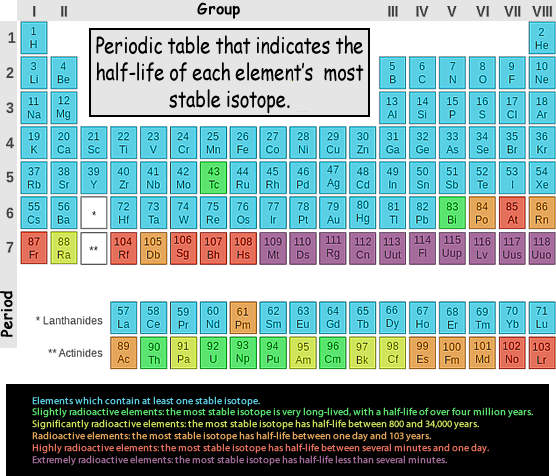
Radioactive Elements List
| Radioactive Element | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass Number | Decay Type | Half-Life |
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | 3 | Beta Decay (β –) | 12.32 years |
| Beryllium (Be) | 4 | 7 | Electron Capture (ε), Gamma Decay) | 53.12 Days |
| Beryllium (Be) | 4 | 8 | Alpha | 7 x 10 -17 sec |
| Beryllium (Be) | 4 | 10 | Beta Decay (β –) | 1,360,000 years |
What is the most common radioactive element?
What is the most common radioactive element? Polonium. Because it is a naturally-occurring element that releases a huge amount of energy, many sources cite polonium as the most radioactive element. Polonium is so radioactive it glows blue, which is caused by excitation of the gas particles by radiation.
How many elements are radioactive?
With that said, 38 elements can be considered radioactive if we take the meaning to be that their most commonly found isotope is radioactive. these elements either have no stable isotopes, ridiculously long half-lives, or else are entirely artificial (all artificial elements have no stable isotopes).
What are the least reactive elements in the periodic table?
Which Is the Least Reactive Element on the Periodic Table? Neon is the least reactive element on the periodic table. As a noble gas, neon is colorless and odorless with extremely low reactivity in its natural state. Neon has an atomic number of 10.
What is the craziest element in the periodic table?
What is the craziest element in the periodic table? Caesium (element 55) Explodes in contact with water, in a much more dramatic fashion than its other alkali-metal brethren. Francium (element 87) Fluorine (element 9) Carbon (element 6) Osmium (element 76) Curium (element 96) Thallium (element 81) Mercury.

What is the term for the element that emits ionizing radiation?
Elements that emit ionizing radiation are called radionuclides. When it decays, a radionuclide transforms into a different atom - a decay product. The atoms keep transforming to new decay products until they reach a stable state and are no longer radioactive.
What is radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay is the emission of energy in the form of ionizing radiation ionizing radiation Radiation with so much energy it can knock electrons out of atoms. Ionizing radiation can affect the atoms in living things, so it poses a health risk by damaging tissue and DNA in genes.. The ionizing radiation that is emitted can include alpha particles alpha particle A form of particulate ionizing radiation made up of two neutrons and two protons. Alpha particles pose no direct or external radiation threat; however, they can pose a serious health threat if ingested or inhaled., beta particles beta particle A form of particulate ionizing radiation made up of small, fast-moving particles. Some beta particles are capable of penetrating the skin and causing damage such as skin burns. Beta-emitters are most hazardous when they are inhaled or swallowed. and/or gamma rays gamma rays A form of ionizing radiation that is made up of weightless packets of energy called photons. Gamma rays can pass completely through the human body; as they pass through, they can cause damage to tissue and DNA.. Radioactive decay occurs in unbalanced atoms called radionuclides.
What is gamma radiation?
gamma rays A form of ionizing radiation that is made up of weightless packets of energy called photons. Gamma rays can pass completely through the human body; as they pass through, they can cause damage to tissue and DNA. . Radioactive decay occurs in unbalanced atoms called radionuclides.
How long does a radionuclide decay?
