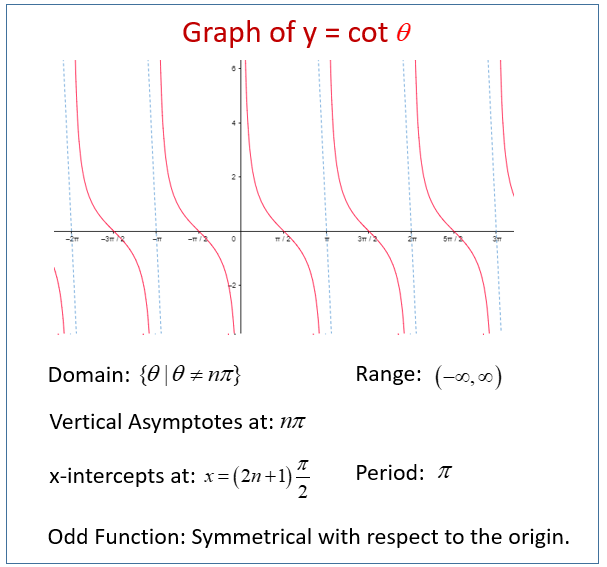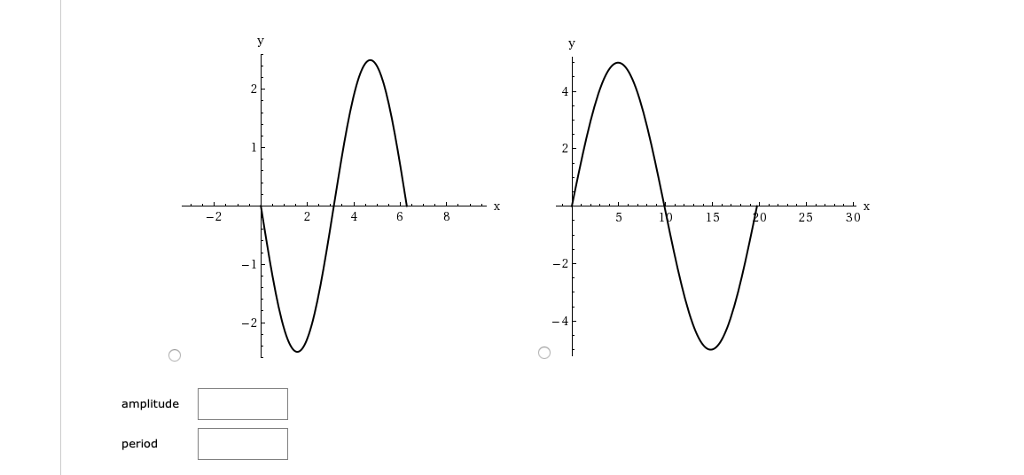
What is the formula for finding period?
Listed below are three main aspects to finding the formula for period:
- Find if it is a periodic function i.e. if the function repeats over at a constant period
- If the formula for period function is represented like f (x) = f (x + p), where p is the real number
- Period means the time interval between the two occurrences of the wave
What is the period of the sine curve?
The period of the sine curve is the length of one cycle of the curve. The natural period of the sine curve is 2π. So, a coefficient of b=1 is equivalent to a period of 2π. To get the period of the sine curve for any coefficient b, just divide 2π by the coefficient bto get the new period of the curve.
How to find phase shift of Sine graph?
How to find the phase shift of a sine function? y = A sin(B(x + C)) + D. amplitude is A; period is 2 π /B; phase shift is C (positive is to the left) vertical shift is D; And here is how it looks on a graph: Note that we are using radians here, not degrees, and there are 2 π radians in a full rotation.
What is the period of a function equation?
The fundamental period of a function is the period of the function which are of the form, f (x+k)=f (x), then k is called the period of the function and the function f is called a periodic function. Now, let us define the function h (t) on the interval [0, 2] as follows:
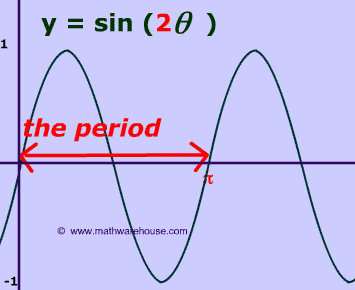
How do you find the period of a sin function?
We have a really easy way to determine the period of the sine function. If we have a sine function of the form f(x) = Asin(Bx + C) + D, then the period of the function is 2π / |B|.
How do you find the period of a graph?
2:524:57Midline, amplitude and period of a function | Khan Academy - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWell here our Y is decreasing. As x increases our slope is positive here our slope is negative here.MoreWell here our Y is decreasing. As x increases our slope is positive here our slope is negative here. So this isn't the same point on the cycle. We need to get to the point where Y.
What is the formula to find period?
How to Find the Period of a Function? If a function repeats over at a constant period we say that is a periodic function. It is represented like f(x) = f(x + p), p is the real number and this is the period of the function. Period means the time interval between the two occurrences of the wave.
How do I find period of sine and cosine on graph?
3:0018:34Graphing Sine and Cosine Trig Functions With Transformations ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPeriod is equal to 2 PI over B B is the number in front of X so it's 2 pi over 2 and so we get PIMorePeriod is equal to 2 PI over B B is the number in front of X so it's 2 pi over 2 and so we get PI for the period.
Why is the period 2pi B?
It means the period is 12, so each cycle is 12 units long. What you say is sort of right: b is the number of cycles per 2pi.
How do you find amplitude and period?
