
Between the wars, Rommel served in the limited army of the Weimar Republic as a popular instructor at the Dresden Infantry School and the German War Academy at Potsdam. In 1934, he met Hitler, who had recently consolidated power in Germany as führer, chancellor, and commander in chief of the army.
What did Erwin Rommel do in WWI?
Rommel served in World War I in France, Romania, and Italy and quickly learned to love the vigor of war. He became known as someone who would participate in dangerous raids and recon missions, causing his men to joke, “ Where Rommel is, there is the front .”
What was Erwin Rommel's first battle in Africa?
Arriving in Africa in February 1941, Rommel quickly took charge of the faltering Axis campaign, scoring several quick victories against British defenses around Cyrenaica and surrounding the coastal fortress of Tobruk by mid-April.
What happened in the interwar years in Europe?
The Interwar Years (1919-1938) With the end of World War I, the old international system was torn down, Europe was reorganized, and a new world was born. The European nations that had fought in the Great War emerged economically and socially crippled.
Was Erwin Rommel aware of the power of propaganda?
In fact, Rommel was acutely aware of the power of propaganda in developing his career and reputation. He assiduously courted the German government's media machine, the Ministry of Information and Propaganda run by Joseph Goebbels.
See more

What was the significance of Rommel?
Erwin Rommel (1891-1944) was a German army officer who rose to the rank of field marshal and earned fame at home and abroad for his leadership of Germany's Afrika Korps in North Africa during World War II. Nicknamed “the Desert Fox,” Rommel also commanded German defenses against the Allied invasion of northern France.
What happened to Rommel during World War II?
On October 14, 1944, German Gen. Erwin Rommel, nicknamed “the Desert Fox,” is given the option of facing a public trial for treason, as a co-conspirator in the plot to assassinate Adolf Hitler, or taking cyanide. He chooses the latter.
What did Rommel do ww1?
Promotion to armoured division commander Following the invasion of Poland, Rommel began lobbying for command of one of Germany's panzer divisions, of which there were then only ten. Rommel's successes in World War I were based on surprise and manoeuvre, two elements for which the new panzer units were ideally suited.
What was Rommel's strategy?
Rommel describes his Stoßtruppen (shock troops) tactics, which used speed, deception, and deep penetration into enemy territory to surprise and overwhelm. Throughout the book, Rommel reports assigning small numbers of men to approach enemy lines from the direction in which attack was expected.
Who was Hitler's deadliest general?
Otto SkorzenyOtto SkorzenyYears of service1932–1945RankObersturmbannführerCommands heldSonder Lehrgang Oranienburg SS Panzer Brigade 150Battles/warsWorld War II Eastern Front Operation Oak Operation Panzerfaust Battle of the Bulge (Operation Greif)7 more rows
What happened to Hitler's generals after the war?
For these and other charges, the arrested military leaders were moved to prisons, stripped of their weapons and papers, and detained. They would all face tribunals or German courts, many of them at the famous Nuremberg Trials.
What was Hitler's lightning war?
The German invasion of Poland was the first test of Germany's newest mili- tary strategy—the blitzkrieg (BLIHTS•kreeg), or “lightning war.” It involved using fast-moving airplanes and tanks, followed by massive infantry forces, to take enemy defenders by surprise and quickly overwhelm them.
Who was the best German general in ww2?
Erich von Manstein, original name Erich Von Lewinski, (born Nov. 24, 1887, Berlin, Ger. —died June 11, 1973, Irschenhausen, near Munich, W. Ger.), German field marshal who was perhaps the most talented German field commander in World War II.
What does the D mean in D-Day?
DayIn other words, the D in D-Day merely stands for Day. This coded designation was used for the day of any important invasion or military operation.
Why did Rommel fail North Africa?
The Axis defeat at El Alamein meant that North Africa would be lost to Hitler and Mussolini. The defeat was due to a variety of factors. These included insufficient Axis numbers, overextended supply lines, and Allied air superiority.
What made Rommel a good leader?
His deep understanding of his men, his unusual courage, and his natural gift of leadership quite early showed promise of a great career. In the Prussian-German army, a career on the general staff was the normal avenue for advancement, yet Rommel declined to take that road.
What was Rommel's role in D Day?
In 1944, after having withdrawn him Afrika Korps, he receives the command of the army group B located in Normandy, in front of England. His delicate task is to defend the beaches of an Allied invasion.
Who was the best German general in ww2?
Erich von Manstein, original name Erich Von Lewinski, (born Nov. 24, 1887, Berlin, Ger. —died June 11, 1973, Irschenhausen, near Munich, W. Ger.), German field marshal who was perhaps the most talented German field commander in World War II.
