
Why are elements on the periodic table not arranged by mass?
Elements are not ordered by mass, but by atomic number, or the number of protons. This is because ordering them by atomic number causes the properties of elements to repeat due to the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus.
How did Dmitri Mendeleev organize the periodic table?
In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged elements in rows by increasing atomic mass. Within a row, elements with lower atomic masses were on the left. Mendeleev started a new row every time the chemical properties of the elements repeated. Thus, all the elements in a column had similar properties.
Why is the periodic table organized by atomic number?
In the modern periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons define the identity of an element (i.e., an element with 6 protons is a carbon atom, no matter how many neutrons may be present).
How were the elements created?
Light elements like hydrogen and helium formed during the big bang, and those up to iron are made by fusion in the cores of stars. Some heavier elements like gallium and bromine need something more, such as a supernova.
Who created the periodic table?
Dmitri MendeleevAlbert GhiorsoPeriodic table/Inventors
Who is the man credited to contributing the most to the periodic table?
Dimitri Mendeleev
What property did Mendelev propose in 1869?
the properties of the elements were a function of their atomic mass
Mendelev is known for grouping his elements on the basis of what?
increasing order of atomic mass
What is the periodic law?
properties of elements are a function of their atomic number rather than their mass.
What is the periodic table?
A way to organize elements by their atomic number (number of protons) and their similar chemical properties.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular array of the chemical elements organized by atomic number, from the element with the lowest atomic number, hydrogen...
What do periodic table groups have in common?
The groups of the periodic table are displayed as vertical columns numbered from 1 to 18. The elements in a group have very similar chemical proper...
Where does the periodic table come from?
The arrangement of the elements in the periodic table comes from the electronic configuration of the elements. Because of the Pauli exclusion princ...
Why does the periodic table split?
The periodic table has two rows at the bottom that are usually split out from the main body of the table. These rows contain elements in the lantha...
How are the columns in the periodic table organized?
The rows and columns are organized by precise characteristics. The elements that are in the same column or in the same rows have common characteristics. For example, magnesium (Mg) and sodium ...
What is the periodic table called?
Let us investigate periods. After all, that is how the periodic table gets its name. Each of the rows from left to right is called a period. What that means in that each and every one of the elements in a row shares similar electron configurations with the others. Or, in other words, each of the elements in the same row has the exact same number of atomic orbitals.
How many electrons does helium have?
Helium (He) is unique among all the elements. It only has two electrons in its outer orbital, also known as the valence shell. All the other noble gases (group 18) have eight electrons in their outer orbital or valence shell.
How many orbitals does an element have?
If you look at all the elements on the top row or, in other words, the elements in the first period, you will see that all of them have one atomic orbital for their electrons. Then, the elements on the second row, or second period, are characterized by having two atomic orbitals in their electrons.
How to read valence electrons?
You have to read groups from left to right. All the elements in the first column, or group one, have one valence electrons (one electron in their outer shell). All the elements in the second column, or group two, have two valence electrons. But all the elements in the third group (group three), have thirteen valance electrons. From then on, you have to add an electron for every group until reaching 18. Simply, counting the columns will allow you to know how many electrons each element has on its outer shell. There are a few exceptions to this, though, because some elements are transition elements that add electrons.
Why do all elements have one thing in common?
Because they all have one thing in common: their respective valence shells are full. This is how the periodic table is organized. Understanding that the position of each and every one of the elements is useful in understanding their properties.
How many valance electrons are in the third group?
But all the elements in the third group (group three), have thirteen valance electrons. From then on, you have to add an electron for every group until reaching 18. Simply, counting the columns will allow you to know how many electrons each element has on its outer shell.
How are the elements in the periodic table arranged?
The Periodic table elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic number. The arrangement of elements in the Periodic table starts from the very first top left corner. The first element with atomic number 1 (i.e hydrogen) is placed in the first cell, then gradually the elements with atomic number 2, 3, 4 upto 118, ...
Why is the periodic table arranged by atomic number?
Periodic table is arranged by Atomic number because of electrons present in the outermost orbit (which are responsible for the chemical properties of the elements.)
What is the relationship between the number of protons and the number of electrons?
What is a relationship between number of protons and number of electrons? Simple answer: In a neutral atom, the number of protons and number of electrons are equal. For example, this is a neutral helium atom. Here you can see that the helium atom has 2 protons and the number of electrons are also 2.
What does atomic number mean?
Atomic number = Number of electrons. The electrons present in the outermost orbit represent the chemical properties of the elements. Hence to classify the elements on the basis of similarities in their chemical properties, they are arranged in the Periodic table on the basis of atomic number. In other words, Atomic number indicates the number ...
What did Rutherford discover about atoms?
Later on in 1911, Rutherford came up with a discovery of atomic structure, and he found that there are protons and neutrons in the central part of atoms (In other words, Rutherford found that there is a nucleus in the central part of atom which consists of protons and neutrons.)
What are electrons responsible for?
These electrons are responsible for the chemical properties of an element. Hence for grouping the elements according to the similar chemical properties, the elements of the Periodic table are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic number. Later on, we saw that there are groups as well as periods on the Periodic table.
