Full Answer
How to naturally overcome the refractory period?
- Reduce waistline / excess stomach fat
- Sleep 8 hours a night
- Reduce stress (cortisol production)
- Lift weights
- Eat a balanced diet of protein, fats and carbs (don’t cut out fats and carbs, they are essential)
- Absorb some sunlight / Vitamin D supplementation
Why do I have a refractory period?
The refractory period occurs right after you reach your sexual climax. It refers to the time between an orgasm and when you feel ready to be sexually aroused again. It’s also called the “resolution” stage. Does everyone have one? Yes! It’s not just limited to people with penises.
What is the refractory period, and can you reduce it?
The refractory period is a period of relative inexcitability that occurs after orgasm and ejaculation. Concretely, during this moment, it is not possible to have an erection and even less an ejaculation. Unlike women, men cannot have two orgasms simultaneous or successive. A normal stage of male sexuality They all “undergo” the obligatory passage where ]
What does 'refractory period' mean?
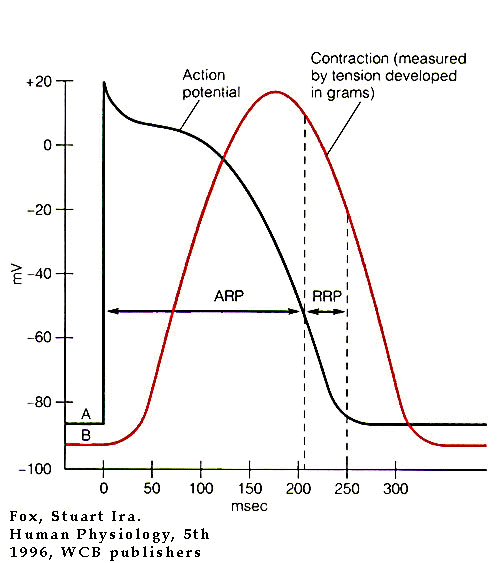
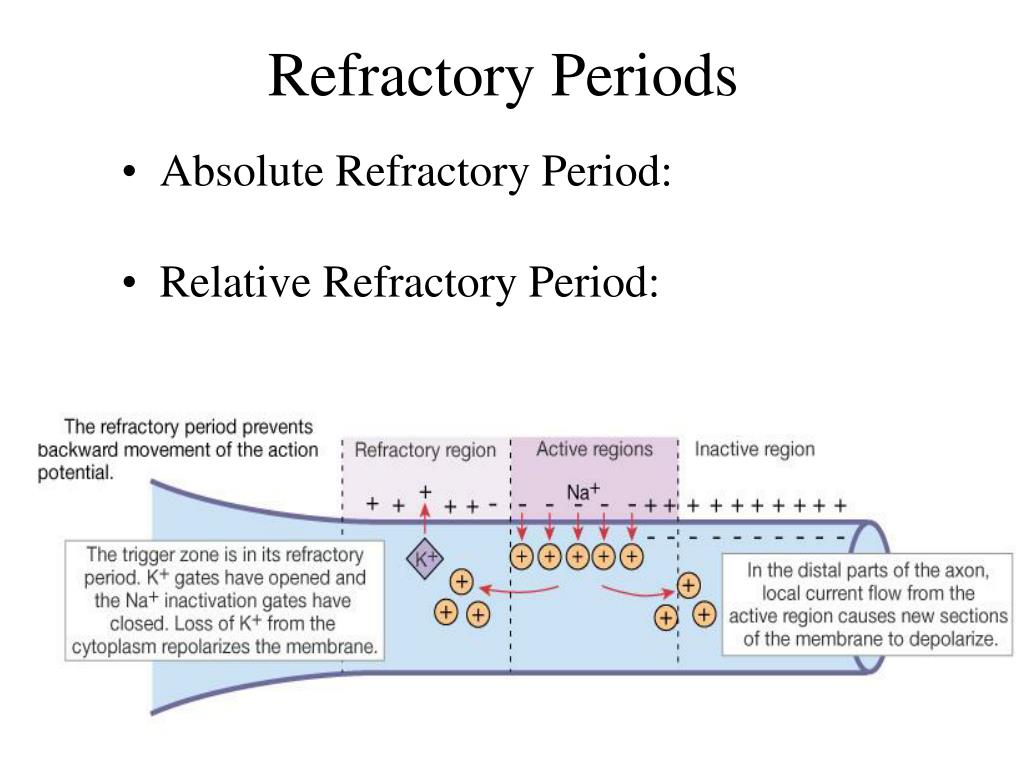
The Refractory period is the period that immediately follows a nerve impulse transmission or an action potential. This is also regarded as the characteristic recovery time of one action potential before the second. There are two main types of refractory periods in physiology; the absolute refractory period and the relative refractory period.
