What are the three general groups on the periodic table?
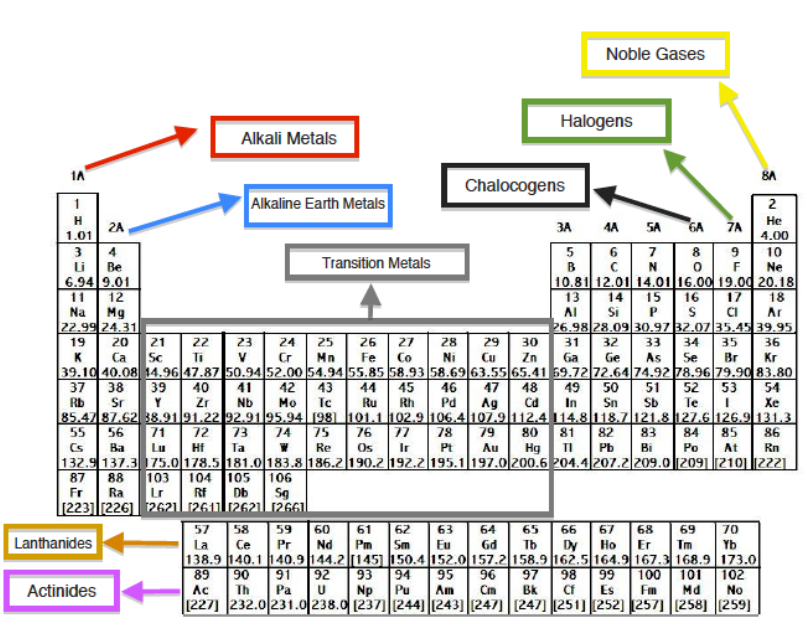
Periodic Table Groups. Group 1: Alkali Metals. Alkali metals are soft, ductile, and good conductors of electricity and heat. This group includes the elements Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium, Cesium, and Francium. Alkali metals are very reactive. Compared to other elements they have a low melting and boiling point. Group 2: Alkaline Earth ...
What are the groups and families on the periodic table?
The vertical columns on the periodic table are called groups or families because of their similar chemical behavior. All the members of a family of elements have the same number of valence electrons and similar chemical properties. The horizontal rows on the periodic table are called periods. Group (family): A vertical column in the periodic table.
What is Group 10 on the periodic table called?
What is Group 10 on the periodic table called? Group 10, numbered by current IUPAC style, is the group of chemical elements in the periodic table that consists of nickel (Ni), palladium (Pd), platinum (Pt), and perhaps also the chemically uncharacterized darmstadtium (Ds). All are d-block transition metals.
What does the group number represent in the periodic table?
The group number in the periodic table represents number of valence electrons of the elements in a certain group. For example, all the elements in Group−1 have 1 electron in their outer most shell.

Are there 8 or 18 groups in the periodic table?
In chemistry, a group (also known as a family) is a column of elements in the periodic table of the chemical elements. There are 18 numbered groups in the periodic table; the f-block columns (between groups 2 and 3) are not numbered.
Are there 7 groups in the periodic table?
Groups are the columns of the periodic table, and periods are the rows. There are 18 groups, and there are 7 periods plus the lanthanides and actinides.
What are the 8 groups of the periodic table?
Name of the eight groups in the periodic table:Alkali metals.Alkaline earth metals.Rare earth metals.Crystallogens.Pnictogens.Chalcogens.Halogens.Noble gases.
What are the 13 groups on the periodic table?
Groups 13-16 | Periodic TableGroup 1: Hydrogen And Alkali Metals.Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals.Groups 3-12: Transition Metals.Groups 13-16.Group 17: Halides.Group 18: Noble Gases.Lanthanoids.Actinoids.
Are there 7 or 18 groups in the periodic table?
In the modern periodic table, there are 18 groups and 7 periods.
Why do we have 18 groups?
The s-, p-, and d-block elements of the periodic table are arranged into 18 numbered columns, or groups. The elements in each group have the same number of valence electrons. As a result, elements in the same group often display similar properties and reactivity.
What is Group 13 called?
boron group elementboron group element, any of the six chemical elements constituting Group 13 (IIIa) of the periodic table. The elements are boron (B), aluminum (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), thallium (Tl), and nihonium (Nh).
What are the 18 groups of the periodic table?