What was Rommel's illness?
Three years later in Romania, he lost quite a bit of blood from a bullet to the arm, and he also continuously suffered from stomach ailments, fevers and exhaustion. More physical hardships came during World War II, from appendicitis to a face wound caused by a shell splinter.
Who defeated Rommel in North Africa?
the British Eighth ArmyIt marked the beginning of the end for the Axis in North Africa. The charismatic Field Marshal Erwin Rommel was comprehensively defeated by the British Eighth Army, and Allied material superiority meant that he had little chance of rallying his broken forces.
What happened to Rommel's wife after the war?
Stemmer died in 1928, when Rommel's wife Lucie was pregnant with the couple's son Manfred. Her cause of death was given as pneumonia, though it is generally accepted that she probably committed suicide.
Early Life and Service in World War I
Rommel was born on November 15, 1891 in Heidenheim, in the kingdom of Württemberg, Germany. While his father was a schoolteacher and headmaster, young Rommel displayed little interest in academics, and his family urged him to pursue a career as an army officer.
Relationship with Adolf Hitler
Between the wars, Rommel served in the limited army of the Weimar Republic as a popular instructor at the Dresden Infantry School and the German War Academy at Potsdam. In 1934, he met Hitler, who had recently consolidated power in Germany as führer, chancellor, and commander in chief of the army.
From Blitzkrieg to the Afrika Korps
Hitler gave Rommel command of the 7th Panzer Division, one of 10 tank divisions that took part in the blitzkrieg invasion of Belgium and France that began on May 10, 1940. As his division drove forward with impressive speed, Rommel insisted on leading his men from the front lines, as opposed to commanding from the rear.
Role in Normandy and the Plot to Kill Hitler
After briefly commanding forces in Italy, Rommel headed to northern France, where he was tasked with fortifying German defenses along the Channel coast ahead of a predicted Allied invasion.
What happened to Rommel in 1914?
In September 1914, for example, Rommel charged three French soldiers with a bayonet after running out of ammunition, only to be shot in the thigh so badly that a hole opened up as big as his fist.
Why did Rommel go to North Africa?
After leading a tank division in the 1940 blitzkrieg of France, Rommel was transferred to North Africa in order to help the struggling Italians fight the British. Almost immediately he reversed the tide, pushing the British back hundreds of miles in a series of audacious assaults, for which he received his “Desert Fox” nickname, along with a promotion to field marshal. Finally, in October 1942, the numerically superior British halted his advance near El Alamein, Egypt. Running low on tanks, ammunition and fuel, Rommel prepared to retreat. But Hitler sent a letter telling him not to yield “even a yard of ground.” “As to your troops,” the führer added, “you can show them no other road than that to victory or death.” Despite his reverence for Hitler, Rommel disobeyed for fear his force would be completely annihilated. He also disregarded an order directing German generals to execute Allied commandos caught behind enemy lines. In the end, Rommel fled all the way to Tunisia, winning a tank battle there against the Americans—and losing one against the British—before returning to Europe in March 1943. Two months later, the Allies kicked the Germans out of North Africa altogether, setting the stage for their invasion of Italy.
Why did Rommel disobey Hitler?
Despite his reverence for Hitler, Rommel disobeyed for fear his force would be completely annihilated.
Where Rommel is there is the front?
Taking part in dangerous raids and reconnaissance missions throughout World War I , his men supposedly joked, “Where Rommel is, there is the front.”. But all of this fighting, including one 52-hour period in which his unit captured some 9,000 Italian prisoners, came with a price.
Did Rommel join the Nazi Party?
In so doing, they portrayed Rommel as a chivalrous combatant, pointing out, among other things, that he apparently never joined the Nazi Party. Yet his devotion to Hitler was incontrovertible. When Hitler took power, Rommel approved of his remilitarization plans, calling him the “unifier of the nation.”.
Is Rommel still celebrated?
8. Rommel is still celebrated in Germany. Unlike other prominent World War II-era Germans, Rommel has escaped mass vilification. In fact, his name still graces two military bases and several streets in Germany, and a monument in his hometown praises him as “chivalrous,” “brave” and a “victim of tyranny.”.
Did Rommel attend Nazi indoctrination?
He also attended Nazi indoctrination courses and signed his letters “Heil Hitler!”. Hitler even gave him an autographed copy of “Mein Kampf.”. Only later did Rommel grow disillusioned, believing that Germany must negotiate with the Allies rather than fight to the bitter end. 4.
What division did Rommel command?
Rommel was then given command of the new 7th Panzer Division for the invasion of France in 1940. The rapidity of this promotion was extraordinary, but so was the young commander's performance in the new, rapid form of warfare known as blitzkrieg.
