What is the name of 11 element?
The Elements, sorted by Atomic NumberAtomic NumberSymbolName11NaSodium12MgMagnesium13AlAluminum14SiSilicon76 more rows
Is element 11 a metal?
All group 11 elements are relatively inert, corrosion-resistant metals. Copper and gold are colored, but silver is not.
What group does element 11 belong to?
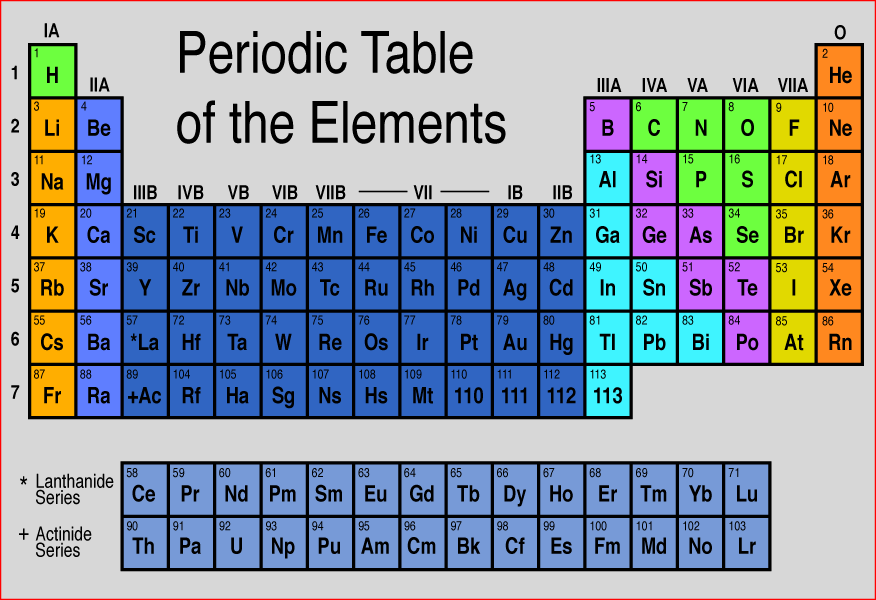
Sodium is the element that is atomic number 11 on the periodic table. It is located in the alkali metals group on the far left side of the periodic table.
Is pure sodium toxic?
The effects of exposure to pure sodium metal by any route – dermal, inhalation, or ingestion – will most likely result in symptoms similar to those of sodium hydroxide exposure, where the caustic effects of the compound on tissues result in mild to severe burns.
What color is Lithium?
silvery-whiteLithium is a soft, silvery-white, metal that heads group 1, the alkali metals group, of the periodic table of the elements. It reacts vigorously with water.
What period is gold?
Period 6Fact boxGroup111064.18°C, 1947.52°F, 1337.33 KPeriod62836°C, 5137°F, 3109 KBlockd19.3Atomic number79196.967State at 20°CSolid197Au2 more rows
What's an atomic number of 11?
sodiumWe know that the atomic number of sodium is 11. This tells us that sodium has 11 protons and because it is neutral it has 11 electrons.
What is atomic number Class 11?
The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom or the number of electrons in an electrically neutral atom. Atomic number = Number of protons. For example, in a sodium atom, there are 11 electrons and 11 protons.
What is an element family?
The vertical columns on the periodic table are called groups or families because of their similar chemical behavior. All the members of a family of elements have the same number of valence electrons and similar chemical properties. The horizontal rows on the periodic table are called periods.
Can salt make you vomit?
The internet lists salt as an emetic to induce vomiting, which is a dangerous practice. “There are cases where someone has tried to induce vomiting to avoid poisoning,” says Pace. “However, the poison is not removed, and the salt causes additional problems even as severe as death.”
How can I flush salt out of my body overnight?
Drinking lots of water helps flush sodium from your kidneys; staying hydrated will also help you feel less bloated.
What do I do if my dog ate salt?
There is no specific treatment for salt toxicosis. Immediate removal of offending feed, water or other suspect material is imperative. Fresh water must be provided to all animals, initially in small amounts at frequent intervals to avoid exacerbation of clinical signs.
Is group 11 a transition metal?
A Group 11 element is one in the series of elements in group 11 (IUPAC style) in the periodic table, consisting of transition metals which are the traditional coinage metals of copper (Cu), silver (Ag), and gold (Au).
Is group 11 a transition element?
The “coinage metals”, copper, silver, and gold, have held great importance in societies throughout history, both symbolically and practically. For centuries, silver and gold have been worn by royalty to parade their wealth and power. On occasion, these metals were even used in art.
Is gold a metal or nonmetal?
metalgold (Au), chemical element, a dense lustrous yellow precious metal of Group 11 (Ib), Period 6, of the periodic table of the elements.