There are total 18 different groups in Periodic table.Group 1: Alkali metals group (hydrogen not included)Group 2: Alkaline earth metals group.Group 3-12: Transition and Inner transition metals group.Group 13: Boron group.Group 14: Carbon group.Group 15: Nitrogen group.Group 16: Oxygen group.Group 17: Halogen group.More items...•
What are the 11 groups on the periodic table?
Group 11, by modern IUPAC numbering, is a group of chemical elements in the periodic table, consisting of copper, silver, and gold. Roentgenium is also placed in this group in the periodic table, although no chemical experiments have yet been carried out to confirm that it behaves like the heavier homologue to gold.
What is group 15 called?
Group 15 elements are also called the Nitrogen family. It includes nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony and bismuth elements.
What is Group 14 called?
carbon group element, any of the six chemical elements that make up Group 14 (IVa) of the periodic table—namely, carbon (C), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), and flerovium (Fl).
What is a group of 16 called?
So, group-16 elements are named chalcogens. Thus, the correct answer is (B). Note: Note that Polonium is the only radioactive element in the group-16 of the periodic table. Remember that oxygen, sulphur and selenium are nonmetals. Tellurium is considered as a metalloid.
What is group 7 also known as?
Group 7A (or VIIA) of the periodic table are the halogens: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). The name "halogen" means "salt former", derived from the Greek words halo- ("salt") and -gen ("formation").
What is 7 on the periodic table?
N NitrogenThe Elements, sorted by Atomic NumberAtomic NumberSymbolName6CCarbon7NNitrogen8OOxygen9FFluorine76 more rows
What is Group 8 called?
the noble gasesGroup 8A (or VIIIA) of the periodic table are the noble gases or inert gases: helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn).
Is halogen group 7 or 17?
The halogen elements are the six elements in Group 17 of the periodic table. Group 17 occupies the second column from the right in the periodic table and contains fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts).
How does the periodic table organize the elements?
The classic Periodic Table organizes the chemical elements according to the number of protons that each has in its atomic nucleus. (Image credit: Karl Tate, Livescience.com contributor)
Which group of the periodic table is alkaline earth metals in?
Alkaline-earth metals: The alkaline-earth metals make up Group 2 of the periodic table, from beryllium (Be) through radium (Ra). Each of these elements has two electrons in its outermost energy level, which makes the alkaline earths reactive enough that they're rarely found alone in nature. But they're not as reactive as the alkali metals. Their chemical reactions typically occur more slowly and produce less heat compared to the alkali metals.
What are the groups of metals that are radioactive?
All are radioactive. The actinides and the lanthanides together form a group called the inner transition metals. Transition metals: Returning to the main body of the table, the remainder of Groups 3 through 12 represent the rest of the transition metals.
What are the elements in the actinides?
Actinides: The actinides line the bottom row of the island and comprise elements 89, actinium (Ac), through 103, lawrencium (Lr). Of these elements, only thorium (Th) and uranium (U) occur naturally on Earth in substantial amounts. All are radioactive. The actinides and the lanthanides together form a group called the inner transition metals.
What is table salt?
The table salt in your kitchen, for example, is a marriage between the alkali metal sodium and the halogen chlorine. Noble gases: Colorless, odorless and almost completely nonreactive, the inert, or noble gases round out the table in Group 18.
How many elements were there at the time of Mendeleev?
There were only about 60 elements known at the time, but Mendeleev realized that when the elements were organized by weight, certain types of elements occurred in regular intervals, or periods. Today, 150 years later, chemists officially recognize 118 elements (after the addition of four newcomers in 2016) and still use Mendeleev's periodic table ...
Why is the period of sodium longer?
Moving down the table, periods are longer because it takes more electrons to fill the larger and more complex outer levels. The columns of the table represent groups, or families, of elements.
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).
How many categories are there in the periodic table?
The elements of the periodic table shown here are divided into nine categories; six for the metals, and two for nonmetals, and a metalloid category. The nine categories (or sets) correspond to those found in the literature for the applicable part of the periodic table. Different authors may use different categorisation schema depending on the properties of interest.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of elements, is a tabular display of the chemical elements, which are arranged by atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The structure of the table shows periodic trends. The seven rows of the table, called periods, generally have metals on ...
What is the atomic number plotted against?
Atomic number plotted against atomic radius, excluding the noble gases. Atomic radii vary in a predictable and explainable manner across the periodic table. For instance, the radii generally decrease along each period of the table, from the alkali metals to the noble gases; and increase down each group.