Every radionuclide has a specific decay rate, which is measured in terms of ". half-life. half-life The time required for half of the radioactive atoms present to decay or transform. Some radionuclides have half-lives of mere seconds, but others have half-lives of hundreds or millions of years. .".
What are alpha particles?
alpha particles A form of particulate ionizing radiation made up of two neutrons and two protons. Alpha particles pose no direct or external radiation threat; however, they can pose a serious health threat if ingested or inhaled. ,
Is each series of radionuclides radioactive?
Each series has its own unique decay chain. The decay products within the chain are always radioactive. Only the final, stable atom in the chain is not radioactive. Some decay products are a different chemical element. Every radionuclide has a specific decay rate, which is measured in terms of ".
Is an element stable or unstable?
Some of these forms are stable; other forms are unstable. Typically, the most stable form of an element is the most common in nature. However, all elements have an unstable form. Unstable forms emit ionizing radiation and are radioactive.
What is the color of the life span of the periodic table?
This graphic plots the life spans, or half-lives, of the periodic table’s unstable elements (blue) on a logarithmic scale. Data for each element’s longest-lived form, or isotope, are included, along with familiar comparisons (green).
What is the timescale of radioactive decay?
The timescale of radioactive decay is known as an element’s half-life, the time it takes for a sample of an element to be reduced by half. Generally for the elements after uranium, the further along they are on the periodic table — the higher their atomic number — the less time they last.
What is the half life countdown?
HALF-LIFE COUNTDOWN Generally, for elements after uranium on the periodic table, the further along elements are — the higher their atomic number — the less time they endure. KamilSD/Alamy Stock Photo.
How do elements decay?
But others have only unstable forms, all of which decay by emitting radiation and transforming into different elements until becoming one that’s stable. The timescale of radioactive decay is known as an element’s half-life, the time it takes for a sample of an element to be reduced by half.
How many orders of magnitude does the Milky Way have?
Half-lives of unstable elements vary by nearly 30 orders of magnitude. For comparison, the Milky Way’s diameter is about 30 orders of magnitude larger than the width of a DNA helix. The graphic below charts the time it takes for the longest-lived isotope — a form having the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons — of each ...
Will all future elements have shorter and shorter half lives?
Will all future elements discovered have shorter and shorter half-lives? Scientists aren’t so sure. They expect to reach a theoretical “island of stability,” where half-lives will buck the trend. These elements might last a few seconds, or a day. No one knows what properties they’ll have, or if these elements could help scientists learn more about how the atom — and thus all of matter — holds itself together. And so researchers keep smashing atoms together, hoping to paddle closer to the island’s fabled shore.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number refers to the number of protons found in the atom of an element . Elements can be categorized into three major groups that include metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. The elements found on the left side of the periodic table are typically metals. While the elements on the right side of the periodic table are non-metals.
How many elements are in pure form?
Thirty-two of the 98 elements are in their pure form. The rest exist as compounds. Eighty of the natural elements are stable, meaning that they cannot be subjected to radioactive decay. Ten of the 98 elements only exist in trace amounts. Typically, all the elements of the periodic table with a higher atomic number than lead are unstable, ...
What is the difference between francium and native elements?
Native elements, on the other hand, are naturally occurring elements in an uncombined form.
What does the number of protons in an element mean?
The number of protons in an element gives the atomic number of the element. An element refers to a substance made of atoms of the same kind. All the atoms in a particular element bear the same atomic number. Elements cannot be broken further into smaller substances using chemical reactions. However, they can only be transformed into other elements ...
What are the properties of an element?
The periodic table outlines each element’s electron configuration, the atomic number of the element, and the chemical properties of the element. The atomic number refers to the number of protons found in the atom of an element.
What are the elements that are found naturally?
Non-metals that fall into this category include nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon.
Is synthetic element unstable?
However, unlike natural elements that can be handled, these synthetic elements are likely to be unstable, thus decaying quickly. Nonetheless, there is a possibility for more exciting discoveries in the atomic world.