What is the meaning of effective refractory period?
The effective refractory period (ERP) is the longest S1-S2 interval that fails to capture or depolarize the tissue of interest, at the designated stimulus amplitude and duration used for the EPS or delivered remotely by the cardiac tissue.
What is the difference between effective refractory period and absolute refractory period?
The resting period where the heart does not respond to a stimulus or produce an action potential is called the effective refractory period (ERP). Additionally, the absolute refractory period (ARP) involves a part of the ERP where it is absolutely impossible to stimulate an action potential.
Why is effective refractory period important?
ERP acts as a protective mechanism and keeps the heart rate in check and prevents arrhythmias, and it helps coordinates muscle contraction. Anti-arrhythmic agents used for arrhythmias usually prolong the ERP.
What increases effective refractory period?
Pharmacological Effects. Quinidine is a Class 1A agent that increases the action potential duration and the effective refractory period. It also reduces the force of contraction of the heart and possesses anticholinergic activity.
What are the two types of refractory periods?
Absolute and relative refractory periods are two types of refractory periods which occur after an action potential. Moreover, they are two of the several phases of an action potential. They are the time taken for an excitable membrane to be ready for a second stimulus.
Which medication prolongs the effective refractory period?
Amiodarone blocks fast sodium channels, beta-receptors, L-type calcium channels, and delayed rectifier potassium channels. It prolongs the effective refractory periods of all cardiac tissue.
What is the refractory period of a man?
Genitalia. As a general rule, the male refractory period is longer than the female refractory period. The average range for men is between a few minutes and two hours before they can ejaculate again; for women, it's between a few seconds and a few minutes before they can achieve another climax.
What is APD and ERP?
One drug, quinidine, of group Ia increases the action potential duration (APD) and effective refractory period (ERP) and slows repolarization by blocking Na channels.
When does the refractory period end?
one millisecondThe refractory period in a neuron occurs after an action potential and generally lasts one millisecond.
How long does action potential last?
Action potentials last about 1 millisecond each, so the fastest rate for a train of action potentials is limited to about a thousand action potentials per second.
What is refractory period in pharmacology?
During phases 0, 1, 2, and part of phase 3, the cell is refractory to the initiation of new action potentials. This is termed the effective refractory period (ERP). During the ERP, stimulation of the cell does not produce new, propagated action potentials.
What is ERP in physiology?
An event-related potential (ERP) is the measured brain response that is the direct result of a specific sensory, cognitive, or motor event. More formally, it is any stereotyped electrophysiological response to a stimulus.
What is the absolute refractory period quizlet?
Absolute Refractory period. The period from the initiation of the action potential to immediately after the peak is referred to as the absolute refractory period (ARP) This is the time during which another stimulus given to the neuron will not lead to a second action potential.
Where is the absolute refractory period on an ECG?
QT Interval – Beginning of QRS Complex to end of T wave – Absolute Refractory Period is the beginning of QRS to PEAK of T wave.
How long does absolute refractory period last?
1–2 ms.The time during which the nerve is refractory to a second stimulus is called the absolute refractory period. It typically lasts for 1–2 ms. Following the absolute refractory period is a second, relative refractory period.
Why does the absolute refractory period occur quizlet?
Absolute refractory period occurs because of the inactivation of sodium channels. Since the sodium channels are inactivated, the neuron can't depolarize and initiate another action potential. Relative refractory period occurs due to the slow inactivation of potassium channels.
What happens in the refractory period?
During the refractory period, the cardiac cell cannot fire another action potential even if a stimulus is received. Sodium channels become inactive...
What are the two types of refractory periods?
Refractory periods are resting periods where the heart cannot produce another action potential. The effective refractory period (ERP) and the absol...
Why is the refractory period important in cardiac muscle?
The refractory period is essential for the cardiac muscle to maintain a normal heart rhythm. Any abnormalities in the refractory period can lead to...
Where are refractory periods measured?
It is important that measurements of refractory periods be taken at specific sites. Measurements of atrial and ventricular ERP are taken at the site of stimulation. Measurements of AVN ERP and HPS ERP are taken from responses in the HB electrogram.
What is excitability in refractory period?
Refractoriness or, more appropriately, excitability is defined by the response of a tissue to premature stimulation. Refractory periods are analyzed by the extrastimulus technique, with progressively premature extrastimuli delivered after a train of 8 to 10 paced beats at a fixed PCL to allow for reasonable (more than 95%) stabilization of refractoriness , which is usually accomplished after 3 or 4 paced beats.