Finding the amplitude, period, and phase shift of a function of the form A × sin(Bx - C) + D or A × cos(Bx - C) + D goes as follows: The amplitude is equal to A ; The period is equal to 2π / B ; and. The phase shift is equal to C / B .
How do you find the amplitude and period of a sine function?
0:000:59Finding the Period and Amplitude of a Sine Function - Quick ExampleYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTo get the amplitude we'll have to take the absolute. Value of negative 1/2 which will simply giveMoreTo get the amplitude we'll have to take the absolute. Value of negative 1/2 which will simply give us positive 1/2. So this function has a period equal to 8 and an amplitude equal to positive 1/2.
How do you find the period of a wave in trigonometry?
If your trig function is either a tangent or cotangent, then you'll need to divide pi by the absolute value of your B. Our function, f(x) = 3 sin(4x + 2), is a sine function, so the period would be 2 pi divided by 4, our B value.
What is the period in trig?
The period is defined as the length of one wave of the function. In this case, one full wave is 180 degrees or radians. You can figure this out without looking at a graph by dividing with the frequency, which in this case, is 2.
What is the period in Cos graph?
0:032:07Finding the Period and Amplitude of a Cosine Function - Quick ExampleYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd vertical shifts of the function y equals negative three-fourths cosine of X plus PI. Minus fiveMoreAnd vertical shifts of the function y equals negative three-fourths cosine of X plus PI. Minus five so the amplitude will be the absolute value of negative three over four which will give us three
What is the period of a cosine function?
The cosine function is a trigonometric function that is periodic. A periodic function is a function that repeats itself over and over in both directions. The period of the cosine function is 2π, therefore, the value of the function is equivalent every 2π units. For example, we know that we have cos(π) = 1.
What is period of a wave?
Wave Period: The time it takes for two successive crests (one wavelength) to pass a specified point. The wave period is often referenced in seconds, e.g. one wave every 6 seconds.
What is the period of a sine function?
The period of the sine function is 2π. This means that the value of the function is the same every 2π units. Similar to other trigonometric functions, the sine function is a periodic function, which means that it repeats at regular intervals. The interval of the sine function is 2π. For example, we have sin (π) = 0. If we add 2π to the input of the function, we have sin (π + 2π), which is equal to sin (3π). Since we have sin (π) = 0, we also have sin (3π) = 0. Every time we add 2π of the input values, we will get the same result.
What happens when x is multiplied by a number greater than 1?
If x is multiplied by a number greater than 1, that “speeds up” the function and the period will be smaller. That means it won’t take long for the function to start repeating itself. For example, if we have the function , this causes the “speed” of the original function to double. In this case, the period is π.
Does the coefficient of x matter when calculating the period?
This formula works even if we have more complex variations of the sine function like . Only the coefficient of x matters when calculating the period, so we would have:
What is the best bet for periodic function?
Begin by realizing we are dealing with a periodic function, so sine and cosine are your best bet.
What does it mean when one wave of a graph goes exactly from 0 to before repeating itself?
One wave of the graph goes exactly from 0 to before repeating itself. This means that the period is .
How many waves are there in a graph?
The graph has 3 waves between 0 and , meaning that the length of each of the waves is divided by 3, or .
Where does the minimum occur on a graph?
The minimum occurs in the middle of the graph , so to figure out where it starts, subtract from the minimum's x-coordinate:
How to tell period of wave?
If you look at a graph, you can see that the period (length of one wave) is . Without the graph, you can divide with the frequency, which in this case, is 1.
Is a cosine function a sine function?
Recall that sine passes through , while cosine passes through . this means that our function must be a sine function, because in order to be a cosien graph, we would need a horizontal translation as well.
What is the amplitude of a sine function?
Amplitude: The amplitude of the graph of a sine function is the vertical distance from the top of a peak to the center line. This is the same as the vertical distance from the top of a peak to the lowest point on the graph, divided by 2.
How to find amplitude and period?
Amplitude and period from an equation: The equation {eq}f (x) = asin (b (x+c)) + d {/eq} has amplitude {eq}a {/eq} and period {eq}dfrac {2pi} {b} {/eq}.
Which graph has amplitude 3 and period?
Therefore, the only graph with amplitude 3 and period {eq}dfrac {pi} {2} {/eq} is graph C.
Who is Lynn Ellis?
She has a Bachelor's degree in Mathematics from Middlebury College and a Master's Degree in Education from the University of Phoenix.
What is vertical translation?
The vertical translation or displacement corresponds to the value of D in the general form of the sine function. The value of D is the vertical displacement of the middle line of the graph. When D is positive, the graph is shifted up. When D is negative, the graph is shifted down. For example, the function has its median line at .
What is the domain of a sine function?
Therefore, the domain of the sine function is equal to all real numbers.
How to find the amplitude of a sine?
Using the general shape of the sine, its amplitude is found using |A|. For example, the amplitude of is 4.
How to find phase of a function?
We can find the phase by rewriting the general form of the function as follows: . Using this form, the phase is equal to . When we have , the graph has a shift to the right. When we have , the graph has a shift to the left.
What is the period of a graph?
Period: . The period is twice the period of the basic function, so the graph will be stretched horizontally.
Where is the sine function on a graph?
On the graph of the sine function, we place the angles on the x -axis and we place the result of the sine of each angle on the y -axis. The graph of the sine is a curve that varies from -1 to 1 and repeats every 2π. These types of curves are called sinusoidal.
What is the distance from the midline to the highest point?
The distance from the midline to the highest point is 0.5. This means that .