Is silver a metal?
Silver is a relatively soft, shiny metal. It tarnishes slowly in air as sulfur compounds react with the surface forming black silver sulfide. Sterling silver contains 92.5% silver. The rest is copper or some other metal.
What is atomic number?
The atomic number of an element is equal to the total number of protons in the nucleus of the atoms of that element. The atomic number can provide...
What is the atomic number and mass number?
The number of protons and the number of neutrons shall determine the mass number of an element. Since the isotopes of an element have slightly diff...
Can two different elements have the same atomic number?
Atoms from two different elements may have the same neutron count, but never the same proton count. The number of protons is unique to the element...
How do we calculate atomic mass?
Add the mass of protons and neutrons to compute the atomic mass of a single atom of an element. Example: Find the atomic mass of a carbon isotope w...
Why is atomic number important?
Atomic number is called the number of protons in an atom. This number is very important, because it is unique to a given element’s atoms. An elemen...
What is sodium hydroxide used for?
Sodium hydroxide can be used to remove sulfur from petrol and diesel, although the toxic soup of by-products that is formed has led to the process being outlawed in most countries. Sodium hydroxide is also used in biodiesel manufacture, and as a key component in products that remove blockages from drains.
What is the best salt to use for water softener?
Sodium carbonate (washing soda) is also a useful sodium salt. It is used as a water softener.
What is sodium salt used for?
The most common compound of sodium is sodium chloride (common salt). It is added to food and used to de-ice roads in winter. It is also used as a feedstock for the chemical industry. Sodium carbonate (washing soda) is also a useful sodium salt.
Where did the story of man and sodium come from?
Aside from being an essential nutrient, the story of man and sodium is said to begin all the way back in the time of the Pharaohs in Ancient Egypt, with the first recorded mention of a sodium compound in the form of hieroglyphics. It is difficult to describe a pictogram through speech but imagine a squiggly line over the top of a hollow eye-shape, over the top of a semicircle, with a left-facing vulture image next to them all. This pictogram meant divine or pure and its name is the root of the word natron, which was used to refer to washing soda, or sodium carbonate decahydrate, as we would know it today. Sodium carbonate was used in soap, and also, in the process of mummification thanks to its water absorbing and bacteria killing pH control properties.
Why is sodanum called sodanum?
In medieval Europe, however, sodium carbonate was also used as a cure for headaches, and so took the name sodanum, from the Arabic suda, meaning headache.
What color is the Bunsen burner?
Unfortunately, the intensity of the colour is such that if any of the compound is spilled into the Bunsen burner, it is cursed to burn with a blue and orange speckled flame seemingly forever. The reaction of sodium with water is a favourite demonstration, and clips of it abound on the internet.
What metal reacts with water?
Sodium is a soft metal that tarnishes within seconds of being exposed to the air. It also reacts vigorously with water.
What metals are used in coins?
Gold, silver, and copper are quite soft metals and so are easily damaged in daily use as coins. Precious metal may also be easily abraded and worn away through use. In their numismatic functions these metals must be alloyed with other metals to afford coins greater durability. The alloying with other metals makes the resulting coins harder, less likely to become deformed and more resistant to wear.
What is the group 11 of the periodic table?
Group 11, by modern IUPAC numbering, is a group of chemical elements in the periodic table, consisting of copper (Cu), silver (Ag), and gold (Au). Roentgenium (Rg) is also placed in this group in the periodic table, although no chemical experiments have yet been carried out to confirm that it behaves like the heavier homologue to gold.
What is the principal ore in copper?
Copper pyrite is the principal ore, and yields nearly 76% of the world production of copper.
What is Group 11?
Group 11, by modern IUPAC numbering, is a group of chemical elements in the periodic table, consisting of copper (Cu), silver (Ag), and gold (Au).
How much silver is in a silver coin?
Silver coins: Silver coins are typically produced as either 90% silver – in the case of pre-1965 US minted coins (which were circulated in many countries), or sterling silver (92.5%) coins for pre-1920 British Commonwealth and other silver coinage, with copper making up the remaining weight in each case. Old European coins were commonly produced with 83.5% silver. Modern silver bullion coins are often produced with purity varying from 99.9% to 99.999%.
How much gold is in a coin?
Gold coins: Gold coins are typically produced as either 90% gold (e.g. with pre-1933 US coins), or 22 carat (91.66%) gold (e.g. current collectible coins and Krugerrands ), with copper and silver making up the remaining weight in each case.
What are the elements in Group 11?
All Group 11 elements are relatively inert, corrosion -resistant metals. Copper and gold are colored. These elements have low electrical resistivity so they are used for wiring. Copper is the cheapest and most widely used. Bond wires for integrated circuits are usually gold. Silver and silver-plated copper wiring are found in some special ...