What is the RRP in physics?
The RRP is defined as the longest premature coupling interval (S 1 -S 2) that results in prolonged conduction of the premature impulse (an increase in stimulus to distal response time) compared with the conduction of the stimulus delivered during the basic drive train. Conduction is slowed when a wavefront encounters tissue that is not completely repolarized. Thus, the RRP marks the end of the full recovery period, the zone during which conduction of the premature and basic drive impulses is identical. The RRP is generally slightly longer than the ERP by an amount called the latency period. During the latency period, the tissue is excitable, but the excitation wavefront conducts with slower or even decremental conduction.
What is the longest premature coupling interval?
The ERP is the longest premature coupling interval (S 1 -S 2) at a designated stimulus amplitude (usually 2× diastolic threshold) that results in failure of propagation of the premature impulse through a tissue (i.e., fails to capture). ERP therefore must be measured proximal to the refractory tissue.
What is the shortest preexcited R-R interval?
A shortest preexcited R-R interval less than 220 to 250 milliseconds during AF has been shown to be the best discriminator of those at risk of VF, with a high sensitivity (88% to 100%) and a high negative predictive value for identifying children and young adults with WPW syndrome at risk for VF. However, the positive predictive value is low (19% to 38%), largely due to the very low incidence of SCD in these patients. Also, a shortest preexcited R-R interval less than 250 milliseconds during AF has been noted in 20% to 26% of asymptomatic adults with a WPW pattern, and in up to 67% when isoproterenol is administered. Thus, although isoproterenol raises the sensitivity of invasive EP testing, it markedly reduces the specificity. 5
What are the variables that are considered in the assessment of refractory periods?
Several variables are considered in the assessment of refractory periods, including the stimulus amplitude and the basic drive CL. Longer drive CLs are generally associated with longer refractory periods. However, refractory periods of different parts of the conducting system do not respond comparably with changes in the drive CLs. 63
How to determine anterograde ERP?
Programmed atrial stimulation is used to evaluate the anterograde ERP of the BT. Because BT refractoriness shortens with decreasing pacing cycle length (PCL), the ERP should be determined at multiple PCLs (preferably ≤400 milliseconds). In addition, atrial stimulation should be performed close to the BT atrial insertion site to obviate the effect of intraatrial conduction delay. Incremental-rate atrial pacing is performed to determine the maximal rate at which 1:1 conduction over the BT occurs. Induction of AF should be performed to determine the average and the shortest R-R interval during preexcited AF. Atrial and ventricular stimulation is also performed to evaluate inducibility of AVRT as well as the number and location of BTs. 5
Where are refractory periods measured?
It is important that measurements of refractory periods be taken at specific sites. Measurements of atrial and ventricular ERP are taken at the site of stimulation. Measurements of AVN ERP and HPS ERP are taken from responses in the HB electrogram.
What is excitability in refractory period?
Refractoriness or, more appropriately, excitability is defined by the response of a tissue to premature stimulation. Refractory periods are analyzed by the extrastimulus technique, with progressively premature extrastimuli delivered after a train of 8 to 10 paced beats at a fixed PCL to allow for reasonable (more than 95%) stabilization of refractoriness , which is usually accomplished after 3 or 4 paced beats.
How to determine anterograde ERP?
Programmed atrial stimulation is used to evaluate the anterograde ERP of the BT. Because BT refractoriness shortens with decreasing pacing cycle length (PCL), the ERP should be determined at multiple PCLs (preferably ≤400 milliseconds). In addition, atrial stimulation should be performed close to the BT atrial insertion site to obviate the effect of intraatrial conduction delay. Incremental-rate atrial pacing is performed to determine the maximal rate at which 1:1 conduction over the BT occurs. Induction of AF should be performed to determine the average and the shortest R-R interval during preexcited AF. Atrial and ventricular stimulation is also performed to evaluate inducibility of AVRT as well as the number and location of BTs. 5
What is the RRP in physics?
The RRP is defined as the longest premature coupling interval (S 1 -S 2) that results in prolonged conduction of the premature impulse (an increase in stimulus to distal response time) compared with the conduction of the stimulus delivered during the basic drive train. Conduction is slowed when a wavefront encounters tissue that is not completely repolarized. Thus, the RRP marks the end of the full recovery period (i.e., the zone during which conduction of the premature and basic drive impulses is identical). The RRP is generally slightly longer than the ERP by an amount called the latency period. During the latency period, the tissue is excitable, but the excitation wavefront conducts with slower or even decremental conduction.
