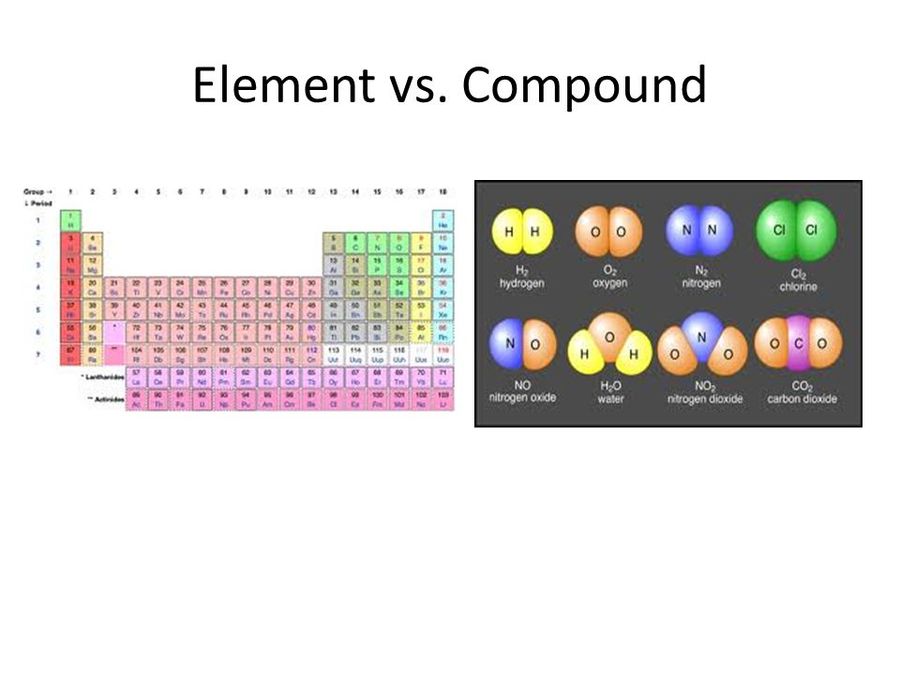
In the context of chemistry and the periodic table, periodicity refers to trends or recurring variations in element properties with increasing atomic number. Periodicity is caused by regular and predictable variations in element atomic structure. Mendeleev
Dmitri Mendeleev
Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev was a Russian chemist and inventor. He formulated the Periodic Law, created a farsighted version of the periodic table of elements, and used it to correct the properties of some already discovered elements and also to predict the properties of eight eleme…
What are periodic trends in chemistry?
Periodic Trends
- Variation of Physical Properties Within a Group. The physical properties (notably, melting and boiling points) of the elements in a given group vary as you move down the table.
- Electron Configurations and Magnetic Properties of Ions. ...
- Atomic Radius. ...
- Ionic Radius. ...
- Ionization Energy. ...
- Electron Affinity. ...
What is periodic law in chemistry?
The periodic table arranges elements according to shared properties. The periodic law is one of the foundations of chemistry. The law suggests that elements, when arranged by atomic weight, tend to have similar characteristics at certain intervals from one another.
What is period and group in chemistry?
Periods are the horizontal rows while the groups, also called families, are the vertical columns. The elements were arranged into groups and periods based on certain characteristics such as chemical/physical properties for groups and electron configurations for the periods. The article unfolds further differences between the periods and groups.
What are the properties of the periodic table?
periodic table is organized like a big grid. Each element is placed in a specific location because of its atomic structure. As with any grid, the periodic table has rows (left to right) and columns (up and down). Each row and column has specific characteristics.Back to Elements List. Group.
What is periodicity with example?
Periodicity is the fact of something happening at regularly-spaced periods of time. An example of periodicity is the full moon happening every 29.5 days. noun. 1. The quality of being periodic; tendency to recur at regular intervals.
What is the definition for periodicity?
Definition of periodicity : the quality, state, or fact of being regularly recurrent or having periods.
What is periodicity in chemistry class 10?
Repetition of properties after a certain interval is called periodicity of properties. If elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic number in the periodic table, then elements repeat their properties after a definite interval.
What is periodicity in chemistry class 11?
The Law states that when the elements are arranged in order of their increasing atomic number, then properties which are similar to different elements are repeated after certain intervals. This Is called the periodicity of the elements.
What is periodicity and its properties?
