
How to Calculate Orbital Period?
- Step 1: Get the density of the central body.
- Step 2: Multiply the density of the centre body by the gravitational constant.
- Step 3: Divide 3π from the product and multiply by the square root of the result.
- Step 4: As a result, the satellite's orbital period is centred on the centre sphere.
What is the formula for an orbital period?
What is the orbital period? Solution: Given that. Density of the earth ρ = 5.21 g/cm³ = 5210 kg/m³. The formula of orbital period is T = √[3π / (G * ρ)] T = √[3 x 3.14 / (6.67408 × 10-11 x 5210)] = √[2.7090 x 10 7] = 5204 seconds = 1.445 hours. Therefore, the orbital period of earth is 1.445 hours
What is the equation for the period of an orbit?
r ( ϕ) = c, begin {aligned} r (phi) = c, end {aligned} r(ϕ) = c, . i.e. a circular orbit. But for more complicated orbits, this periodicity means that the orbit closes: r ( 0) r (0) r(0) and. r ( 2 π) r (2pi) r(2π) are the same point in space.
How do you find the orbital period?
- Planets orbit in ellipses, with the Sun at one focus.
- Angular momentum L z L_z Lz is conserved (Kepler would say this differently, "equal areas swept out in equal times".)
- The period of the orbit is given by the formula we just found.
How to calculate the sidereal period?
number of sidereal days per orbital period = −1 + number of solar days per orbital period. or, equivalently: length of solar day = length of sidereal day1 + length of sidereal dayorbital period. Click to see full answer
How do you find the orbital period of the moon?
4:157:20How to Calculate Orbital Period and Orbital Speed - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo if we want to know the period the orbital. Period that off that's going to be equal to theMoreSo if we want to know the period the orbital. Period that off that's going to be equal to the distance. 2 PI R divided by the speed.
What is orbital period of electron?
Orbital period is given as T = 2πrn / v where r is radius of nth orbit v is the velocity of electron is nth orbit.
What is orbital period measured in?
The orbital period must be measured in years, where 1 year is 365.25 days. This relation has many uses: determining the mass of a planet by looking at its moon(s), studying binary star systems, even determining the mass of the Galaxy!
How do you calculate the orbital period of Mercury?
Mercury is 57.91 million kilometers or 57.91149.6=0.3871 57.91 149.6 = 0.3871 AU from the Sun. We can plug this into our solved equation. This means Mercury's orbital period is 0.2409 Earth years long, or 0.2409×365=87.9 0.2409 × 365 = 87.9 Earth days long.
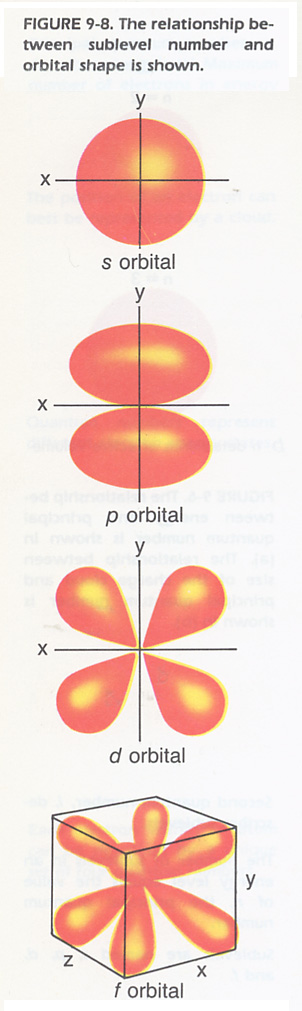
What is an orbital in an atom?
1) An orbital is a three dimensional description of the most likely location of an electron around an atom. Below is a diagram that shows the probability of finding an electron around the nucleus of a hydrogen atom. Notice that the 1s orbital has the highest probability.
How many electrons are in each orbital?
two electronsEach orbital holds two electrons which differ in a property known as spin. Orbital: A region of space within an atom where an electron in a given subshell can be found. Any orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons with opposite spin.
What is rotation period?
Period of Rotation. The period of rotation of a Solar System object is the length of time it takes that object to spin once around on its axis. For example the Earth takes 24 hours to spin once around its axis. Its period of rotation is 24 hours or a day.
What is meant by orbital in chemistry?
orbital, in chemistry and physics, a mathematical expression, called a wave function, that describes properties characteristic of no more than two electrons in the vicinity of an atomic nucleus or of a system of nuclei as in a molecule.
1. How to calculate the orbital period of a binary star system?
To find the binary star system orbital period, you have to know the semi-major axis, first & second bodies mass. Divide the cube of the axis by the...
2. What is Kepler's third law formula?
Kepler's 3rd law states that the square of the period is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of the orbit. Its formula is T = √(a34π²/G...
3. What are the types of orbits?
There are different types of orbits, they are low earth orbit, transfer orbits, medium earth orbit, geostationary transfer orbit and sun-synchronou...
4. What are the factors that affect the satellite orbital period?
The factor that affects the orbital period of a satellite is the central body density. By increasing the central body density, the orbital period v...
How to calculate orbital period of a satellite?
The formula to calculate the orbital period of a satellite around the central body is T = √ [3π / (G * ρ)]
What is the orbital period?
The orbital period is the time taken by an astronomical object to complete one orbit around the other object. In general, it applies to the planets, sun, moon, stars and many more. Kepler's third law or Kepler's laws planetary motion describes how a planet orbits around another.
