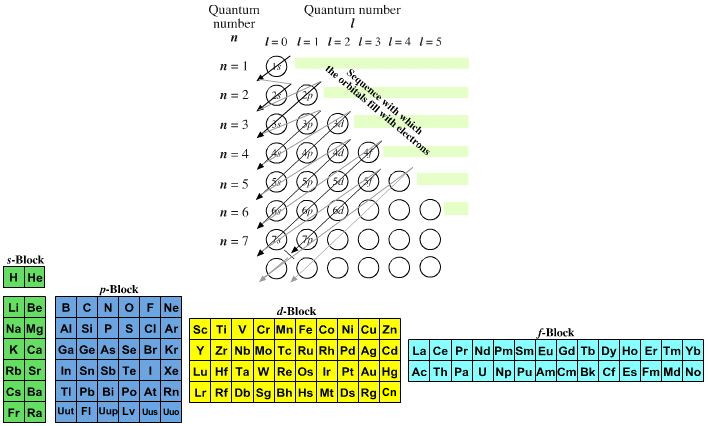
What are the 4 blocks of the periodic table?
- s-block.
- p-block.
- d-block.
- f-block.
Can identify the four blocks of the periodic table?
There are 4 blocks in the periodic table. The blocks are: s-block. p-block. d-block. f-block. All the elements in a block are very similar but each one is slightly different than the other. All of the s-block elements are metals. Generally they are shiny, silvery, good conductors of heat and electricity, and lose their valence electrons easily.
What do the different blocks on the periodic table represent?
What does each block of the periodic table represent? A block of the periodic table is a set of chemical elements having their differentiating electrons predominately in the same type of atomic orbital. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital: s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block. Click to see full answer.
What are the individual blocks on the periodic table called?
- s-block. The first two groups of the periodic table, the s-block metals:
- p-block. P-block elements include the last six element groups of the periodic table, excluding helium.
- d-block.
- f-block.

What is an orbital block on the periodic table?
A block of the periodic table is a set of elements unified by the atomic orbitals their valence electrons or vacancies lie in. The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital: s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block.
How many types of blocks are there in the periodic table?
These elements have electrons in the f orbital (1 to 14), the penultimate energy level d orbital (0 to 1), and the outermost orbital. So, we conclude that the 4 blocks of the periodic table are s,p,d and f.
How many elements are in each block?
The s-block is situated on the left-hand side of the periodic table. It contains 13 elements in two groups (1 and 2). p-block elements: Those elements (except He) in which the last electron enters into the p-subshell of the outermost main energy level, are called p-block elements.
What are s-block p-block d-block and f-block elements called?
s-Block, p-block, and Group 12 elements are called main group elements and d-block elements other than Group 12 and f-block elements are called transition elements.
Where are the 4 blocks of the periodic table?
A periodic table block is a group of elements linked by the atomic orbitals whose valence electrons or vacant positions reside. The s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block are designated after their respective orbitals. Except for helium, the s-block elements are all on the periodic table's left side.
How do you find a block on the periodic table?
Complete step by step answer: -When we have filled all the electrons, the orbital in which the last electron is in, represents the block in which the element is placed. -Now, to determine the period in which the element is placed, we need to look at the principal quantum number of the valence electron.
How many d-block are there?
There are four series in the d block corresponding to the filling up of 3d, 4d, 5d or 6d orbitals.
How many electrons are in the d-block?
10 electronsFor the transition metals, we are concerned mainly with d-orbitals, also known as the d-block elements. The d-orbital can hold, at most, 10 electrons. Valence electrons are those electrons required to form bonds with other elements. They are responsible for reactivity.
How many blocks are in the long form of the periodic table?
It is divided into four blocks. They are : (i) s-block , (ii) p-block (iii) d- block and (iv) f-block. Was this answer helpful?
What are SP and d-block elements?
The elements for which the last electron has entered in s- orbital are called s- block elements, p-block elements are those for which the last electron has entered in the p - orbital, d-block elements are those in which the last electron has entered the d- orbital.
What is the name of d-block elements?
Elements of d-block are called transition elements.
What is the name of p-block?
Collectively, these p-block elements are known as the halogens. They have five electrons in their p orbital and are known for being extremely greedy for electrons. They like to steal electrons from metal elements to become 1- ions.
What are s-block elements Class 11?
S-block comprises 14 elements namely hydrogen (H), lithium (Li), helium (He), sodium (Na), beryllium (Be), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), rubidium (Rb), calcium (Ca), cesium (Cs), strontium (Sr), francium (Fr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).
What are D and f-block elements?
The d-block of the periodic table contains the elements of the groups 3-12 in which the d orbitals are progressively filled in each of the four long periods. The f-block consists of elements in which 4 f and 5 f orbitals are progressively filled. They are placed in a separate panel at the bottom of the periodic table.
What are the three special blocks in the periodic table?
The element blocks are s, p, d, and f. They are determined by the valence electron orbital. Periodic table blocks are sets of elements grouped by their valence electron orbitals. The four block names are s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block.
How many p-block elements are there?
35 p-block elementsThe p-block is the region of the periodic table that includes columns IIIA to column VIIIA and does not include helium. There are 35 p-block elements, all of which are in p orbital with valence electrons.
What are the types of elements in the periodic table?
The three types of elements found in the modern periodic table are metals, metalloids, and nonmetals.
What are the 4 blocks of the periodic table?
The four blocks are s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block.
What do the blocks mean on the periodic table?
The blocks in the periodic table mean which electron sublevel is in the process of being filled.
What is the SPDF?
SPDF are subshells of Orbitals. The orbital names s, p, d, and f stand for names given to groups of lines originally noted in the spectra of the el...
Why does Period 4 have 18 elements?
