Which planet has the longest orbital period?
Venus Subsequently, question is, what dwarf planet has the longest orbital period? The new planet, named HD 21749b, orbitsa bright, nearby dwarfstar about 53 light years away, in the constellation Reticulum, and appears to have the longest orbital periodof the three planets so far identified by TESS.
What planet orbits around the Sun the fastest?
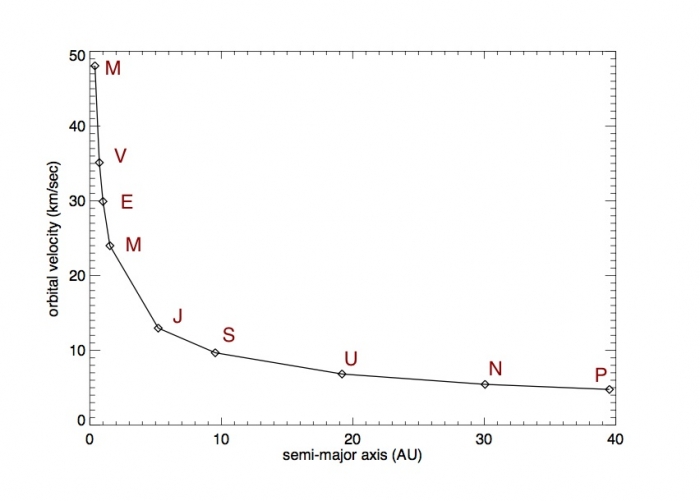
- Mercury: 47.87 km/s (107,082 miles per hour), or a period of about 87.97 days
- Venus: 35.02 km/s (78,337 miles per hour), or a period of about 224.7 days
- Earth: 29.78 km/s (66,615 miles per hour), or a period of about 365.256365 days
- Mars: 24.077 km/s (53,853 miles per hour), or a period of about 686.93 days
How do you find the period of an orbit?
How do you calculate the orbital period of a planet? By observing the time between transits, we know the orbital period. Kepler’s Third law can be used to determine the orbital radius of the planet if the mass of the orbiting star is known (R3=T2−Mstar/Msun, the radius is in AU and the period is in earth years).
Do inner planets take less time to orbit the Sun?
Orbit the Sun quickly. Because they are quite close to the Sun, the Inner Planets complete an orbit quickly. Mercury takes only 88 days to orbit the Sun. Mars takes 687 days. Orbit the Sun slowly. The Outer Planets orbit the Sun from millions of miles and have a much greater distance to cover to complete an orbit, so take much longer to do so.

What determines the orbital period of a planet?
Planetary Orbits. The square (second power) of the period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube (third power) of its orbital radius (P2 = R3). This is because the closer a planet lies to the Sun, the faster it must spin to resist the gravitational attraction (and to avoid falling into the Sun). (A.U.)
How do you find the orbit of a planet?
The orbit formula, r = (h2/μ)/(1 + e cos θ), gives the position of body m2 in its orbit around m1 as a function of the true anomaly. For many practical reasons we need to be able to determine the position of m2 as a function of time.
How do you calculate the orbital period of Mars?
Mars' orbital period is (1.524)3/2 = 1.88 years and it will move 136 degrees in its orbit during the probe's trip to Mars. Of course the Earth will have moved 0.709*360 = 255 degrees in its orbit during this time.
How do you calculate orbital period GCSE?
1:122:10Orbital velocity (orbital speed) calculation - GCSE PhysicsYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLet's write down the equation orbital velocity is 2 pi r divided by time period substituting someMoreLet's write down the equation orbital velocity is 2 pi r divided by time period substituting some numbers in that gives us 8.85 times 10 to the power of 4. The units will be kilometers.
How do you calculate the orbital period of Venus?
We can use the equation for Kepler's third law, P2∝a3. For Venus, P2=0.62×0.62=0.38 years and a3=0.72×0.72×0.72=0.37 AU (rounding numbers sometimes causes minor discrepancies like this). The orbital period (0.38 year) approximates the semimajor axis (0.37 AU).
How do you calculate the orbital period of Saturn?
Answer: Orbit circumference = 2 π r km, but r = 60300 R so C = 2 (3.141) x 60300 R , C = 379,000 R km, wnhere R is in Saturn radius units. Since the orbit speed is V = 24.9/R1/2, then Time = C/V = 15220 R3/2 seconds. Since 1 hour = 3600 seconds, we have T = 4.22 R3/2 hours.
How do you calculate the orbital period of Mercury?
Mercury is 57.91 million kilometers or 57.91149.6=0.3871 57.91 149.6 = 0.3871 AU from the Sun. We can plug this into our solved equation. This means Mercury's orbital period is 0.2409 Earth years long, or 0.2409×365=87.9 0.2409 × 365 = 87.9 Earth days long.
How do you find the period of an orbital radius?
By observing the time between transits, we know the orbital period. Kepler's Third law can be used to determine the orbital radius of the planet if the mass of the orbiting star is known (R3=T2−Mstar/Msun, the radius is in AU and the period is in earth years).
What is orbital period of electron?
Orbital period is given as T = 2πrn / v where r is radius of nth orbit v is the velocity of electron is nth orbit.
How do you calculate the orbital period of the moon?
0:2210:52Orbital Period of the Moon - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThen all this is times a cubed a is the average distance. And we need to cube. It.MoreThen all this is times a cubed a is the average distance. And we need to cube. It.
How do you find the orbital period of a semi-major axis?