The basic law governing modern periodic table states that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic number. These properties reappear at regular intervals or follow a particular trend at regular intervals. This phenomenon is known as the periodicity of elements.
What is periodicity Class 9?
When the elements are arranged in the modern periodic table in order of increasing atomic number, the occurrence of similar properties of elements after a definite interval is termed as periodicity of an element. Suggest Corrections. 1. Same exercise questions.
What is another word for periodicity?
Similar words for periodicity: cyclicity (noun) frequency (noun) other relevant words (noun) regularity (noun)
Who discovered periodicity?
MendeleevMendeleev discovered the periodic table (or Periodic System, as he called it) while attempting to organise the elements in February of 1869.
What is the cause of periodicity Class 11?
The cause of periodicity of properties of elements is due to the repetition of similar electronic configuration of their atoms in the outermost energy shell after certain regular interval.
What is meant by periodicity in properties of elements Class 10?
The occurrence of the elements with similar properties after certain regular intervals when they are arranged in increasing order of atomic number is called periodicity. The periodic repetition of the properties is due to the recurrence of similar valence shell configuration after regular intervals.
Is periodicity the same as periodic law?
The periodic table is an arrangement of the elements based upon their atomic masses. The chemical and physical properties of these elements are periodic functions of their atomic masses (periodic law).
What is periodicity BYJU's?
Periodicity means, something repeats after fixed interval.
What is periodicity of atomic radius?
An atom gets larger as the number of electronic shells increases. Therefore, the radius of the atom increases as one goes down a specific group in the periodic table of elements. The size of an atom generally decreases as one moves from left to right for a certain period.
What are the 3 classifications of the periodic table?
Ans: Based on the properties, elements are classified into \(3\) types. They are metals, non-metals and metalloids.
Why is periodicity important?
With growth in productivity, an economy is able to produce—and consume—increasingly more goods and services for the same amount of work. Productivity is important to individuals (workers and consumers), business leaders, and analysts (such as policymakers and government statisticians).
What are the 7 periodic properties?
7. S: Periodic Properties of the Elements (Summary)7.1: Development of the Periodic Table.7.2: Effective Nuclear Charge.7.3: Sizes of Atoms and Ions.7.4: Ionization Energy.7.5: Electron Affinities.7.6: Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids.7.7: Group Trends for the Active Metals.7.8: Group Trends for Selected Nonmetals.
How is periodicity observed?
Periodicity is observed due to similar electronic configuration . Was this answer helpful?
What is electronegativity in chemistry class 11?
The tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself is known as electronegativity.
What causes periodicity?
The cause of periodicity of properties of elements is due to the repetition of similar electronic configuration of their atoms in the outermost energy shell after certain regular interval.
Is periodicity the same as periodic law?
The periodic table is an arrangement of the elements based upon their atomic masses. The chemical and physical properties of these elements are periodic functions of their atomic masses (periodic law).
What is periodicity in research?
Periodicity refers to the frequency of compilation of the data. Context: In SDMX, "Periodicity" is closely associated with "Frequency" to form a single entity, named "Frequency and Periodicity".
What is the periodicity of atomic radius?
Atomic radius is the distance from the atom's nucleus to the outer edge of the electron cloud. In general, atomic radius decreases across a period and increases down a group. Across a period, effective nuclear charge increases as electron shielding remains constant.
What is chemical periodicity?
The chemical periodicity is a trend or pattern exhibiting chemical elements for a set of chemical and physical properties. It comes to be a kind of kinship, which was a fundamental guide for the fathers of chemistry to organize and classify all the elements in the now known periodic table.
Why is it important to understand the chemical periodicity of the periodic table?
Likewise, it enables the prediction of chemical, and even physical, properties between elements of different atomic masses.
What are some examples of periodicity outside the periodic properties?
An example of chemical periodicity outside the periodic properties is seen in the hydrides of the p- block elements .
What is the hydride of oxygen?
Another similar case occurs with group 16. The hydride of oxygen is H 2 O, water. It is to be expected, again, that the elements S, Se, Te and Po possess hydrides with the same formulas, but with abysmally different properties. And so it is: H 2 S, H 2 Se, H 2 Te and H 2 Po. This is due to chemical periodicity.
What is the ionization energy of an element?
Ionization energy, EI, is one of the most outstanding periodic properties. The larger the atom of an element, the easier it will be to remove one of its last electrons; that is to say, those of Valencia. Therefore: atoms with small radii will have large EI, while atoms with large radii will have small EI.