What is the electron configuration of a neutral atom?
The electron configuration or organisation of electrons orbiting neutral atoms shows a recurring pattern or periodicity. The electrons occupy a series of electron shells (numbered 1, 2, and so on). Each shell consists of one or more subshells (named s, p, d, f and g). As atomic number increases, electrons progressively fill these shells and subshells more or less according to the Madelung rule or energy ordering rule, as shown in the diagram. The electron configuration for neon, for example, is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. With an atomic number of ten, neon has two electrons in the first shell, and eight electrons in the second shell; there are two electrons in the s subshell and six in the p subshell. In periodic table terms, the first time an electron occupies a new shell corresponds to the start of each new period, these positions being occupied by hydrogen and the alkali metals.
What are metals and nonmetals?
In chronological order, this section discusses metals and nonmetals (and metalloids); categories of elements; groups and periods; and periodic table blocks. While the recognition of metals as solid, fusible and generally malleable substances dates from antiquity, Antoine Lavoisier may have the first to formally distinguish between metals and nonmetals ('non-métalliques') in 1789 with the publication of his 'revolutionary' Elementary Treatise on Chemistry. In 1811, Berzelius referred to nonmetallic elements as metalloids, in reference to their ability to form oxyanions. In 1825, in a revised German edition of his Textbook of Chemistry, he subdivided the metalloids into three classes. These were: constantly gaseous 'gazolyta' (hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen); real metalloids (sulfur, phosphorus, carbon, boron, silicon); and salt-forming 'halogenia' (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine). Only recently, since the mid-20th century, has the term metalloid been widely used to refer to elements with intermediate or borderline properties between metals and nonmetals. Mendeleev published his periodic table in 1869, along with references to groups of families of elements, and rows or periods of his periodic table. At the same time, Hinrichs wrote that simple lines could be drawn on a periodic table in order to delimit properties of interest, such as elements having metallic lustre (in contrast to those not having such lustre). Charles Janet, in 1928, appears to have been the first to refer to the periodic table's blocks.
How many electrons are in neon?
The electron configuration for neon, for example, is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. With an atomic number of ten, neon has two electrons in the first shell, and eight electrons in the second shell; there are two electrons in the s subshell and six in the p subshell. In periodic table terms, the first time an electron occupies a new shell corresponds to ...
What are the columns of periodic table called?
The seven rows of the table, called periods, generally have metals on the left and nonmetals on the right. The columns, called groups , contain elements with similar chemical behaviours.
How many periods are there in the periodic table?
Elements within a period display periodic table trends, moving from left to right, involving atomic and ionic radius, electronegativity, There are seven element periods. Some periods contain more elements than others because the number of included elements depends on the number of electrons allowed in an energy sublevel.
What is the difference between periodic table groups and periods?
Periodic Table Groups and Periods. A periodic table group is a column, while a periodic table period is a row. Groups and periods organize elements on the periodic table of the elements. A group is a vertical column down the periodic table, while a period is a horizontal row across the table. Both groups and periods reflect the organization ...
What are the elements that chemists classify?
These groups go by the names alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, basic metals, nonmetals, halogens, noble gases, lanthanides, and actinides.
How many valence electrons are in group 17?
For example, elements in group 1 have 1 valence electron, elements in groups 3-12 have a variable number of valence electrons, and elements in group 17 have 7 valence electrons. The lanthanides and actinides, located below the main table, all fit within group 3.
How does the atomic number of an element increase?
Element atomic number increases as you move down a group from top to bottom or across a period from left to right. An element group is a vertical column on the periodic table. Atoms in a group share the same number of valence electrons. An element period is a horizontal row on the periodic table. Atoms in a period have the same number ...
What are the different types of nonmetals?
The nonmetals, halogens, and noble gases are all types of nonmetals. The metalloids have properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals. The alkali metals, alkaline earths, lanthanides, actinides, transition metals, and basic metals are all groups of metals.
How many periods are there in the periodic table?
Periods are the horizontal rows of the periodic table. There are seven periods total and each element in a period has the same number of atomic orbitals. The top period, which contains hydrogen and helium, has only two orbitals. As you go down the rows, the number of orbitals increases.
How are elements organized in the periodic table?