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is equal to the total number of protons in the nucleus of the atoms of that element. The atomic number can provide insight into the electronic configuration of the element. For example, carbon has an electron configuration of [He] 2s 2 2p 2, since its atomic number is 6.
What is the number of protons in the nucleus called?
The number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number. The atomic number of each element is unique.
Why is the atomic number of each element unique?
While the atomic number always stays the same some elements have atoms with different atomic mass numbers. This is because some elements have a different number of neutrons in the nucleus.
How to find the mass of an element?
The number of protons and the number of neutrons shall determine the mass number of an element. Since the isotopes of an element have slightly different mass numbers, it calculates the atomic mass by obtaining the mean of the mass numbers for its isotopes.
How can periodic trends be observed?
Periodic trends in the properties of the elements can be observed down the groups and across the periods of the modern periodic table. Every chemical element has a specific atomic number, which provides insight into the number of protons present within its nucleus.
Why is the atomic number important?
This number is very important, because it is unique to a given element’s atoms. An element’s atoms all have the same number of protons and each element has a different number of protons in its atoms. Test your knowledge on periodic table elements.
What is the name of the tabular arrangement of all the elements on the basis of their respective atomic numbers?
The periodic table is the tabular arrangement of all the chemical elements on the basis of their respective atomic numbers. In the periodic table , the vertical columns are called ‘groups’ and the horizontal rows are called ‘periods’.
Why do scientists use the periodic table?
Scientists use the periodic table to quickly refer to information about an element, like atomic mass and chemical symbol. The periodic table’s arrangement also allows scientists to discern trends in element properties, including electronegativity, ionization energy, and atomic radius.
What is the name of the table of chemical elements?
Periodic Table of Chemical Elements. The periodic table of chemical elements, often called the periodic table, organizes all discovered chemical elements in rows (called periods) and columns (called groups) according to increasing atomic number.
How many elements are in the periodic table?
Since then, the periodic table has evolved to reflect over 150 years of scientific development and understanding in chemistry and physics. Today, with 118 known elements, it is widely regarded as one of the most significant achievements in science.
How many elements are there in the periodic table?
Mendeleev left spaces for elements he expected to be discovered, and today’s periodic table contains 118 elements, starting with hydrogen and ending with oganesson, a chemical element first synthesized in 2002 at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) in Dubna, Russia, by a team of Russian and American scientists.
Which element has endured in Mendeelev's periodic table?
They had even been organized by similar properties before. So why is Mendeelev's periodic table the one that has endured? Lou Serico explains via eka-aluminum, an element whose existence Mendeelev predicted years before it was discovered.
How old is the periodic table of chemical elements?
Go into any scientist’s office or lecture hall anywhere in the world and you are likely to see one. Its story is over 200 years old, and throughout its history, it has been a subject for debate, dispute and alteration.
What element makes high tech work?
One of my favorite elements is Dysprosium because it takes part in making many of our high tech systems work due to extra strong high temperature magnets that it facilitates.
What is periodic chemistry?
The term “periodic” is based on the discovery that elements show patterns in their chemical properties at certain regular intervals. Were it not for the simplification provided by this chart, students of chemistry would need to learn the properties of all 118 known elements.
What metal has the highest melting temperature?
Tungsten! It’s the metal with the highest melting temperature (over 3400ºC!) and extremely strong. It’s used in fusion as a plasma-facing material because of its ability to withstand extreme environments.
Who created the periodic table?
Attempts to classify elements and group them in ways that explained their behavior date back to the 1700s, but the first actual periodic table is generally credited to Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev, a Russian chemist who in 1869 arranged 63 known elements according to their increasing atomic weight.
What is the energy of ionization?
The first ionization energy is the energy it takes to remove one electron from an atom, the second ionization energy is the energy it takes to remove a second electron from the atom, and so on. For a given atom, successive ionization energies increase with the degree of ionization. For magnesium as an example, the first ionization energy is 738 kJ/mol and the second is 1450 kJ/mol. Electrons in the closer orbitals experience greater forces of electrostatic attraction; thus, their removal requires increasingly more energy. Ionization energy becomes greater up and to the right of the periodic table.
What is the atomic number plotted against?
Atomic number plotted against atomic radius, excluding the noble gases. Atomic radii vary in a predictable and explainable manner across the periodic table. For instance, the radii generally decrease along each period of the table, from the alkali metals to the noble gases; and increase down each group.
What is the electron configuration of a neutral atom?
The electron configuration or organisation of electrons orbiting neutral atoms shows a recurring pattern or periodicity. The electrons occupy a series of electron shells (numbered 1, 2, and so on). Each shell consists of one or more subshells (named s, p, d, f and g). As atomic number increases, electrons progressively fill these shells and subshells more or less according to the Madelung rule or energy ordering rule, as shown in the diagram. The electron configuration for neon, for example, is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. With an atomic number of ten, neon has two electrons in the first shell, and eight electrons in the second shell; there are two electrons in the s subshell and six in the p subshell. In periodic table terms, the first time an electron occupies a new shell corresponds to the start of each new period, these positions being occupied by hydrogen and the alkali metals.