Why was Rommel important to the Allies?
The image of Rommel as an extraordinary general helped take the edge off the numerous failings of the British army in the desert. It was, after all, easier to explain away the numerous defeats by highlighting their enemy's strengths, than it was to face up to British shortcomings.
Why was Rommel interested in Hitler?
Rommel's interest arose from the fact that his position in the German army was entirely dependent on Hitler's patronage. Since he had never been staff trained, the normal professional route to high command was not open to him.
What was the battle that Tobruk fell to?
Within days, Tobruk had fallen to Rommel's forces © The Battle of Gazala, fought from 26 May to 20 June 1942, was Rommel's greatest triumph. In a daring and risky move, he drove his army around the flank of the British army and into its rear.
What did Rommel's lack of staff training mean?
His lack of staff training meant that, for all his tactical success, he never properly understood the broader context of 'his' war in North Africa - or the fact that the campaign was essentially defensive for the Axis. Most importantly, his failure to understand the complex logistics of the North African theatre meant that his daring advances were never sustainable.
Why did Rommel have a fingertip feel?
Much of Rommel's 'fingertip feel' for the battlefield was due to his excellent signals intelligence. Signals Intercept Company 621, which listened into British radio transmissions, provided him with unparalleled tactical insights, and was actually responsible for many of his most striking successes. During 1942, the US Military Attaché in Cairo, through transmissions decrypted by Italian intelligence, gave him invaluable operational intelligence. When these sources were discovered and stopped by the British in 1942, his tactical feel was never again as accomplished.
Who was the German general who attacked the Egyptian fortress of Tobruk?
But Rommel attacked before the British were ready. And his lightning-fast offensive caught his opponents completely off balance. Very quickly the German forces, soon to be famous as the Afrika Korps, were established on the Egyptian frontier along with their Italian allies, while simultaneously besieging the Allied fortress of Tobruk in Libya. The camera loved Rommel, and Goebbels made sure that this victorious general now received plenty of attention from the German media.
What was Rommel's success?
In the fall of 1942, Rommel’s success would turn with the British recapture of Tobruk at the Battle of El Alamein and the eventual loss of North Africa in May 1943.
How old was Rommel when he joined the army?
Source: Wikipedia. In 1909, as an eighteen-year-old, Rommel first attempted to join the military either in the artillery or as an engineer, but was rejected. Finally, however, in 1910, Rommel was accepted into the Germany infantry. As a cadet, Rommel was considered to be a “useful soldier,” an appellation that the rest of his military career would ...
What did Rommel do at the Battle of Caporetto?
At the Battle of Caporetto, Rommel’s leadership of his company in a surprise attacked captured Mount Matajur and outflanked thousands of Italian troops, meriting the Blue Max. Rommel would proudly wear his Blue Max medal for the rest of his life.
How did Rommel die?
On October 14, 1944, German officers arrived at Rommel’s home to take him to a remote location where Rommel committed suicide through a cyanide capsule. He was 52 years old and received a full military burial, likely to appease the German public who did not know of Rommel’s connection to the assassination attempt.
Why did Rommel change his tune?
Although Rommel had trusted Hitler’s leadership up until this point and did not question the Fuhrer, Rommel began to change his tune in 1944 because he believed that Germany was going to lose the war. Although Rommel doubted Hitler’s abilities for peace-making, evidence suggests that he did not want to dispose of him.
How many miles did Rommel cover in one week?
During the Battle of France, Rommel’s 7th Panzer division raced from Sedan on the border of Germany and France to the coast of the English Channel, covering 200 miles in just one week and capturing over 100,000 Allied troops as well as the French garrison of Cherbourg.
Who was Hitler's bodyguard?
Two years later, Hitler gave Rommel command of his personal bodyguard during the Invasion of Poland in 1939. Finally, in February 1940, Hitler named Rommel as the commander of the 7th Panzer division, one of the new panzer units.
What was the political atmosphere of the inter-war years?
The political atmosphere of the inter-war years was sharply divided between those who thought the extreme left could solve Europe's problems, and those who desired leadership from the extreme right. There were very few moderates, and this situation kept the governments of Britain, France, and Eastern Europe in constant turmoil, swinging wildly between one extreme and the next. Extreme viewpoints won out in the form of totalitarian states in Europe during the inter-war years, and communism took hold in the Soviet Union, while fascism controlled Germany, Italy and Spain.
Who came to power in Germany in the 1930s?
In Germany, Adolf Hitler's fascist Nazi Party came to power during the 1930s and prepared once again to make war on Europe. With Britain and France tied up in their own affairs, the path to World War II lay clear.
What happened to Europe after World War 1?