What is the longest premature coupling interval?
The ERP is the longest premature coupling interval (S 1 -S 2) at a designated stimulus amplitude (usually 2× diastolic threshold) that results in failure of propagation of the premature impulse through a tissue (i.e., fails to capture). ERP therefore must be measured proximal to the refractory tissue.
How is FRP measured?
Because the FRP is a measure of output from a tissue, it is described by measuring points distal to that tissue. It is helpful to think of the FRP as a response-to-response measurement (in contrast, the ERP is a stimulus-to-stimulus measurement).
What are the variables that are considered in the assessment of refractory periods?
Several variables are considered in the assessment of refractory periods, including the stimulus amplitude and the basic drive CL. Longer drive CLs are generally associated with longer refractory periods. However, refractory periods of different parts of the conducting system do not respond comparably with changes in the drive CLs. 63
What is Refractory Period?
To understand the refractory period, you need to know about how electrical messages are transferred from nerve cell to nerve cell or from nerve cell to other tissue cells.
Why is the relative refractory period important?
The relative refractory period is extremely important in terms of stimulus strength. The rate at which a neuron transmits action potentials decides how important that stimulus is. There is no such thing as a weak or strong action potential as all require the same level of electrical or chemical stimulus to occur.
Which type of refractory period is found in heart pacemaker cells?
In heart pacemaker cells that act very similarly to neurons, another type of refractory period exists – the effective refractory period or ERP.
What is a refractory period?
Summary. The refractory period is the span of time after having an orgasm during which a person is not sexually responsive. The refractory period can have both mental and physiological effects. During the refractory period, a person might lose interest in sex, or they might not be able to have sex. It may not be possible for a person ...
How long does a refractory period last?
The length of the refractory period varies greatly from person to person, from a few minutes to 24 hours, or longer.
What is a physiological refractory period?
This type of response is a physiological refractory period, meaning a person is physically unable to have sex again. Unlike males, many females can have multiple orgasms, suggesting they do not usually experience a physiological refractory period.
What factors can influence the length of a refractory period?
Many factors can influence the length of the refractory period, including: a person’s overall health. relationship quality. quality of sex. frequency of sex. Dopamine plays a key role during sex. A review. Trusted Source. of the research suggests that dopamine levels may influence whether a male can get an erection.
Is a refractory period male or female?
Scientists have thoroughly documented the refractory period in males. In females, the refractory period is more controversial.
Does a teenager's refractory period change as they age?
The refractory period a person has when they are young will also determine how it changes as they age. Someone with a long refractory period as a teenager may find it continues to get longer over time.
Does refractory period increase with age?
While the refractory period tends to increase with age, other factors may influence the time a person cannot have sex again, such as their cardiovascular health .
What is the refractory period?
The refractory period occurs right after you reach your sexual climax. It refers to the time between an orgasm and when you feel ready to be sexually aroused again. It’s also called the “resolution” stage.
What happens when your body is refractory?
Resolution. Your muscles start to relax, your blood pressure and heart rate go down, and your body becomes less responsive to sexual stimulation. This is where the refractory period begins.
Can a penis be refractory?
Yes! It’s not just limited to people with penises. All people experience a refractory period as the final stage in a four-part sexual response cycle called the Masters and Johnson’s Four-Phase Model.
Does everyone have a different refractory period?
It’s important to remember that everyone has a different refractory period. You may even notice that your individual refractory period varies from session to session.

Definition
What Is Refractory period?
- To understand the refractory period, you need to know about how electrical messages are transferred from nerve cell to nerve cell or from nerve cell to other tissue cells.
Absolute vs Relative Refractory Period
- With the above information, it is now possible to understand the difference between the absolute refractory period and relative refractory period. In terms of an action potential, refractory periods prevent the overlapping of stimuli. In theory, each action potential requires around one millisecond to be transmitted. This means we could expect a single axon to forward at least one thousand a…
Effective Refractory Period
- In heart pacemaker cells that act very similarly to neurons, another type of refractory period exists – the effective refractory period or ERP. This timespan occurs at the same time as the ARP but ends immediately before the RRP. It is often ignored in textbooks, as is the case in the above image. We should imagine the absolute refractory period en...
Refractory Period in Psychology
- The word refractory means stubborn or resistant to a process. In terms of action potentials and neurons, this is self-explanatory. A neuron is resistant to a second action potential during refractory periods. In psychology, refractory period means a delay in response. This is not something to do with our intelligence but our reaction times – this refractory period is, therefore…