Kepler's third law: An object's orbital period squared is equal to the cube of its semi-major axis. This can be represented by the equation p2=a3 p 2 = a 3 , where p is the period of the planet's orbit, and a is the planet's semi-major axis.
What does Kepler's third law mean?
Kepler's Third Law: the squares of the orbital periods of the planets are directly proportional to the cubes of the semi-major axes of their orbits. Kepler's Third Law implies that the period for a planet to orbit the Sun increases rapidly with the radius of its orbit.
What type of orbit do planets have?
All orbits are elliptical, which means they are an ellipse, similar to an oval. For the planets, the orbits are almost circular. The orbits of comets have a different shape. They are highly eccentric or "squashed." They look more like thin ellipses than circles.
What is Earth's orbit?
365 daysEarth / Orbital period
What is the distance of Earth's orbit?
149.6 million kilometersEarth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.6 million kilometers every 365.2564 days.
Which way do the planets orbit the Sun?
counterclockwise directionA: The planets of our solar system orbit the Sun in a counterclockwise direction (when viewed from above the Sun's north pole) because of the way our solar system formed. Our Sun was born from a cloud of dust and gas, the remnants of which — called the solar nebula — became the planets.
1. How to calculate the orbital period of a binary star system?
To find the binary star system orbital period, you have to know the semi-major axis, first & second bodies mass. Divide the cube of the axis by the...
2. What is Kepler's third law formula?
Kepler's 3rd law states that the square of the period is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of the orbit. Its formula is T = √(a34π²/G...
3. What are the types of orbits?
There are different types of orbits, they are low earth orbit, transfer orbits, medium earth orbit, geostationary transfer orbit and sun-synchronou...
4. What are the factors that affect the satellite orbital period?
The factor that affects the orbital period of a satellite is the central body density. By increasing the central body density, the orbital period v...
How to calculate the orbital period of a planet?
The simplest way to calculate orbital period of a planet is by taking the time difference between two moments at which it is observed to be in the same place in the sky.
Who discovered that the planets are elliptical?
The orbits of the planets are not entirely circular: they were discovered to be elliptical by Kepler; but again, as the question assumed that we don't know Kepler's laws, we don't know that they are elliptic (Kepler's 1st law).
How to reduce uncertainty on P?
The uncertainty on P can be reduced by taking not one but multiple periods.
Is the orbit of the planets circular?
The orbits of the planets are not entirely circular: they were discovered to be elliptical by Kepler; but again, as the question assumed that we don't know Kepler's laws, we don't know that they are elliptic (Kepler's 1st law). But, even then, this provides us with a good approximate.
How to calculate orbital period of a satellite?
The formula to calculate the orbital period of a satellite around the central body is T = √ [3π / (G * ρ)]
What is the orbital period?
The orbital period is the time taken by an astronomical object to complete one orbit around the other object. In general, it applies to the planets, sun, moon, stars and many more. Kepler's third law or Kepler's laws planetary motion describes how a planet orbits around another.
How to find the orbital period of a binary star system?
To find the binary star system orbital period, you have to know the semi-major axis, first & second bodies mass. Divide the cube of the axis by the product of gravitational constant & sum of masses. Get the square root of the result with 2π to check the binary star orbital period.
What factors affect the orbital period of a satellite?
The factor that affects the orbital period of a satellite is the central body density. By increasing the central body density, the orbital period value decreases.
How long is the orbital period of Earth?
Therefore, the orbital period of earth is 1.445 hours
What is the formula for the square of the period?
Kepler's 3rd law states that the square of the period is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of the orbit. Its formula is T = √ (a 3 4π²/G (M + m)).
Which star system has two stars that are close to each other?
The binary star system has two stars that are close to each other and have similar masses that stars orbit around each other without a material central body. It has elliptical orbits.
How long is the orbit of the Sun?
It orbits a sun-like star at a distance of 1.15 AU or 172 million kilometres in a nearly circular orbit. Its rotational period is 19 hours, 38 minutes. Its mass is 6.15 × 10 24 k g and its radius is about 6,743 kilometres. I have to calculate its orbital period and density but I'm weak in maths and don't know how to.
How to find volume of a sphere?
As for density, the volume of a sphere is given by the formula V = 4 3 π r 3 ; density ( ρ = M V, with M the mass) is usually given in grams per cubic centimeter, so it makes sense to convert to those units. That gives the following calculation:
Is the mass of the planet relevant?
Note that in this case, the mass of the planet is not relevant. What we need instead is the mass of the star, which you have not given. Since you assumed a sun-like star, we can insert the sun's standard gravitational parameter for G × M:
Which law states that the square of the period of an object's orbit is proportional to the cube of its?
Kepler's Third Law: The square of the period of an object's orbit is proportional to the cube of its semi-major axis,$$T^2 propto a^3 $$and in particular,
How long is the period of Earth's semi major axis?
We know that the Earth has a semi-major axis of 150 million km and a period of 365.3 days What is the period of the Earth-like planet?
Which axis is the smallest diameter of the ellipse?
The smallest diameter of the ellipse is the semi-minor axis while the largest diameter is the semi-major axis.
How long is the Earth's life?
The Earth-like planet has a period of 740 days .
What is Kepler's Third Law?
Kepler found that massive objects have elliptical orbits with the center of mass of the system located at one of the ellipse's two foci. The smallest diameter of the ellipse is the semi-minor axis while the largest diameter is the semi-major axis.