According to Pauli's exclusion principle, each orbital can accommodate only two electrons. Hence, 9 orbitals, at the maximum, can have 18 electrons...
Which elements of Group 1 and Group 2 belong to the S block?
The elements of Group 1 ( alkali metals) and Group 2 ( alkaline earth metals) which have ns1 and ns2 outermost electronic configuration belong to the s-Block Elements.
What is the modern periodic table?
The modern periodic table is the arrangement of all the known elements such that elements with similar characteristics are grouped. We know that the modern periodic table is made up of horizontal periods and vertical groups. In this article, we are going to study the similarities and periodicity of elements across the periodic table. We will study the different blocks: s-block, p-block, d-block, f-block and their characteristic properties, metals, metalloids, nonmetals, halogens, and noble gases.
What is the F block?
The f-block consists of two series lanthanides and actinides of the periodic table.
How many metalloids are there?
There are 7 metalloids i.e. Boron, Silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium and polonium.
What type of electron enters in a D block?
In d-block elements, a valence electron enters in d-orbital.
What is the electronic configuration of halogens?
The general electronic configuration of halogens is ns2np5.
Why are noble gases called noble gases?
These gases are inert under normal conditions and that’s why they are called Noble gases.
What is a block in the periodic table?
A block of the periodic table is a set of elements unified by the atomic orbitals their valence electrons or vacancies lie in. The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital: s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block.
How many electrons are in a P-block?
The p orbital can hold a maximum of six electrons, hence there are six columns in the p-block. Elements in column 13, the first column of the p-block, have one p-orbital electron. Elements in column 14, the second column of the p-block, have two p-orbital electrons.
How are p-block elements unified?
The p-block elements are unified by the fact that their valence (outermost) electrons are in the p orbital. The p orbital consists of six lobed shapes coming from a central point at evenly spaced angles. The p orbital can hold a maximum of six electrons, hence there are six columns in the p-block. Elements in column 13, the first column of the p-block, have one p-orbital electron. Elements in column 14, the second column of the p-block, have two p-orbital electrons. The trend continues this way until column 18, which has six p-orbital electrons.
Why are group 3 elements considered main group elements?
The group 3 elements are sometimes considered main group elements due to their similarities to the s-block elements. Groups (columns) in the f-block (between groups 2 and 3) are not numbered. Helium is an s-block element, with its outer (and only) electrons in the 1s atomic orbital, although its chemical properties are more similar to ...
What is horizontal similarity in elements?
The…elements show a horizontal similarity in their physical and chemical properties as well as the usual vertical relationship . This horizontal similarity is so marked that the chemistry of the first…series…is often discussed separately from that of the second and third series, which are more similar to one another than to the first series.
What are the elements in the P block?
The p-block elements can be described on a group-by-group basis as: group 13, the icosagens; 14, the crystallogens; 15, the pnictogens; 16, the chalcogens; 17, the halogens; and 18, the helium group, composed of the noble gases (excluding helium) and oganesson.
Why are f block elements so challenging?
Because of their complex electronic structure, the significant electron correlation effects, and the large relativistic contributions, the f-block elements are probably the most challenging group of elements for electronic structure theory.
What are the first two groups of the periodic table?
S-block: The first two groups of the periodic table, the s-block metals: Are either alkali metals or alkaline earth metals. Are soft and have low melting points. Are electropositive and chemically active. P-block: P-block elements include the last six element groups of the periodic table, excluding helium.
What Is an Element Block?
An element block is a set of elements located in adjacent element groups. Charles Janet first applied the term (in French). The block names (s, p, d, f) originated from descriptions of spectroscopic lines of atomic orbitals: sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. No g-block elements have been observed to date, but the letter was chosen because it is next in alphabetical order after f .
What are the two groups of metals?
S-block: The first two groups of the periodic table, the s-block metals: 1 Are either alkali metals or alkaline earth metals. 2 Are soft and have low melting points. 3 Are electropositive and chemically active.
What are P block elements?
The p-block elements include all of the nonmetals except for hydrogen and helium, the semimetals, and the post-transition metals. P-block elements:
What elements are involved in the chemical interaction?
Include carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, halogens, and many other common elements. Interact with other chemicals by losing, gaining, or sharing the valence electrons. Mostly form covalent compounds (though the halogens form ionic compounds withs-block metals).
How to group elements?
One way to group elements is by element blocks, sometimes known as element families. Element blocks are distinct from periods and groups because they were developed based on a very different way of categorizing atoms.
What is a D block?
D-block elements behave in a manner that is somewhere between that of highly reactive electropositive alkali metals and the covalent compound forming elements (which is why they are called "transition elements"). Have high melting and boiling points. Typically form colored salts. Are generally good catalysts.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table shows us the sequential filling of the electrons . The energy of the orbitals determines the sequence of filling- Lower energy orbitals are always preferred over high energy ones.The table is thus divided into 4 blocks namely – s,p,d, f blocks, depending on the occupation of the respective orbitals by the valence electrons of an element.
Which electrons occupy the p orbital?
The valence electrons occupy p orbitals i.e the last electron enters the p-orbital.
How many electrons can be in a valence shell?
There can be maximum 2 electrons in the valence shell as s-orbital can only accommodate 2 electrons in it. Alkali (Group 1) and Alkaline earth metals (Group2) and Helium are all s-block elements. Group 1 elements – [Noble gas configuration] ns1 , where n = 2 to 7.
How many electrons are in the outer shell of an element?
There can be maximum 6 electrons in the p orbital and 2 electrons in the s orbital.So according to the electronic configurations given above, there can be 3 to 8 electrons in the outer shell of these elements. ( Note – The outer shell/orbit of these elements consists of s and p orbitals).
Where are inner transition elements located?
These are called the inner transition elements and they are placed separately at the bottom of the main periodic table.