Which group of elements have a low EI?
The elements Li, Na and K belong to the group of alkali metals, characterized by their low EI. On the other hand, the elements He, Ne and Ar correspond to the noble gases, with very high EI, because their atoms are the smallest among all the elements for the same period of the periodic table.
Which group of metals has two oxides?
For example, copper and silver belong to group 11. One has two oxides: CuO (Cu 2+ ) and Cu 2 O (Cu + ); while the other has just one: AgO (Ag + ).
What Is Periodicity?
Periodicity refers to the recurring trends that are seen in the element properties. These trends became apparent to Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (1834–1907) when he arranged the elements in a table in order of increasing mass. Based on the properties that were displayed by the known elements, Mendeleev was able to predict where there were "holes" in his table, or elements yet to be discovered.
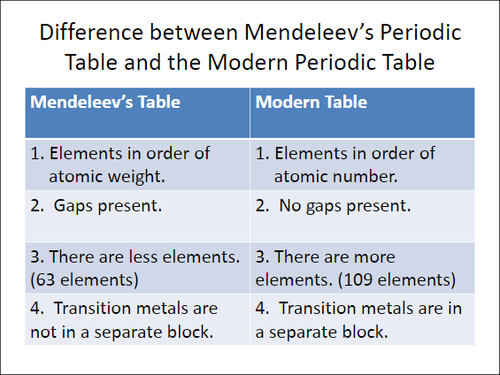
How are elements ordered in the periodic table?
The modern periodic table is very similar to Mendeleev's table, but elements today are ordered by increasing atomic number, which reflects the number of protons in an atom. There aren't any "undiscovered" elements, although new elements can be created that have even higher numbers of protons.
What is the measure of the ability of an atom to form a chemical bond?
Atomic radius: half the distance between the centers of two atoms that are touching each other. Electronegativity: the measure of the ability of an atom to form a chemical bond. Electron affinity: the ability of an atom to accept an electron.
What is periodicity in science?
Periodicity is defined as the tendency of a series of events to follow a recurring pattern. An example of periodicity is the movement of the planets and satellites, which let us have a consistent measure of time.
Why does periodicity occur?
Periodicity in the properties happen because of the similar outer shell layer configuration mentioned previously. Information about this configuration is also important. You can understand a lot of things from this information, such as the bond between atoms or the behavior of an atom.
What are the four properties of the periodic table?
Properties. There are four periodic properties within a periodic table: ionization energy, atomic radius, electronegativity, and electron affinity. These properties form a pattern when lined up with a periodic table.
What is periodic table?
Periodicity in Chemistry. The periodic table is a table of elements sorted by its atomic number. This table has an uncommon shape. The shape was first proposed by a Russian chemist, Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. The first design of the periodic table includes unknown elements, so it has a different amount of elements in each row.
How did Mendeleev discover the periodic table?
Using periodicity, Mendeleev discovered elements by predicting their properties. The current periodic table is arranged so that elements with similar types and properties are grouped together.
Why is the periodic table color coded?
The tables are color coded, so you can see the elements grouped as a type. This arrangement helps you visually remember the properties and the connection between elements.
Is periodicity only in chemistry?
This is just one example of periodicity and only in chemistry. There are other patterns that you can call a periodicity which forms the law of science. For example, the moon’s rotation causes tides to rise or fall. Spotting the periodicity of nature makes it easier for scientists to produce new discoveries.
Content
The chemical periodicity It is a trend or pattern that chemical elements exhibit for a set of their chemical and physical properties. It becomes a kind of kinship, which was a fundamental guide for the fathers of chemistry to organize and classify all the elements in the now known periodic table.
Patterns and groups
Chemical periodicity is observed, as is to be expected, in the periodic properties. These are characterized by the trend of their values as they are evaluated throughout a period or group of the periodic table.
Ionization energy
The ionization energy, EI, is one of the most outstanding periodic properties. The larger the atom of an element, the easier it will be to remove one of its last electrons; that is to say, those of Valencia. Therefore: atoms with small radii will have large EI, while atoms with large radii will have small EI.
Block hydrides p
An example of chemical periodicity outside the periodic properties is seen in the hydrides of the block elements p.
Halogen molecules
If fluorine is known to be in the elemental state as molecule F 2, then it is to be assumed that the other halogens (Cl, Br, I and At) are also forming diatomic molecules. And so it is, being the molecules Cl 2, Br 2 and I 2 the best known.
