What are the 8 groups of the periodic table?
Name of the eight groups in the periodic table:Alkali metals.Alkaline earth metals.Rare earth metals.Crystallogens.Pnictogens.Chalcogens.Halogens.Noble gases.
How do you find the group in the periodic table?
1:163:03What Are Periods & Groups In The Periodic Table? | Properties of MatterYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe columns going down from top to bottom are the groups elements in the same group also haveMoreThe columns going down from top to bottom are the groups elements in the same group also have something in common elements in the same group have the same number of electrons in their outermost shell.
What is the difference between a group and a period?
The columns of the periodic table are called groups. Members of the same group in the table have the same number of electrons in the outermost shells of their atoms and form bonds of the same type. The horizontal rows are called periods.
Why are elements arranged in groups?
The chemical elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The horizontal rows are called periods and the vertical columns are called groups. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties. This is because they have the same number of outer electrons and the same valency.
What is the difference between periodic table groups and periods?
Periodic Table Groups and Periods. A periodic table group is a column, while a periodic table period is a row. Groups and periods organize elements on the periodic table of the elements. A group is a vertical column down the periodic table, while a period is a horizontal row across the table. Both groups and periods reflect the organization ...
How many periods are there in the periodic table?
Elements within a period display periodic table trends, moving from left to right, involving atomic and ionic radius, electronegativity, There are seven element periods. Some periods contain more elements than others because the number of included elements depends on the number of electrons allowed in an energy sublevel.
What are the different types of nonmetals?
The nonmetals, halogens, and noble gases are all types of nonmetals. The metalloids have properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals. The alkali metals, alkaline earths, lanthanides, actinides, transition metals, and basic metals are all groups of metals.
What are the elements that chemists classify?
These groups go by the names alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, basic metals, nonmetals, halogens, noble gases, lanthanides, and actinides.
How many valence electrons are in group 17?
For example, elements in group 1 have 1 valence electron, elements in groups 3-12 have a variable number of valence electrons, and elements in group 17 have 7 valence electrons. The lanthanides and actinides, located below the main table, all fit within group 3.
How does the atomic number of an element increase?
Element atomic number increases as you move down a group from top to bottom or across a period from left to right. An element group is a vertical column on the periodic table. Atoms in a group share the same number of valence electrons. An element period is a horizontal row on the periodic table. Atoms in a period have the same number ...
How many groups are there in the periodic table?
In chemistry, a group (also known as a family) is a column of elements in the periodic table of the chemical elements. There are 18 numbered groups in the periodic table; the f-block columns (between groups 2 and 3) are not numbered. The elements in a group have similar physical or chemical characteristics of the outermost electron shells ...
What is a group of elements made of hydrogen?
In history, several sets of group names have been used: a Group 1 is composed of hydrogen (H) and the alkali metals. Elements of the group have one s-electron in the outer electron shell. Hydrogen is not considered to be an alkali metal as it is not a metal, though it is more analogous to them than any other group.
What group is the noble gases in?
b Group 18 , the noble gases, were not discovered at the time of Mendeleev's original table. Later (1902), Mendeleev accepted the evidence for their existence, and they could be placed in a new "group 0", consistently and without breaking the periodic table principle.
What is the group 8 of elements?
An exception is the " iron group ", which usually refers to " group 8 ", but in chemistry may also mean iron, cobalt, and nickel, or some other set of elements with similar chemical properties. In astrophysics and nuclear physics, it usually refers to iron, cobalt, nickel , chromium, and manganese .
When did group 1 and 18 change to group 18?
The modern numbering system of "group 1" to "group 18" has been recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) since about 1990. It replaces two older incompatible naming schemes, used by the Chemical Abstract Service (CAS, more popular in the US), and by IUPAC before 1990 (more popular in Europe).
Is hydrogen an alkali metal?
Hydrogen is not considered to be an alkali metal as it is not a metal, though it is more analogous to them than any other group. This makes the group somewhat exceptional. b Group 18, the noble gases, were not discovered at the time of Mendeleev's original table.
Which group of the periodic table is the noble gas located in?
The noble gases, also known as the inert gases, are located in Group VIII of the periodic table. The noble gases are relatively nonreactive. This is because they have a complete valence shell. They have little tendency to gain or lose electrons.
What group is the alkaline earth in?
The alkaline earths are the elements located in Group IIA of the periodic table. The alkaline earths possess many of the characteristic properties of metals. Alkaline earths have low electron affinities and low electronegativities.
How are nonmetals separated from metals?