The periodic table is organized into groups (vertical columns), periods (horizontal rows), and families (groups of elements that are similar). Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. Meanwhile, elements in the same period have the same number of occupied electron shells. In 1869 Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev noticed there existed an innate pattern of organization for the chemical elements. From this deduction, he formed the periodic table. It is important to note how the location of elements on this table tells us about their properties. A quick way to understand an element’s chemical and physical properties is to know the periodic trends. These trends tell you where the highest and lowest types of properties are concentrated on the periodic table. For a more in-depth explanation of periodic trends, click here.
What group are alkali metals in?
The Alkali Metals (Group 1) The alkali metals consist of all of the elements in group one with the exception of hydrogen. These elements are extremely reactive and for this reason, are usually found in compounds. In addition, they are water-sensitive (they react violently with water), so they must be stored in oil.
What are noble gases?
The noble gases, also called aerogens, are inert gases. Some examples include argon, krypton, and neon. They can be found in group eighteen on the periodic table. Likewise, this means they have a complete valence shell. For this reason, they are stable and relatively unreactive.
What is an element in the periodic table?
Vocabulary. Elements: A pure substance composed of a single atom. Groups: The vertical column of the periodic table that signifies the number of valence electrons in an element. Periods: The horizontal rows in the periodic table that signify the number of electron shells in an element. Families: Elements that have the same number ...
What is the name of the group of elements that are found in the three states of matter at standard temperature?
The name halogen means “salt formers” in greek. This is evident in nature as halogens interact with metals to form various salts. On another note, the halogens are a unique group of elements. They are the only periodic family that contains elements in the three states of matter at standard temperature. There are 6 halogens and they are located in group 17. These elements include fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). They are highly reactive, highly electronegative, and highly toxic non-metals.
Which metals are the second most reactive?
The alkaline earth metals are the second most reactive family on the periodic table (following behind the alkali metals). Moreover, they are strong reducing agents which means they donate electrons in chemical reactions. They are also good thermal and electrical conductors.
Answer
A group is a vertical column of the periodic table based on the organization of the outer shell electrons. There are a total of 18 groups. From left to right in the periodic table, there are two groups (1 and 2) of elements in the hydrogen block, ten groups (3 through 12) in the transition block, and six groups (13 through 18) in the main block.
New questions in Physics
a Explain why the sound produced by the horn of an approaching car seems to have a higher frequency than one that is stationary.

Summary
Overview
The periodic table is a 2-dimensional structured table. The elements are placed in table cells, in reading order of ascending atomic number. The table columns are called groups, the rows are called periods. The breaks at the end of each period occur according to a repetition (or periodicity) of physical and chemical properties of the elements.
Periodic trends
As chemical reactions involve the valence electrons, elements with similar outer electron configurations may be expected to react similarly and form compounds with similar proportions of elements in them. Such elements are placed in the same group, and thus there tend to be clear similarities and trends in chemical behaviour as one proceeds down a group. As analogous configurations return …
Classification of elements
Many terms have been used in the literature to describe sets of elements that behave similarly. The group names alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, pnictogen, chalcogen, halogen, and noble gas are acknowledged by IUPAC; the other groups can be referred to by their number, or by their first element (e.g., group 6 is the chromium group). Some divide the p-block elements from groups 13 to …
History
In 1817, German physicist Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner began to formulate one of the earliest attempts to classify the elements. In 1829, he found that he could form some of the elements into groups of three, with the members of each group having related properties. He termed these groups triads. Chlorine, bromine, and iodine formed a triad; as did calcium, strontium, and barium; lithi…
Current questions
Although the modern periodic table is standard today, some variation can be found in period 1 and group 3. Discussion is ongoing about the placements of the relevant elements. The controversy has to do with conflicting understandings of whether chemical or electronic properties should primarily decide periodic table placement, and conflicting views of how the evidence should be used. A similar potential problem has been raised by theoretical investigations of the superheav…
Future extension beyond the seventh period
The most recently named elements – nihonium (113), moscovium (115), tennessine (117), and oganesson (118) – completed the seventh row of the periodic table. Future elements would have to begin an eighth row. These elements may be referred to either by their atomic numbers (e.g. "element 119"), or by the IUPAC systematic element names which directly relate to the atomic …
Alternative periodic tables
The periodic law may be represented in multiple ways, of which the standard periodic table is only one. Within 100 years of the appearance of Mendeleev's table in 1869, Edward G. Mazurs had collected an estimated 700 different published versions of the periodic table. Many forms retain the rectangular structure, including Janet's left-step periodic table (pictured below), and the m…