Oxides and sulfides
Analogously as mentioned with the hydrides of the block p, the oxides and sulfides for elements of the same group show a kind of correspondence in their respective chemical formulas. For example, lithium oxide is Li 2 Or, the oxides for the other alkali metals or group 1 being: Na 2 OKAY 2 O, Rb 2 O and Cs 2 OR.
Hydrocarbons and silanes
Both carbon and silicon have the ability to form C-C or Si-Si bonds, respectively. The C-C bonds are much more stable, so that the structures of hydrocarbons can become disproportionately more numerous and varied than those of their silane counterparts.
What is periodicity in math?
Periodicity is the recurring trends that are seen in the element properties. These trends became apparent to Mendeleev when he arranged the elements in order of increasing mass. Based on the properties that were displayed by the elements, Mendeleev was able to predict where there were 'holes' in his... read more.
What does periodicity mean in chemistry?
Periodic properties in chemistry means that if elements are arranged in an order, the properties of elements would repeat after some period. COMPLETE ANSWER: Period: Time interval Peridiocity: Thing repeats after this time... read more.
What are periodic properties?
The periodic properties are: ionization energy - energy required to remove an electron from an ion or gaseous atom atomic radius - half the distance between the centers of two ... read more. Periodicity refers to the recurring trends that are seen in the element properties.
What are properties that repeat themselves after a certain interval in the periodic table?
Properties which repeat themselves after a certain interval in periodic table are called periodic properties.
How does valence affect the chemical behaviour of an element?
Valence: the chemical behaviour of an element depends upon the number of electrons in the outermost shell of its atom. All elements in a group show the same valency. The valence electrons increases in going from left to right in a period. Hence valency of elements in a period first increases and then decreases.

Ionization Energy
Hydrides of Block p
- An example of chemical periodicity outside the periodic properties is seen in the hydrides of the p-block elements . For example, group 15 is made up of the elements N, P, As, Sb, and Bi. If it is known that ammonia, NH 3, has nitrogen with an oxidation number of +3, then it can be expected, by simple periodicity, that the remaining elements also h...
Halogen Molecules
- If fluorine is known to be in the elemental state as a molecule F 2, then it is to be assumed that the other halogens (Cl, Br, I and At) are also forming diatomic molecules. And so it is, being the molecules Cl 2, Br 2and I 2the best known.
Oxides and Sulfides
- Similarly, as mentioned with the p-block hydrides , the oxides and sulfides for elements of the same group show a kind of correspondence in their respective chemical formulas. For example, lithium oxide is Li 2O, the oxides for the other alkali metals or group 1 being: Na 2O, K 2O, Rb 2O and Cs 2O. This is due to the fact that all of them have metals with an oxidation number of +1, in…
Hydrocarbons and Silanes
- Both carbon and silicon have the ability to form CC or Si-Si bonds, respectively. CC bonds are much more stable, so that the structures of hydrocarbons can become disproportionately more numerous and varied than those of their silane counterparts. This conclusion is due again to chemical periodicity. For example, ethane, CH 3CH 3or C 2H 6has its homologue disilane, SiH 3S…
Content
Patterns and Groups
Ionization Energy
Block Hydrides p
Halogen Molecules
- Chemical periodicity is observed, as is to be expected, in the periodic properties. These are characterized by the trend of their values as they are evaluated throughout a period or group of the periodic table. A zigzag, a saw or a steep mountain can be chosen for comparison purposes: with ups and downs. That is to say, the periodic properties os...
Oxides and Sulfides
- The ionization energy, EI, is one of the most outstanding periodic properties. The larger the atom of an element, the easier it will be to remove one of its last electrons; that is to say, those of Valencia. Therefore: atoms with small radii will have large EI, while atoms with large radii will have small EI. Note, for example, in the image above that the elements Li, Na and K have the lowest EI…
Hydrocarbons and Silanes
- An example of chemical periodicity outside the periodic properties is seen in the hydrides of the block elements p. For example, group 15 is made up of the elements N, P, As, Sb, and Bi. If ammonia, NH3, has nitrogen with an oxidation number of +3, so it can be expected, by simple periodicity, that the remaining elements also present similar hydrides. And indeed it is: NH3, PH…
References
- If fluorine is known to be in the elemental state as molecule F2, then it is to be assumed that the other halogens (Cl, Br, I and At) are also forming diatomic molecules. And so it is, being the molecules Cl2, Br2 and I2the best known.