
What does C stand for on the periodic table?
What is C on the periodic table? Carbon - Element information, properties and uses. Periodic Table. What is number 4 on the periodic table? The element with atomic number 4 is beryllium, which means each atom of beryllium has 4 protons. The symbol for atomic number 4 is Be.
What does Cu mean on the periodic table?
Copper (Cu), chemical element, a reddish, extremely ductile metal of Group 11 (Ib) of the periodic table that is an unusually good conductor of electricity and heat. Copper is found in the free metallic state in nature.
Where is carbon found on the periodic table?
Carbon is the sixth element on the periodic table. It is located in period 2 and group 14. Element homologues are elements in the same column or group of the periodic table. They share some common chemical and physical properties because of the way valence electrons are distributed.
What are the 5 traditional elements?
What Are the 5 Traditional Elements?
- Babylonian 5 Elements
- Medieval Alchemy. The number of traditional elements in medieval alchemy varies from 4, 5, or 8. The first four are always found.
- Greek 5 Elements
- Chinese 5 Elements - Wu Xing
- Japanese 5 Elements - Godai
- Hindu and Buddhist 5 Elements. Akasha is the equivalent to Aristotle's aether, in the Greek tradition. ...
- Tibetan 5 Elements (Bon)
What period is C in on the periodic table?
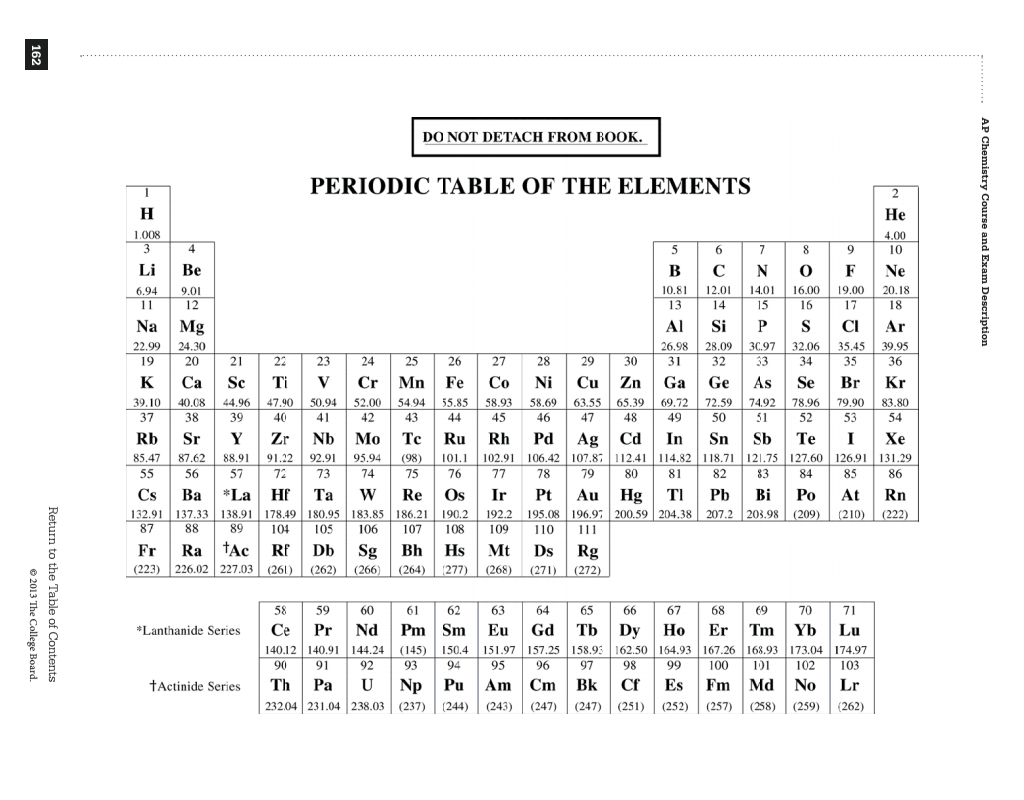
Period 2Fact boxGroup14Sublimes at 3825°C, 6917°F, 4098 KPeriod2Sublimes at 3825°C, 6917°F, 4098 KBlockp3.513 (diamond); 2.2 (graphite)Atomic number612.011State at 20°CSolid12C, 13C, 14C2 more rows
What is the elements name for C?