What are metals and nonmetals?
In chronological order, this section discusses metals and nonmetals (and metalloids); categories of elements; groups and periods; and periodic table blocks. While the recognition of metals as solid, fusible and generally malleable substances dates from antiquity, Antoine Lavoisier may have the first to formally distinguish between metals and nonmetals ('non-métalliques') in 1789 with the publication of his 'revolutionary' Elementary Treatise on Chemistry. In 1811, Berzelius referred to nonmetallic elements as metalloids, in reference to their ability to form oxyanions. In 1825, in a revised German edition of his Textbook of Chemistry, he subdivided the metalloids into three classes. These were: constantly gaseous 'gazolyta' (hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen); real metalloids (sulfur, phosphorus, carbon, boron, silicon); and salt-forming 'halogenia' (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine). Only recently, since the mid-20th century, has the term metalloid been widely used to refer to elements with intermediate or borderline properties between metals and nonmetals. Mendeleev published his periodic table in 1869, along with references to groups of families of elements, and rows or periods of his periodic table. At the same time, Hinrichs wrote that simple lines could be drawn on a periodic table in order to delimit properties of interest, such as elements having metallic lustre (in contrast to those not having such lustre). Charles Janet, in 1928, appears to have been the first to refer to the periodic table's blocks.
How many electrons are in neon?
The electron configuration for neon, for example, is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. With an atomic number of ten, neon has two electrons in the first shell, and eight electrons in the second shell; there are two electrons in the s subshell and six in the p subshell. In periodic table terms, the first time an electron occupies a new shell corresponds to ...
What are the columns of periodic table called?
The seven rows of the table, called periods, generally have metals on the left and nonmetals on the right. The columns, called groups , contain elements with similar chemical behaviours.
How many categories are there in the periodic table?
The elements of the periodic table shown here are divided into nine categories; six for the metals, and two for nonmetals, and a metalloid category. The nine categories (or sets) correspond to those found in the literature for the applicable part of the periodic table. Different authors may use different categorisation schema depending on the properties of interest.

Overview
Group 11, by modern IUPAC numbering, is a group of chemical elements in the periodic table, consisting of copper (Cu), silver (Ag), and gold (Au). Roentgenium (Rg) is also placed in this group in the periodic table, although no chemical experiments have yet been carried out to confirm that it behaves like the heavier homologue to gold. Group 11 is also known as the coinage metals, due to their …
History
All the elements of the group except roentgenium have been known since prehistoric times, as all of them occur in metallic form in nature and no extraction metallurgy is necessary to produce them.
Copper was known and used around 4000 BC and many items, weapons and materials were made and used with copper.
Characteristics
Like other groups, the members of this family show patterns in electron configuration, especially in the outermost shells, resulting in trends in chemical behavior, although roentgenium is probably an exception:
All group 11 elements are relatively inert, corrosion-resistant metals. Copper and gold are colored, but silver is not. Roentgenium is expected to be silvery, though it has not been produced in large …
Occurrence
Copper occurs in its native form in Chile, China, Mexico, Russia and the USA. Various natural ores of copper are: copper pyrites (CuFeS2), cuprite or ruby copper (Cu2O), copper glance (Cu2S), malachite, (Cu(OH)2CuCO3), and azurite (Cu(OH)22CuCO3).
Copper pyrite is the principal ore, and yields nearly 76% of the world production of copper.
Production
Silver is found in native form, as an alloy with gold (electrum), and in ores containing sulfur, arsenic, antimony or chlorine. Ores include argentite (Ag2S), chlorargyrite (AgCl) which includes horn silver, and pyrargyrite (Ag3SbS3). Silver is extracted using the Parkes process.
Applications
These metals, especially silver, have unusual properties that make them essential for industrial applications outside of their monetary or decorative value. They are all excellent conductors of electricity. The most conductive (by volume) of all metals are silver, copper and gold in that order. Silver is also the most thermally conductive element, and the most light reflecting element. Silver also has the unusual property that the tarnish that forms on silver is still highly electrically condu…
Biological role and toxicity
Copper, although toxic in excessive amounts, is essential for life. Copper is shown to have antimicrobial properties which make it useful for hospital doorknobs to keep diseases from being spread. Eating food in copper containers is known to increase the risk of copper toxicity.
Elemental gold and silver have no known toxic effects or biological use, although gold salts can be toxic to liver and kidney tissue. Like copper, silver also has antimicrobial properties. The prolong…