
How many naturally occurring element are in the periodic table?
The naturally occurring elements in the periodic table include the 94 chemical elements from atomic number 1 to 94. Six of these 94 elements (technetium, promethium, astatine, francium, neptunium, and plutonium) are available in extreme trace amounts.
How many identified elements does the periodic table show?
SHOW ANSWER. Periodic table shows 118 identified elements. So, option C is your answer. Hope this helps! Answer from: erikloza12pdidtx. SHOW ANSWER. C. 118. Explanation: Depending on what version you are using, most periodic tables have more than 92 elements on a periodic table.
What are the first 20 elements?
These are the first 20 elements, listed in order: H - Hydrogen He - Helium Li - Lithium Be - Beryllium B - Boron C - Carbon N - Nitrogen O - Oxygen F - Fluorine Ne - Neon Na - Sodium Mg - Magnesium Al - Aluminum Si - Silicon P - Phosphorus S - Sulfur Cl - Chlorine Ar - Argon K - Potassium Ca - ...
What is 44 on the periodic table?
Atomic Number: 44; Group: 8; Period: 5; Series: Transition Metals. Ruthenium's Name in Other Languages. Latin: Ruthenium; Czech: Ruthenium; Croatian: Rutenij; French: Ruthénium; German: Ruthenium - s; Italian: Rutenio; Norwegian: Ruthenium; Portuguese: Rutênio; Russian: Рутений; Spanish: Rutenio; Swedish: Rutenium. Atomic Structure of Ruthenium. Atomic Radius: 1.89Å
How many elements are there in the periodic table 2022?
118 elementsThis list contains the 118 elements of chemistry.
Are there 119 elements?
Ununennium, also known as eka-francium or element 119, is the hypothetical chemical element with symbol Uue and atomic number 119....UnunenniumAlternative nameselement 119, eka-franciumUnunennium in the periodic table26 more rows
How many elements are there?
118 elementsAt present, 118 elements are known to us. All these have different properties. Out of these 118, only 94 are naturally occurring. As different elements were being discovered, scientists gathered more and more information about the properties of these elements.
Are there 118 elements?
The current standard table contains 118 confirmed elements as of 2021.
Is element 140 possible?
In real-life science, element 140 has yet to be discovered. A placeholder name based on its number, "unquadnilium", has been suggested to document the possible existence of this substance.
What is the 200th element?
Polonium-200 atom | Po - PubChem.
What are 118 elements called?
The permanent names for elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 are nihonium, moscovium, tennessine, and oganesson.
Is fire an element?
Fire is one of the four classical elements along with Earth, Water and Air in ancient Greek philosophy and science. Fire is considered to be both hot and dry and, according to Plato, is associated with the tetrahedron.
What are the main elements?
According to the five elements theory, everything in nature is made up of five elements: Earth, Water, Fire, Air, and Space.
Is element 120 possible?
The Mendeleev table is currently composed of 118 chemical elements. Benoît Gall travelled to Russia and Japan in search of elements 119 and 120, that have never yet been observed.
Are there 112 or 118 elements?
The Periodic Table is made up of 118 Elements.
Is element 122 possible?
Unbibium, also known as element 122 or eka-thorium, is the hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table with the placeholder symbol of Ubb and atomic number 122.
Is there a 120th element?
Unbinilium, also known as eka-radium or simply element 120, is the hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table with symbol Ubn and atomic number 120.
What would element 119 look like?
Thus the IUPAC name for the element 119 is Ununennium. The symbol for this element is uue and has a predicted electronic configuration of 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 8, and 1. M2O and MCl are the formula of its most stable oxide and chloride.
Is there an element 123?
Unbitrium (pronounced /uːnˈbaɪtriəm/), also known as eka-protactinium or element 123, is the possible chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubt and has the atomic number 123.
Has element 122 been discovered?
Despite several attempts, unbibium has not yet been synthesized, nor have any naturally occurring isotopes been found to exist. There are currently no plans to attempt to synthesize unbibium.
What is atomic number?
The atomic number of an element is equal to the total number of protons in the nucleus of the atoms of that element. The atomic number can provide...
What is the atomic number and mass number?
The number of protons and the number of neutrons shall determine the mass number of an element. Since the isotopes of an element have slightly diff...
Can two different elements have the same atomic number?
Atoms from two different elements may have the same neutron count, but never the same proton count. The number of protons is unique to the element...
How do we calculate atomic mass?
Add the mass of protons and neutrons to compute the atomic mass of a single atom of an element. Example: Find the atomic mass of a carbon isotope w...
Why is atomic number important?
Atomic number is called the number of protons in an atom. This number is very important, because it is unique to a given element’s atoms. An elemen...