CarbonCarbon (from Latin carbo 'coal') is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up only about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust.
What are 3 facts about carbon?
More Carbon FactsCarbon usually has a valence of +4, which means each carbon atom can form covalent bonds with four other atoms. ... Three isotopes of carbon occur naturally. ... Inorganic carbon sources include carbon dioxide, limestone, and dolomite. ... Carbon black was the first pigment used for tattooing.More items...•
What names start with C and end with e?
Baby Names FinderCharlotteRemoved from listChevelleRemoved from listCharlizeRemoved from listCheyanneRemoved from listCharleneRemoved from list36 more rows
Is nitrogen a element?
Nitrogen; Nitrogen is a chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless and mostly inert gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.1% by volume of Earth's atmosphere.
What is NE in elements?
neon (Ne), chemical element, inert gas of Group 18 (noble gases) of the periodic table, used in electric signs and fluorescent lamps.
Is Aluminium a compound or element?
aluminum (Al), also spelled aluminium, chemical element, a lightweight silvery white metal of main Group 13 (IIIa, or boron group) of the periodic table. Aluminum is the most abundant metallic element in Earth's crust and the most widely used nonferrous metal.
What is the symbol for fluorine on the periodic table?
(F)fluorine (F), most reactive chemical element and the lightest member of the halogen elements, or Group 17 (Group VIIa) of the periodic table.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular array of the chemical elements organized by atomic number, from the element with the lowest atomic number, hydrogen...
What do periodic table groups have in common?
The groups of the periodic table are displayed as vertical columns numbered from 1 to 18. The elements in a group have very similar chemical proper...
Where does the periodic table come from?
The arrangement of the elements in the periodic table comes from the electronic configuration of the elements. Because of the Pauli exclusion princ...
Why does the periodic table split?
The periodic table has two rows at the bottom that are usually split out from the main body of the table. These rows contain elements in the lantha...
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).
What is the CIAAW?
Since 1899 the IUPAC Commission on Isotopic Abundances and Atomic Weights ( CIAAW) has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. For example, Carbon had an atomic weight of 12.00 in 1902 but today it is [12.0096, 12.0116]! Times sure have changed as the source of the sample will determine the value.
What is PubChem working with?
PubChem is working with IUPAC to help make information about the elements and the periodic table machine-readable.
Who is responsible for deciding what needs to be changed?
While much of what is in the periodic table is stable and unlikely to change, the IUPAC organization is responsible for deciding what needs to be changed. They have created criteria for what constitutes the discovery of a new element.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Did Mendeleev's predictions get dismissed?
There were plenty of skeptics and it took years to gain international acceptance, but once newly-discovered elements matched the ones that Mendeleev predicted, his patterns could not be dismissed. In addition, some of the properties that he "fudged" were later recalculated and found to be much closer to his predictions.
What group is carbon in?
This electron arrangement indicates that the outermost orbit of Carbon (C) has 4 electrons. Hence, it lies in group 14.
Which block will the elements lie in?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
What happens when Carbon is burnt?
When carbon (C) is burnt in air, it reacts with oxygen (O 2) and produces carbon dioxide (CO 2 ).
Why is Carbon black in color?
First of all, I want to clarify that the pure form of carbon is diamond and it is not black but it is colorless.
Why Graphite is a good conductor of electricity and Diamond is not?
The simple answer: Graphite has free electrons which conducts electricity. While the diamond does not have free electrons, so it does not conduct electricity.
Why is carbon atom smaller than silicon?
Due to small size of carbon atom, it attracts the shared electron pair with a greater force. While silicon atom is bigger in size, so it attracts the electron pair with lesser force. Hence, as the carbon atom is smaller than silicon atom, it is more electronegative than silicon.
How many orbits does carbon have?
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in carbon is 2. Hence, as carbon has 2 orbits, it lies in period 2 of the Periodic table.
What is the periodic table?
periodic table, in full periodic table of the elements, in chemistry, the organized array of all the chemical elements in order of increasing atomic number —i.e., the total number of protons in the atomic nucleus. When the chemical elements are thus arranged, there is a recurring pattern called the “periodic law” in their properties, ...