How to find the orbital period of a binary star system?
To find the binary star system orbital period, you have to know the semi-major axis, first & second bodies mass. Divide the cube of the axis by the product of gravitational constant & sum of masses. Get the square root of the result with 2π to check the binary star orbital period.
What factors affect the orbital period of a satellite?
The factor that affects the orbital period of a satellite is the central body density. By increasing the central body density, the orbital period value decreases.
How long is the orbital period of Earth?
Therefore, the orbital period of earth is 1.445 hours
What is the formula for the square of the period?
Kepler's 3rd law states that the square of the period is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of the orbit. Its formula is T = √ (a 3 4π²/G (M + m)).
What are some examples of orbital periods?
Examples of some of the common orbital ones include the following: The sidereal period is the amount of time that it takes an object to make a full orbit, relative to the stars, the sidereal year. This is the orbital period in an inertial (non-rotating) frame of reference.
What determines the orbital period of a low orbit?
Thus the orbital period in low orbit depends only on the density of the central body, regardless of its size.
What are the characteristics of two bodies that orbit a third body in different orbits?
One of the observable characteristics of two bodies which orbit a third body in different orbits, and thus have different orbital periods, is their synodic period , which is the time between conjunctions .
What is the anomalistic period?
The anomalistic period is the time that elapses between two passages of an object at its periapsis (in the case of the planets in the Solar System, called the perihelion ), the point of its closest approach to the attracting body. It differs from the sidereal period because the object's semi-major axis typically advances slowly.
What is the synodic period of the solar system?
Table of synodic periods in the Solar System, relative to Earth: In the case of a planet's moon, the synodic period usually means the Sun-synodic period, namely, the time it takes the moon to complete its illumination phases, completing the solar phases for an astronomer on the planet's surface.
How long is the orbital period of water?
Thus, as an alternative for using a very small number like G, the strength of universal gravity can be described using some reference material, such as water: the orbital period for an orbit just above the surface of a spherical body of water is 3 hours and 18 minutes.
How far does a small body have to orbit?
For instance, for completing an orbit every 24 hours around a mass of 100 kg, a small body has to orbit at a distance of 1.08 meters from the central body's center of mass . In the special case of perfectly circular orbits, the orbital velocity is constant and equal (in m/s) to.
How many elements are in an elliptical orbit?
in its elliptical orbit is given by 3 "orbital elements":
What is the drawing on the right of the orbital ellipse?
The drawing on the right gives a geometric construction of those angles (no, don't try to puzzle out the details). The orbital ellipse is enclosed in a circle of radius a, and given a position Pof the satellite, a corresponding point Qon the circle can be drawn, sharing the same line perpendicular to the ellipse's axis.
What plane is the longitude of the ascending node?
The longitude of the ascending node Ω(capital omega). To orient the orbit in 3 dimensions requires a reference plane and a reference direction. For satellite orbits, the reference plane--the horizontal plane in the drawing--is usually the Earth's equatorial plane (sometimes it is the plane of the ecliptic).
Can a formula give Ein terms of M?
No matter which form is used, mathematics knows no formula which gives Ein terms of M. However, solutions can often be approximated to any degree of accuracy by iteration--by starting with an approximate solution, then improving it again and again by an appropriate procedure ("algorithm"--more about that word, here). If the eccentricity e is not too big--the ellipse not much different from a circle--then Mand Eare not too different. So an initial guess

Overview
Two bodies orbiting each other
In celestial mechanics, when both orbiting bodies' masses have to be taken into account, the orbital period T can be calculated as follows:
where:
• a is the sum of the semi-major axes of the ellipses in which the centers of the bodies move, or equivalently, the semi-major axis of the ellipse in which one b…
Related periods
There are many periods related to the orbits of objects, each of which are often used in the various fields of astronomy and astrophysics, particularly they must not be confused with other revolving periods like rotational periods. Examples of some of the common orbital ones include the following:
• The sidereal period is the amount of time that it takes an object to make a full orbit, relative to the fixed …
Small body orbiting a central body
According to Kepler's Third Law, the orbital period T of two point masses orbiting each other in a circular or elliptic orbit is:
where:
• a is the orbit's semi-major axis
• μ = GM is the standard gravitational parameter
Effect of central body's density
For a perfect sphere of uniform density, it is possible to rewrite the first equation without measuring the mass as:
where:
• r is the sphere's radius
• a is the orbit's semi-major axis in metres,
Synodic period
One of the observable characteristics of two bodies which orbit a third body in different orbits, and thus have different orbital periods, is their synodic period, which is the time between conjunctions.
An example of this related period description is the repeated cycles for celestial bodies as observed from the Earth's surface, the synodic period, applying to the elapsed time where planet…
Examples of sidereal and synodic periods
Table of synodic periods in the Solar System, relative to Earth:
In the case of a planet's moon, the synodic period usually means the Sun-synodic period, namely, the time it takes the moon to complete its illumination phases, completing the solar phases for an astronomer on the planet's surface. The Earth's motion does not determine this value for other planets because an Earth observer is not orbited by the moons in question. For example, Deimos'…
See also
• Geosynchronous orbit derivation
• Rotation period – time that it takes to complete one revolution around its axis of rotation
• Satellite revisit period
• Sidereal time