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).
What is the CIAAW?
Since 1899 the IUPAC Commission on Isotopic Abundances and Atomic Weights ( CIAAW) has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. For example, Carbon had an atomic weight of 12.00 in 1902 but today it is [12.0096, 12.0116]! Times sure have changed as the source of the sample will determine the value.
What is PubChem working with?
PubChem is working with IUPAC to help make information about the elements and the periodic table machine-readable.
Who is responsible for deciding what needs to be changed?
While much of what is in the periodic table is stable and unlikely to change, the IUPAC organization is responsible for deciding what needs to be changed. They have created criteria for what constitutes the discovery of a new element.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Did Mendeleev's predictions get dismissed?
There were plenty of skeptics and it took years to gain international acceptance, but once newly-discovered elements matched the ones that Mendeleev predicted, his patterns could not be dismissed. In addition, some of the properties that he "fudged" were later recalculated and found to be much closer to his predictions.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is equal to the total number of protons in the nucleus of the atoms of that element. The atomic number can provide insight into the electronic configuration of the element. For example, carbon has an electron configuration of [He] 2s 2 2p 2, since its atomic number is 6.
What is the number of protons in the nucleus called?
The number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number. The atomic number of each element is unique.
Why is the atomic number of each element unique?
While the atomic number always stays the same some elements have atoms with different atomic mass numbers. This is because some elements have a different number of neutrons in the nucleus.
How to find the mass of an element?
The number of protons and the number of neutrons shall determine the mass number of an element. Since the isotopes of an element have slightly different mass numbers, it calculates the atomic mass by obtaining the mean of the mass numbers for its isotopes.
How can periodic trends be observed?
Periodic trends in the properties of the elements can be observed down the groups and across the periods of the modern periodic table. Every chemical element has a specific atomic number, which provides insight into the number of protons present within its nucleus.
Why is the atomic number important?
This number is very important, because it is unique to a given element’s atoms. An element’s atoms all have the same number of protons and each element has a different number of protons in its atoms. Test your knowledge on periodic table elements.
What is the name of the tabular arrangement of all the elements on the basis of their respective atomic numbers?
The periodic table is the tabular arrangement of all the chemical elements on the basis of their respective atomic numbers. In the periodic table , the vertical columns are called ‘groups’ and the horizontal rows are called ‘periods’.
What is the energy of ionization?
The first ionization energy is the energy it takes to remove one electron from an atom, the second ionization energy is the energy it takes to remove a second electron from the atom, and so on. For a given atom, successive ionization energies increase with the degree of ionization. For magnesium as an example, the first ionization energy is 738 kJ/mol and the second is 1450 kJ/mol. Electrons in the closer orbitals experience greater forces of electrostatic attraction; thus, their removal requires increasingly more energy. Ionization energy becomes greater up and to the right of the periodic table.
What is the atomic number plotted against?
Atomic number plotted against atomic radius, excluding the noble gases. Atomic radii vary in a predictable and explainable manner across the periodic table. For instance, the radii generally decrease along each period of the table, from the alkali metals to the noble gases; and increase down each group.
What is the electron configuration of a neutral atom?
The electron configuration or organisation of electrons orbiting neutral atoms shows a recurring pattern or periodicity. The electrons occupy a series of electron shells (numbered 1, 2, and so on). Each shell consists of one or more subshells (named s, p, d, f and g). As atomic number increases, electrons progressively fill these shells and subshells more or less according to the Madelung rule or energy ordering rule, as shown in the diagram. The electron configuration for neon, for example, is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. With an atomic number of ten, neon has two electrons in the first shell, and eight electrons in the second shell; there are two electrons in the s subshell and six in the p subshell. In periodic table terms, the first time an electron occupies a new shell corresponds to the start of each new period, these positions being occupied by hydrogen and the alkali metals.
What are metals and nonmetals?
In chronological order, this section discusses metals and nonmetals (and metalloids); categories of elements; groups and periods; and periodic table blocks. While the recognition of metals as solid, fusible and generally malleable substances dates from antiquity, Antoine Lavoisier may have the first to formally distinguish between metals and nonmetals ('non-métalliques') in 1789 with the publication of his 'revolutionary' Elementary Treatise on Chemistry. In 1811, Berzelius referred to nonmetallic elements as metalloids, in reference to their ability to form oxyanions. In 1825, in a revised German edition of his Textbook of Chemistry, he subdivided the metalloids into three classes. These were: constantly gaseous 'gazolyta' (hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen); real metalloids (sulfur, phosphorus, carbon, boron, silicon); and salt-forming 'halogenia' (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine). Only recently, since the mid-20th century, has the term metalloid been widely used to refer to elements with intermediate or borderline properties between metals and nonmetals. Mendeleev published his periodic table in 1869, along with references to groups of families of elements, and rows or periods of his periodic table. At the same time, Hinrichs wrote that simple lines could be drawn on a periodic table in order to delimit properties of interest, such as elements having metallic lustre (in contrast to those not having such lustre). Charles Janet, in 1928, appears to have been the first to refer to the periodic table's blocks.