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element . Hydrogen has 1 proton, and oganesson has ...
What elements are triads?
Döbereiner in 1817 showed that the combining weight, meaning atomic weight, of strontium lies midway between those of calcium and barium, and some years later he showed that other such “ triads ” exist (chlorine, bromine, and iodine [halogens] and lithium, sodium, and potassium [alkali metals]). J.-B.-A. Dumas, L. Gmelin, E. Lenssen, Max von Pettenkofer, and J.P. Cooke expanded Döbereiner’s suggestions between 1827 and 1858 by showing that similar relationships extended further than the triads of elements, fluorine being added to the halogens and magnesium to the alkaline-earth metals, while oxygen, sulfur, selenium, and tellurium were classed as one family and nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth as another family of elements.
Why do the elements in the periodic table have different orbits?
The arrangement of the elements in the periodic table comes from the electronic configuration of the elements. Because of the Pauli exclusion principle, no more than two electrons can fill the same orbital. The first row of the periodic table consists of just two elements, hydrogen and helium. As atoms have more electrons, they have more orbits available to fill, and thus the rows contain more elements farther down in the table.
What are the elements that are related to the first seven?
Newlands proposed classifying the elements in the order of increasing atomic weights, the elements being assigned ordinal numbers from unity upward and divided into seven groups having properties closely related to the first seven of the elements then known: hydrogen, lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen . This relationship was termed the law of octaves, by analogy with the seven intervals of the musical scale.
Who proposed the periodic law?
Then in 1869, as a result of an extensive correlation of the properties and the atomic weights of the elements, with special attention to valency (that is, the number of single bonds the element can form), Mendeleyev proposed the periodic law, by which “the elements arranged according to the magnitude of atomic weights show a periodic change of properties.” Lothar Meyer had independently reached a similar conclusion, published after the appearance of Mendeleyev ’s paper.
When the chemical elements are thus arranged, there is a recurring pattern called the periodic law?
When the chemical elements are thus arranged, there is a recurring pattern called the “periodic law” in their properties, in which elements in the same column (group) have similar properties. The initial discovery, which was made by Dmitry I. Mendeleyev in the mid-19th century, has been of inestimable value in the development of chemistry.
What is the first group of elements in the periodic table?
Group 1: Alkali metals group. Alkali metals group is the very first group (group 1) on the periodic table. The elements included in the Alkali metals group are; Lithium (Li)
Why are the elements in the bottom two rows of the periodic table included in group 3?
The elements in the two bottom rows of the periodic table are also included in these groups. They are placed in the two separate rows at the bottom because they show few different properties. Actually, the elements in the bottom rows are the extension of group 3 only. So they are included in group 3. But as these elements have few different ...
How many groups are there in the periodic table?
Groups are the vertical columns on the periodic table. There are total 18 vertical columns on periodic table. Hence there are 18 groups. The elements lying in the same groups show similar chemical properties and they also have same number of valence electrons.
What is the oxygen group on the periodic table?
Oxygen group is the group 16 on the periodic table.
What is an example of group 18?
Example of group 18. All the elements of group 18 are chemically inert (that means they do not easily react with other elements). And all the elements of group 18 have a complete octet (that means they have 8 electrons in their outer shell).
Which group is alkaline earth metals?
Alkaline earth metals are the group 2 elements on the periodic table.
Is the Interactive Periodic Table free?
Checkout Interactive Periodic table and download it’s high resolution image now ( It’s FREE)
What is the line between metals and nonmetals called?
Metalloids (or Semimetals ) There is a zig-zag line toward the right side of the periodic table that acts as a sort of border between metals and nonmetals. Elements on either side of this line exhibit some properties of metals and some of the nonmetals. These elements are the metalloids, also called semimetals.
What are the properties of nonmetals?
The elements on the right-hand side of the periodic table are the nonmetals. Nonmetals properties are: 1 usually poor conductors of heat and electricity 2 often liquids or gases at room temperature and pressure 3 lack metallic luster 4 readily gain electrons (high electron affinity) 5 high ionization energy
Why do metals bond to other metals?
