
What is the easiest way to learn the periodic table?
- Try and picture something for each element. For example, for hydrogen picture a star, or for uranium picture a power plant. ...
- Memorize in chunks or five, then each day add 5 elements. Do that for 23 days more or less and you have memorized 115 elements, basically the periodic table.
- The third method isn’t really a method. ...
What is 101 on the periodic table?
face-centered cubic (fcc) Mendelevium is a synthetic element with the symbol Md ( formerly Mv) and atomic number 101. A metallic radioactive transuranic element in the actinide series, it is the first element by atomic number that currently cannot be produced in macroscopic quantities through neutron bombardment of lighter elements.
What are some interesting facts about the periodic table?
Interesting Facts On Periodic Table of Elements
- Founder of Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleyev is the father of the modern periodic table of elements. ...
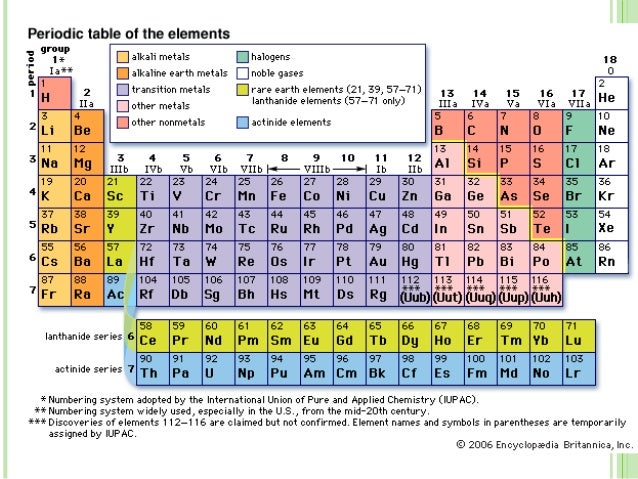
- Columns of the Periodic Table. The periodic table has 18 vertical columns called groups and seven horizontal columns called Periods.
- Size of the Atom. ...
- Unique Elements. ...
- Properties of Elements. ...
- Facts About Hydrogen. ...
How do you understand the periodic table?
Vocabulary
- Elements: Substances consisting of only one atom.
- Groups: The vertical column of the periodic table signifies the number of valence electrons in an element.
- Periods: The horizontal rows in a periodic table indicate the number of electron shells in an element.
How do you read a periodic table element?
On the periodic table, elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number.Elements in the same row are in the same period. ... Elements in the same column are in the same group. ... Here's a close-up look at the carbon square from the Periodic Table.
How do you read the periodic table for dummies?
0:073:07The Periodic Table Explained - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFirst the letters are symbols. Each box represents an element each element is made up of the sameMoreFirst the letters are symbols. Each box represents an element each element is made up of the same kind of atom with a specific number of protons in its nucleus.
What do the numbers mean on the periodic table?
In the modern periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons define the identity of an element (i.e., an element with 6 protons is a carbon atom, no matter how many neutrons may be present).
What is the easiest way to learn periodic table?
Memorization StrategiesBreak down the table into sections. ... Spread out the memorization process. ... Learn the elements in a song. ... Make nonsense words made from element symbols. ... Use color to learn element groups. ... Use a mnemonic device to help remember the order of the elements.
How do you read groups and periods on a periodic table?
Groups and periods are two ways of categorizing elements in the periodic table. Periods are horizontal rows (across) the periodic table, while groups are vertical columns (down) the table. Atomic number increases as you move down a group or across a period.
What are the 7 families of the periodic table?
Families of the Periodic Table. On the periodic table, there are families which are groups of elements with similar properties. These families are alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, post-transition metals, metalloids, halogens, noble metals, and noble gases.
How do you read atomic symbols?
The symbol for an atom indicates the element via its usual two-letter symbol, the mass number as a left superscript, the atomic number as a left subscript (sometimes omitted), and the charge as a right superscript.
How do you use the periodic table?
Scientists use the periodic table to quickly refer to information about an element, like atomic mass and chemical symbol. The periodic table's arrangement also allows scientists to discern trends in element properties, including electronegativity, ionization energy, and atomic radius.
How do you read the atomic number?
0:072:23Understanding Atomic Number and Atomic Mass - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe number that appears below the element symbol is called the atomic mass the mass of an atomMoreThe number that appears below the element symbol is called the atomic mass the mass of an atom depends on the number of protons neutrons.
What is the rhyme to remember the periodic table?
Healthy Little Beggar Boys Catching Newts Or Fish. Hell, Here Little Beatniks Brandish Countless Number Of Flick kNives. Nagging Maggie Always Sighs, "Please Stop Clowning Around." Here He Lies Beneath Bed Clothes, Nothing On, Feeling Nervous.