With the end of World War I, the old international system was torn down , Europe was reorganized, and a new world was born. The European nations that had fought in the Great War emerged economically and socially crippled. Economic depression prevailed in Europe for much of the inter-war period, and debtor nations found it impossible ...
Which countries were fascist during the inter-war years?
Extreme viewpoints won out in the form of totalitarian states in Europe during the inter-war years, and communism took hold in the Soviet Union, while fascism controlled Germany, Italy and Spain.
What happened to Trotsky in 1927?
By 1927, Trotsky had lost his position on the Central Committee, and was expelled from the party. He fled to Turkey, and eventually to Mexico, where he was killed in 1940 by a Stalinist agent.
What did Trotsky advocate?
Trotsky advocated 'permanent world revolution,' claiming that the Soviet Union should strive continuously to encourage proletarian revolutions throughout the world. Stalin contrasted Trotsky's view with a 'socialism in one country' message, which stressed the consolidation of the communist regime within the Soviet Union, ...
How many people were killed by Stalin in the 1930s?
Stalin would accept no resistance, and initiated a reign of terror during 1929 and 1930, during which as many as 3 million were killed. During the 1930s, Stalin sought to eliminate all barriers to his complete and total exercise of power.
Which idea enabled the rise of the totalitarian state?
Most can agree, however, that the Marxist idea of "dictatorship of the proletariat" enabled the rise of the totalitarian state. Whether or not there was an aspect of totalitarianism inherent in Lenin's philosophy, he never consolidated power to the same extent as Stalin did.
Was totalitarianism a part of Marxism?
Historians disagree over whether or not totalitarianism is an inherent aspect of Marxist-Leninist theory, or whether Joseph Stalin, as many claim, deviated from the true tenets of Marxism-Leninism in constructing his government. Most can agree, however, that the Marxist idea of "dictatorship of the proletariat" enabled the rise of the totalitarian state. Whether or not there was an aspect of totalitarianism inherent in Lenin's philosophy, he never consolidated power to the same extent as Stalin did. Indeed, upon his deathbed, dictating his last testament, Lenin decried the dictatorial nature of his government and expressed the fear that in the wrong hands, totalitarianism could be used in a manner antagonistic to the masses, for which the government was intended to work.
Who was Stalin's successor?
He served under Lenin as commissar for nationalities, and in 1923 became general secretary of the party. Lenin supported Trotsky over Stalin as his successor, claiming Stalin was "too rude" to lead the government.
Who was the first totalitarian state to establish itself after World War 1?
Summary. The Soviet Union was the first totalitarian state to establish itself after World War One. In 1917, Vladimir Lenin seized power in the Russian Revolution, establishing a single-party dictatorship under the Bolsheviks. After suffering a series of strokes, Lenin died on January 21, 1924, with no clear path of succession.
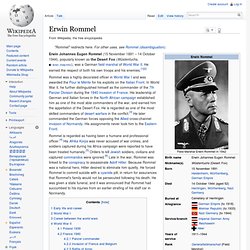
Early Life and Service in World War I
- Rommel was born on November 15, 1891, in Heidenheim, in the kingdom of Württemberg, Germany. While his father was a school teacher and headmaster, young Rommel displayed little interest in academics, and his family urged him to pursue a career as an army officer. As the more prestigious cavalry and guard regiments were limited to those with noble or military background…
Relationship with Adolf Hitler
- Between the wars, Rommel served in the limited army of the Weimar Republic as a popular instructor at the Dresden Infantry School and the German War Academy at Potsdam. In 1934, he met Hitler, who had recently consolidated power in Germany as führer, chancellor, and commander in chief of the army. The following year, Hitler reintroduced conscription, a policy th…
from Blitzkrieg to The Afrika Korps
- Hitler gave Rommel command of the 7th Panzer Division, one of 10 tank divisions that took part in the blitzkrieginvasion of Belgium and France that began on May 10, 1940. As his division drove forward with impressive speed, Rommel insisted on leading his men from the front lines, as opposed to commanding from the rear. Less than a year later, this ...
Role in Normandy and The Plot to Kill Hitler
- After briefly commanding forces in Italy, Rommel headed to northern France, where he was tasked with fortifying German defenses along the Channel coast ahead of a predicted Allied invasion. In contrast with other German generals, he favored a bold counterattack strategy after the Allied landings, a disagreement that would ultimately weaken the German response when the invasion …
Sources
- Pier Paolo Battistelli. Erwin Rommel. (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2012) Robert Citino. “Drive to Nowhere: The Myth of the Afrika Korps, 1941-43.” National World War II Museum, June 14, 2018. Erwin Rommel - Holocaust Encyclopedia. U.S. Holocaust Memorial Museum.