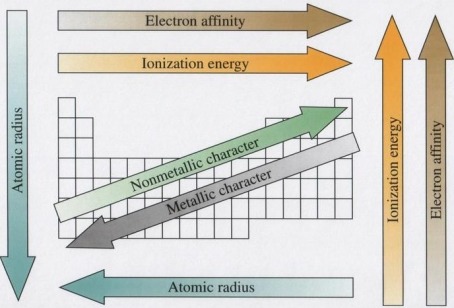
Nonmetals are separated from metals by a line that cuts diagonally through the region of the periodic table. Nonmetals have high ionization energies and electronegativities. They are generally poor conductors of heat and electricity. Solid nonmetals are generally brittle, with little or no metallic luster.
What are the physical properties of halogens?
These reactive elements have seven valence electrons. As a group, halogens exhibit highly variable physical properties . Halogens range from solid to liquid to gaseous at room temperature . The chemical properties are more uniform. The halogens have very high electronegativities. Fluorine has the highest electronegativity of all elements. The halogens are particularly reactive with the alkali metals and alkaline earths, forming stable ionic crystals.
What are the properties of metals?
Many of the properties of metals, including large atomic radius, low ionization energy, and low electronegativity, are due to the fact that the electrons in the valence shell of a metal atoms can be removed easily. One characteristic of metals is their ability to be deformed without breaking.
Where are the metalloids located?
The metalloids or semimetals are located along the line between the metals and nonmetals in the periodic table. The electronegativities and ionization energies of the metalloids are between those of the metals and nonmetals, so the metalloids exhibit characteristics of both classes.
What are transition metals?
The transition metals are located in groups IB to VIIIB of the periodic table. These elements are very hard, with high melting points and boiling points. The transition metals have high electrical conductivity and malleability and low ionization energies. They exhibit a wide range of oxidation states or positively charged forms. The positive oxidation states allow transition elements to form many different ionic and partially ionic compounds. The complexes form characteristic colored solutions and compounds. Complexation reactions sometimes enhance the relatively low solubility of some compounds.
How does the periodic table organize the elements?
The classic Periodic Table organizes the chemical elements according to the number of protons that each has in its atomic nucleus. (Image credit: Karl Tate, Livescience.com contributor)
Which group of the periodic table is alkaline earth metals in?
Alkaline-earth metals: The alkaline-earth metals make up Group 2 of the periodic table, from beryllium (Be) through radium (Ra). Each of these elements has two electrons in its outermost energy level, which makes the alkaline earths reactive enough that they're rarely found alone in nature. But they're not as reactive as the alkali metals. Their chemical reactions typically occur more slowly and produce less heat compared to the alkali metals.
What are the groups of metals that are radioactive?
All are radioactive. The actinides and the lanthanides together form a group called the inner transition metals. Transition metals: Returning to the main body of the table, the remainder of Groups 3 through 12 represent the rest of the transition metals.
What are the elements in the actinides?
Actinides: The actinides line the bottom row of the island and comprise elements 89, actinium (Ac), through 103, lawrencium (Lr). Of these elements, only thorium (Th) and uranium (U) occur naturally on Earth in substantial amounts. All are radioactive. The actinides and the lanthanides together form a group called the inner transition metals.
What is table salt?
The table salt in your kitchen, for example, is a marriage between the alkali metal sodium and the halogen chlorine. Noble gases: Colorless, odorless and almost completely nonreactive, the inert, or noble gases round out the table in Group 18.
How many elements were there at the time of Mendeleev?
There were only about 60 elements known at the time, but Mendeleev realized that when the elements were organized by weight, certain types of elements occurred in regular intervals, or periods. Today, 150 years later, chemists officially recognize 118 elements (after the addition of four newcomers in 2016) and still use Mendeleev's periodic table ...
Why is the period of sodium longer?
Moving down the table, periods are longer because it takes more electrons to fill the larger and more complex outer levels. The columns of the table represent groups, or families, of elements.
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).
What are element families and element groups?
For the most part, element families and element groups are the same things. Both describe elements that share common properties, usually based on the number of valence electrons. Usually, either family or group refers to one or more columns of the periodic table.
What is an element family?
Element families are elements that have the same number of valence electrons. Most element families are a single column of the periodic table, although the transition elements consist of several columns, plus the elements located below the main body of the table. An example of an element family is the nitrogen group or pnictogens.
How many valence electrons does a halogen have?
The halogens have 7 valence electrons, while the noble gasses have 8 valence electrons (or 0, depending on how you look at it).
Do element groups always have the same number of valence electrons?
Element groups, defined this way, do not always have the same number of valence electrons. For example, the halogens and noble gasses are distinct element groups, yet they also belong to the larger group of nonmetals.