Metals also bond to other metals to share valence electrons in what becomes an electron sea surrounding all the affected atoms. Atoms of different metals form alloys, which have distinct properties from their component elements. Because the electrons can move freely, metals readily conduct electricity. Cite this Article.
What are the two rows of elements below the body of the periodic table called?
The two rows of elements below the body of the periodic table are metals. Specifically, they are a collection of transition metals that are called the lanthanides and actinides or the rare earth metals.
What are the three categories of elements?
The three broad categories of elements are metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Most elements are metals. Nonmetals are located on the righthand side of the periodic table. Metalloids have properties of both metals and nonmetals.
Why is the periodic table important?
To get the most out of the table, it helps to know the parts of the periodic table and how to use the chart to predict element properties.
What are the rows of the periodic table called?
The rows of the periodic table are called periods. All elements within a period share the same highest electron energy level.
How are atomic nuclei determined?
Properties of atomic nuclei (atomic mass, nuclear cross-sections) are determined by the number of protons and number of neutrons (neutron number). It must be noted, especially nuclear cross-sections may vary by many orders from nuclide with the neutron number N to nuclide with the neutron number N+1. For example, actinides with odd neutron number are usually fissile (fissionable with slow neutrons) while actinides with even neutron number are usually not fissile (but are fissionable with fast neutrons). Heavy nuclei with an even number of protons and an even number of neutrons are (due to Pauli exclusion principle) very stable thanks to the occurrence of ‘paired spin’. On the other hand, nuclei with an odd number of protons and neutrons are mostly unstable.
How does electronegativity affect a compound?
In general, an atom’s electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. The most electronegative atom, fluorine, is assigned a value of 4.0, and values range down to cesium and francium which are the least electronegative at 0.7. Electronegativity is related with ionization energy and electron affinity. Electrons with low ionization energies have low electronegativities because their nuclei do not exert a strong attractive force on electrons. Elements with high ionization energies have high electronegativities due to the strong pull exerted by the positive nucleus on the negative electrons. Therefore the electronegativity is greatest at the top-right of the periodic table and decreases toward the bottom-left.
How many protons does calcium have?
Calcium is a chemical element with atomic number 20 which means there are 20 protons and 20 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Calcium is Ca.
What are the two forces that make up the nucleus?
Atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons, which attract each other through the nuclear force, while protons repel each other via the electric force due to their positive charge. These two forces compete, leading to various stability of nuclei. There are only certain combinations of neutrons and protons, which forms stable nuclei.
What is the charge of an atom?
Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs. In a neutral atom there are as many electrons as protons moving about nucleus. It is the electrons that are responsible for the chemical bavavior of atoms, and which identify the various chemical elements.
How to determine the stability of an isotope?
To determine the stability of an isotope you can use the ratio neutron/proton (N/Z). Also to help understand this concept there is a chart of the nuclides, known as a Segre chart. This chart shows a plot of the known nuclides as a function of their atomic and neutron numbers. It can be observed from the chart that there are more neutrons than protons in nuclides with Z greater than about 20 (Calcium). These extra neutrons are necessary for stability of the heavier nuclei. The excess neutrons act somewhat like nuclear glue. Only two stable nuclides have fewer neutrons than protons: hydrogen-1 and helium-3.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements.
What are the horizontal rows on the periodic table called?
The horizontal rows on the periodic table are known as Periods.
Why is period 1 the shortest period?
Period 1 of the periodic table is given the name shortest period because there are only two elements in period 1.
Why are period 4 and period 5 called long periods?
Period 4 and period 5 are given the name long periods of the periodic table because there are 18 elements in these periods. The elements of the long periods are shown in tables below.
How many periods are there in 2021?
Periods in Periodic table: The periods are the horizontal rows on a Periodic table. There are 7 horizontal rows on Periodic table. Hence there are total 7 periods on the Periodic table.
Why is period 2 called a short period?
Period 2 and period 3 of the periodic table are named as the short period because there are 8 elements in these periods.
Which period has the longest period?
Period 6 and 7: Longest period. Period 5 and period 6 are named as longest periods of the periodic table because there are 32 elements in these periods. The elements of the longest periods are shown in tables below.
How many energy shells does period 2 have?
All the elements of period 2 have two energy shells (or orbits).