How many electrons are in neon?
The electron configuration for neon, for example, is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. With an atomic number of ten, neon has two electrons in the first shell, and eight electrons in the second shell; there are two electrons in the s subshell and six in the p subshell. In periodic table terms, the first time an electron occupies a new shell corresponds to ...
What are the columns of periodic table called?
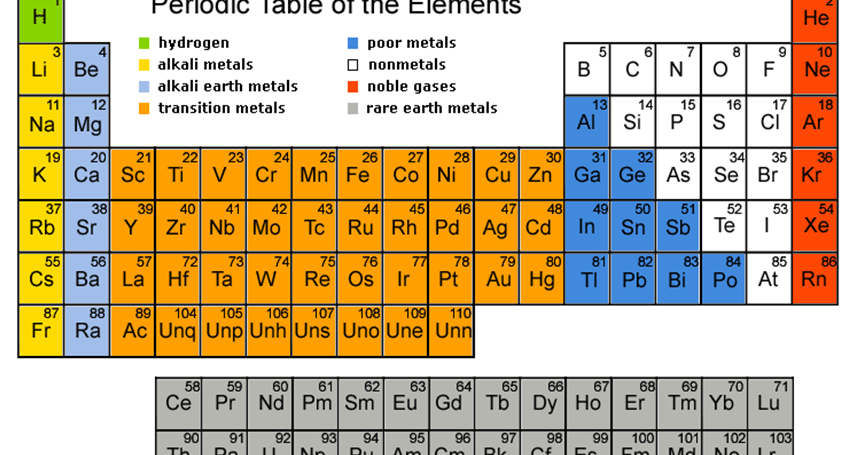
The seven rows of the table, called periods, generally have metals on the left and nonmetals on the right. The columns, called groups , contain elements with similar chemical behaviours.
How many categories are there in the periodic table?
The elements of the periodic table shown here are divided into nine categories; six for the metals, and two for nonmetals, and a metalloid category. The nine categories (or sets) correspond to those found in the literature for the applicable part of the periodic table. Different authors may use different categorisation schema depending on the properties of interest.

Summary
Classification of elements
Many terms have been used in the literature to describe sets of elements that behave similarly. The group names alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, pnictogen, chalcogen, halogen, and noble gas are acknowledged by IUPAC; the other groups can be referred to by their number, or by their first element (e.g., group 6 is the chromium group). Some divide the p-block elements from groups 13 to …
Overview
The periodic table is a 2-dimensional structured table. The elements are placed in table cells, in reading order of ascending atomic number. The table columns are called groups, the rows are called periods. The breaks at the end of each period occur according to a repetition (or periodicity) of physical and chemical properties of the elements.
Periodic trends
As chemical reactions involve the valence electrons, elements with similar outer electron configurations may be expected to react similarly and form compounds with similar proportions of elements in them. Such elements are placed in the same group, and thus there tend to be clear similarities and trends in chemical behaviour as one proceeds down a group. As analogous configurations return …
History
In 1817, German physicist Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner began to formulate one of the earliest attempts to classify the elements. In 1829, he found that he could form some of the elements into groups of three, with the members of each group having related properties. He termed these groups triads. Chlorine, bromine, and iodine formed a triad; as did calcium, strontium, and barium; lithi…
Current questions
Although the modern periodic table is standard today, some variation can be found in period 1 and group 3. Discussion is ongoing about the placements of the relevant elements. The controversy has to do with conflicting understandings of whether chemical or electronic properties should primarily decide periodic table placement, and conflicting views of how the evidence should be used. A similar potential problem has been raised by theoretical investigations of the superheav…
Future extension beyond the seventh period
The most recently named elements – nihonium (113), moscovium (115), tennessine (117), and oganesson (118) – completed the seventh row of the periodic table. Future elements would have to begin an eighth row. These elements may be referred to either by their atomic numbers (e.g. "element 119"), or by the IUPAC systematic element names which directly relate to the atomic …
Alternative periodic tables
The periodic law may be represented in multiple ways, of which the standard periodic table is only one. Within 100 years of the appearance of Mendeleev's table in 1869, Edward G. Mazurs had collected an estimated 700 different published versions of the periodic table. Many forms retain the rectangular structure, including Janet's left-step periodic table (pictured below), and the m…