How can I memorize Chemistry?
Here are some of the best (and worst) ways to memorize chemistry.Memorizing Chemistry Using Repetition.Memorizing Chemistry Using Mnemonic Devices.Using Memory Palaces To Memorize Chemistry.Using a Memory Palace To Memorize Numbers.
How can I memorize faster?
Simple memory tips and tricksTry to understand the information first. Information that is organized and makes sense to you is easier to memorize. ... Link it. ... Sleep on it. ... Self-test. ... Use distributed practice. ... Write it out. ... Create meaningful groups. ... Use mnemonics.More items...
How do you read atomic symbols?
The symbol for an atom indicates the element via its usual two-letter symbol, the mass number as a left superscript, the atomic number as a left subscript (sometimes omitted), and the charge as a right superscript.
How do you read the atomic number?
0:072:23Understanding Atomic Number and Atomic Mass - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe number that appears below the element symbol is called the atomic mass the mass of an atomMoreThe number that appears below the element symbol is called the atomic mass the mass of an atom depends on the number of protons neutrons.
How do you read protons and neutrons on the periodic table?
The atomic number (number at the top) is the amount of protons and the amount of electrons. So if an element has an atomic number of 5, you know that it has 5 protons and 5 electrons. The atomic mass (number at the bottom) is the amount of protons and neutrons added together.
What are the elements of the periodic table in order?
List of Periodic Table ElementsElement 1: H-Hydrogen. Element 2: He-Helium. ... Element 4: Be-Beryllium. Element 5: B-Boron. ... Element 7: N-Nitrogen. Element 8: O-Oxygen. ... Element 10: Ne-Neon. Element 11: Na-Sodium. ... Element 13 : Al-Aluminum. ... Element 16 : S-Sulfur. ... Element 19 : K-Potassium. ... Element 22 : Ti-Titanium.More items...
How many periods are there in the periodic table?
Periods are the horizontal rows of the periodic table. There are seven periods total and each element in a period has the same number of atomic orbitals. The top period, which contains hydrogen and helium, has only two orbitals. As you go down the rows, the number of orbitals increases.
How are elements organized in the periodic table?
The periodic table is organized into groups (vertical columns), periods (horizontal rows), and families (groups of elements that are similar). Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. Meanwhile, elements in the same period have the same number of occupied electron shells. In 1869 Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev noticed there existed an innate pattern of organization for the chemical elements. From this deduction, he formed the periodic table. It is important to note how the location of elements on this table tells us about their properties. A quick way to understand an element’s chemical and physical properties is to know the periodic trends. These trends tell you where the highest and lowest types of properties are concentrated on the periodic table. For a more in-depth explanation of periodic trends, click here.
What is an element in the periodic table?
Vocabulary. Elements: A pure substance composed of a single atom. Groups: The vertical column of the periodic table that signifies the number of valence electrons in an element. Periods: The horizontal rows in the periodic table that signify the number of electron shells in an element. Families: Elements that have the same number ...
Which scientist discovered that elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells?
Meanwhile, elements in the same period have the same number of occupied electron shells. In 1869 Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev noticed there existed an innate pattern of organization for the chemical elements. From this deduction, he formed the periodic table.
What order are elements listed on the periodic table?
On the periodic table, elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number.
How to keep track of elements?
To keep track of the elements, scientists use the Periodic Table, a chart that shows all the elements. ( Click here for a pdf version of the Periodic Table.) Scientists can quickly find out basic information about an element just by looking at the Periodic Table.
What is the atomic number of an atom?
Atomic Number: the number of protons in the nucleus (which is the same as the number of electrons in the atom).
What is the periodic table?
Periodic Table An arrangement of the elements by their properties and their atomic number. Element A substance that cannot be divided into simpler substances by chemical means. Symbol A one- or two-letter abbreviation used to represent an element. The first letter is capitalized. Any second letter is always lower case.
Where is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of the element is represented by the number in the upper right-hand corner of the entry. This number represents the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom which determines the element. For this example, the atomic number is 12.
What does period number mean?
The period number signifies the number of electron energy levels, or the highest level of energy an electron occupies. Take the alkaline metal column for example: lithium (Li) is on period 2 and contains two electron energy levels; sodium (Na), period 3, has three levels; potassium (K), period 4, has four; and so on.
What are the rows in a periodic table called?
The table’s rows are called periods , since each starts with an element in the first column which behaves as an alkali metal, goes on to an alkaline earth metal, and ends with a halogen and a noble gas. Each row expresses a whole range of elements, with their typical chemical properties.
How are elements arranged?
Let’s start with the most obvious arrangement – the atomic number. The elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. Each element has a unique atomic number, which indicates how many protons it has. For example, oxygen’s atomic number is 8, telling us that its nucleus contains eight protons.