Why are elements 58 to 71 and 90 to 103 in separate rows?
These elements are placed in separate rows at the bottom of the Periodic table because they differ in the chemical properties, plus by placing them at the bottom, ...
What is the periodic table?
periodic table, in full periodic table of the elements, in chemistry, the organized array of all the chemical elements in order of increasing atomic number —i.e., the total number of protons in the atomic nucleus. When the chemical elements are thus arranged, there is a recurring pattern called the “periodic law” in their properties, ...
Why do the elements in the periodic table have different orbits?
The arrangement of the elements in the periodic table comes from the electronic configuration of the elements. Because of the Pauli exclusion principle, no more than two electrons can fill the same orbital. The first row of the periodic table consists of just two elements, hydrogen and helium. As atoms have more electrons, they have more orbits available to fill, and thus the rows contain more elements farther down in the table.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element . Hydrogen has 1 proton, and oganesson has ...
What elements are triads?
Döbereiner in 1817 showed that the combining weight, meaning atomic weight, of strontium lies midway between those of calcium and barium, and some years later he showed that other such “ triads ” exist (chlorine, bromine, and iodine [halogens] and lithium, sodium, and potassium [alkali metals]). J.-B.-A. Dumas, L. Gmelin, E. Lenssen, Max von Pettenkofer, and J.P. Cooke expanded Döbereiner’s suggestions between 1827 and 1858 by showing that similar relationships extended further than the triads of elements, fluorine being added to the halogens and magnesium to the alkaline-earth metals, while oxygen, sulfur, selenium, and tellurium were classed as one family and nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth as another family of elements.
What are the elements that are related to the first seven?
Newlands proposed classifying the elements in the order of increasing atomic weights, the elements being assigned ordinal numbers from unity upward and divided into seven groups having properties closely related to the first seven of the elements then known: hydrogen, lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen . This relationship was termed the law of octaves, by analogy with the seven intervals of the musical scale.
Who proposed the periodic law?
Then in 1869, as a result of an extensive correlation of the properties and the atomic weights of the elements, with special attention to valency (that is, the number of single bonds the element can form), Mendeleyev proposed the periodic law, by which “the elements arranged according to the magnitude of atomic weights show a periodic change of properties.” Lothar Meyer had independently reached a similar conclusion, published after the appearance of Mendeleyev ’s paper.
Who proposed the atomic weights of the elements?
Attempts were later made to show that the atomic weights of the elements could be expressed by an arithmetic function, and in 1862 A.-E.-B. de Chancourtois proposed a classification of the elements based on the new values of atomic weights given by Stanislao Cannizzaro’s system of 1858.
How many elements are in the periodic table?
Based on an earlier (1882) model of T. Bayley, J. Thomsen in 1895 devised a new table. This was interpreted in terms of the electronic structure of atoms by Niels Bohr in 1922. In this table there are periods of increasing length between the noble gases; the table thus contains a period of 2 elements, two of 8 elements, two of 18 elements, one of 32 elements, and an incomplete period. The elements in each period may be connected by tie lines with one or more elements in the following period. The principal disadvantage of this table is the large space required by the period of 32 elements and the difficulty of tracing a sequence of closely similar elements. A useful compromise is to compress the period of 32 elements into 18 spaces by listing the 14 lanthanoids (also called lanthanides) and the 14 actinoids (also called actinides) in a special double row below the other periods.
What is the long period form of the periodic system?
Long-period form of periodic system of elements. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. With the discovery of the noble gases helium, neon, argon, krypton, radon, and xenon by Lord Rayleigh (John William Strutt) and Sir William Ramsay in 1894 and the following years, Mendeleyev and others proposed that a new “zero” group to accommodate them be added to ...
What elements did Mendeleyev predict?
Mendeleyev was also able to predict the existence, and many of the properties, of the then undiscovered elements eka-boron, eka-aluminum, and eka-silicon, now identified with the elements scandium, gallium, and germanium, respectively. Similarly, after the discovery of helium and argon, the periodic law permitted the prediction of the existence ...
How does the atomic weight of an element show its position in the periodic system?
That the exact atomic weight of an element is of small significance for its position in the periodic system is shown by the existence of isotopes of every element —atoms with the same atomic number but different atomic weights. The chemical properties of the isotopes of an element are essentially the same, and all the isotopes of an element occupy the same place in the periodic system in spite of their differences in atomic weight.
Which elements were put in positions out of the order of atomic weights?
In the pairs argon and potassium, cobalt and nickel, and tellurium and iodine, for example, the first element had the greater atomic weight but the earlier position in the periodic system. The solution to this difficulty was found only when the structure of the atom was better understood.
How many spaces are there in a period of 32?
A useful compromise is to compress the period of 32 elements into 18 spaces by listing the 14 lanthanoids (also called lanthanides) and the 14 actinoids (also called actinides) in a special double row below the other periods.
What is the short period of the periodic table?
The “short-period” form of the periodic table, with Groups 0, I , II,…VIII, became popular and remained in general use until about 1930. Short-period form of periodic system of elements, listing the elements known by 1930. At that time it was not clear that thorium (90), protactinium (91), and uranium (92) were part of the actinide series, ...