Why do elements in a table have similar chemical properties?
Why? Because each element in the column has the same number of electrons in its outer shell. These electrons have the most significant influence on how the element reacts with other elements or substances. All the elements in the first column, for example, have one electron in their valence shell, and therefore will have a very strong reaction to water.
Why is the periodic table important?
The periodic table is considered to be the outcome of a stroke of genius. It is so much more than just an arrangement of elements – the table sorts the elements according to their chemical families and chemical behaviors, so that its organizing principles enable predicting the behavior of an unfamiliar element according to our knowledge of the adjacent elements. Knowing how to read the periodic table enables expanding our chemical knowledge and thus better understanding the material world in and around us.
Which column of the periodic table contains alkaline earth metals?
The second column includes the alkaline earth metals, which have two electrons in their outer shells. They have similar properties to the alkali metals, but they are less reactive chemically. Because they have two electrons in their shells, they tend to produce different compounds from the alkali metals.
Who developed the table of elements?
Dmitri Mendeleev, who developed it, organized the elements in a way that captured their properties. He relied on all the information available in 1869 about the known elements, and looked for a way to contain all the knowledge of these elements and set it out before the readers by the very form of the table.
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Did Mendeleev's predictions get dismissed?
There were plenty of skeptics and it took years to gain international acceptance, but once newly-discovered elements matched the ones that Mendeleev predicted, his patterns could not be dismissed. In addition, some of the properties that he "fudged" were later recalculated and found to be much closer to his predictions.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).

CORE Concepts
Related Articles
Vocabulary
- Elements: A pure substance composed of a single atom.
- Groups: The vertical column of the periodic table that signifies the number of valence electrons in an element.
- Periods: The horizontal rows in the periodic table that signify the number of electron shells in an element.
- Elements: A pure substance composed of a single atom.
- Groups: The vertical column of the periodic table that signifies the number of valence electrons in an element.
- Periods: The horizontal rows in the periodic table that signify the number of electron shells in an element.
- Families: Elements that have the same number of valence electrons and therefore similar properties.
The Periodic Table and The Periodic Trends
- The periodic table is organized into groups (vertical columns), periods (horizontal rows), and families (groups of elements that are similar). Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. Meanwhile, elements in the same period have the same number of occupied electron shells. In 1869 Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev noticed...
Periods on The Periodic Table
- So what is a period on the periodic table? Periods are the horizontal rows of the periodic table. There are seven periods total and each element in a period has the same number of atomic orbitals. The top period, which contains hydrogen and helium, has only two orbitals. As you go down the rows, the number of orbitals increases. Below is a table to help visuals the periodic nu…
Groups of The Periodic Table
- As previously mentioned, the vertical columns on the periodic table are called “groups”. There is eighteen groups on the periodic table in total, and each periodic table group contains elements with the same number of valence electrons. The number of valence electrons present dictates the properties of an element. The reason for this is that the valence electrons, which are the electro…
Families of The Periodic Table
- On the periodic table, there are familieswhich are groups of elements with similar properties. These families are alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, post-transition metals, metalloids, halogens, noble metals, and noble gases. Many of these families belong to a single group on the periodic table. However, not all of the families overlap with periodic table groups. F…
How to Read The Periodic table?
- Vocabulary
1. Elements:Substances consisting of only one atom. 2. Groups:The vertical column of the periodic table signifies the number of valence electrons in an element. 3. Periods:The horizontal rows in a periodic table indicate the number of electron shells in an element. 4. Families:Elemen…
The Periodic Table and The Periodic Trends
- A periodic table is organized into groups (vertical columns), periods (horizontal rows), and families (groups of similar elements). The number of electrons in the valence electrons of elements belong to the same group. In the meantime, elements in the same period have the same number of occupied electron shells. Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev noticed there was an inn…
Periods on The Periodic Table
- What is a period on the periodic table? Periodsare the horizontal rows of a periodic table. In total, there are seven periods, each with the same number of atomic orbitals. There are only two orbitals in the maximum period, which contains hydrogen and helium. The number of orbitals increases as you move down the rows.
Groups of The Periodic Table
- As previously mentioned, the vertical columns on the periodic table are called “groups.” There are eighteen groups on the periodic table in total, and each periodic table groupcontains elements with the same number of valence electrons. Element properties are determined by the number of valence electrons present. This is because valence electrons, which are electrons in the outerm…
Families of The Periodic Table
- On the periodic table, some families are groups of elements with similar properties. Alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, post-transition metals, metalloids, halogens, noble metals, and noble gases comprise these families. On the periodic table, most of these families are in one group. There are, however, some families that overlap with periodic table groups. As an example…