
Full Answer
What is the refractory period, and can you reduce it?
The refractory period is a period of relative inexcitability that occurs after orgasm and ejaculation. Concretely, during this moment, it is not possible to have an erection and even less an ejaculation. Unlike women, men cannot have two orgasms simultaneous or successive. A normal stage of male sexuality They all “undergo” the obligatory passage where ]
What happens to a cell during the absolute refractory?
What happens to a cell during the absolute refractory? When the voltage-gated sodium channels are either open or inactivated, the cell is unable to fire another action potential regardless of the strength of the stimulus acting on the cell. This segment of the action potential is called the absolute refractory period.
How long is absolute refractory period for skeletal muscles?
This time of non-responsiveness is called the refractory period. In skeletal muscle cells, the contraction last from fifteen to one hundred milliseconds or more with a refractory period of one to two milliseconds.
What are the advantages of the refractory period?
The refractory period causes 3 things to occur:
- The brain will be able to perceive nerve impulses as separated events since there is a time lag between them.
- The number of generated impulses or repetitive firing rate of a neuron will be limited in a given period of time.
- The nerve impulses will only travel in one direction. ...
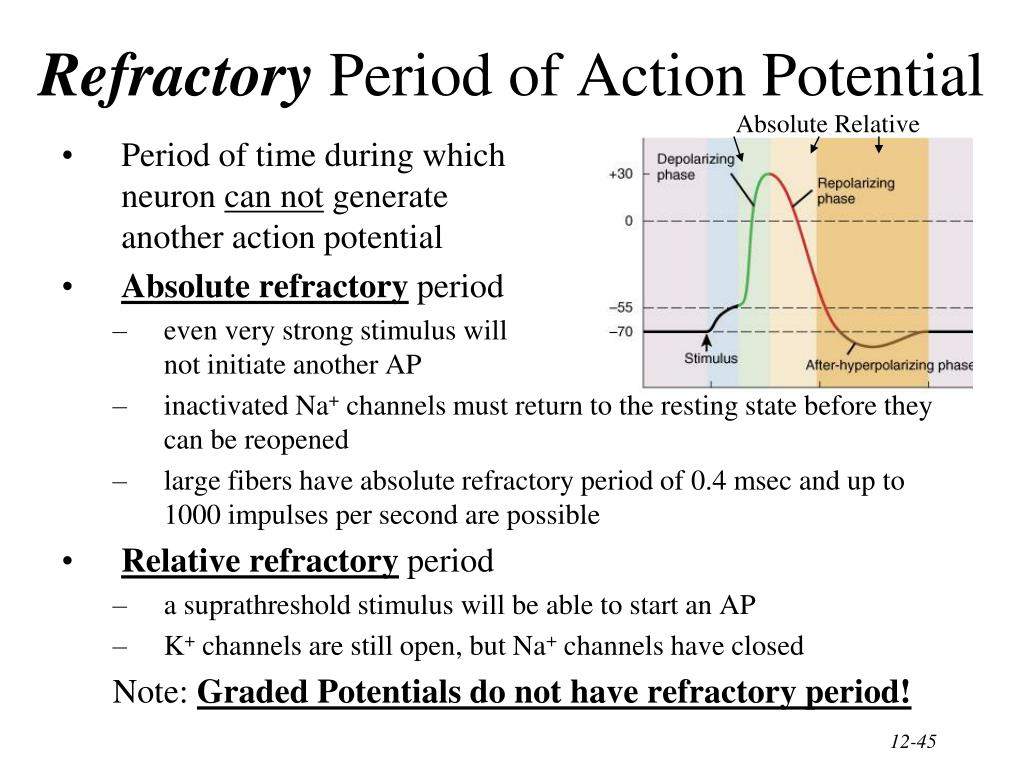
What is meant by absolute refractory period?
Medical Definition of absolute refractory period : the period immediately following the firing of a nerve fiber when it cannot be stimulated no matter how great a stimulus is applied. — called also absolute refractory phase. — compare relative refractory period.
What is absolute refractory period quizlet?
Absolute Refractory period. The period from the initiation of the action potential to immediately after the peak is referred to as the absolute refractory period (ARP) This is the time during which another stimulus given to the neuron will not lead to a second action potential.
What is meant by the absolute refractory period and what causes it?
The absolute refractory period is a period of time when the neuron is not able to send additional action potentials. It is caused by the voltage gated sodium channels shutting and not opening for a short period of time.
What happens after the absolute refractory period?
This is called the absolute refractory period, and it is followed by a relative refractory period, during which another action potential can be generated, but only by a greater stimulus current than that originally needed.
Which statement best describes the absolute refractory period?
Correct answer: Absolute refractory period occurs because of the inactivation of sodium channels. Since the sodium channels are inactivated, the neuron can't depolarize and initiate another action potential. Relative refractory period occurs due to the slow inactivation of potassium channels.
What is the refractory period in psychology quizlet?
refractory period. The minimum length of time after an action potential during which another action potential cannot begin.
What is absolute and relative refractory period?
Absolute: Is the period of time during which a second action potential ABSOLUTELY cannot be initiated, no matter how large the applied stimulus is. Relative: Is the interval immediately following the Absolute Refractory Period during which initiation of a second action potential is INHIBITED, but not impossible.
What is refractory in simple words?
refractory • \rih-FRAK-tuh-ree\ • adjective. 1 : resisting control or authority : stubborn, unmanageable 2 : resistant to treatment or cure 3 : capable of enduring high temperatures.
What is purpose of refractory period?
These transitory changes make it harder for the axon to produce subsequent action potentials during this interval, which is called the refractory period. Thus, the refractory period limits the number of action potentials that a given nerve cell can produce per unit time.
How long does the absolute refractory period last?
1–2 ms.The time during which the nerve is refractory to a second stimulus is called the absolute refractory period. It typically lasts for 1–2 ms. Following the absolute refractory period is a second, relative refractory period.
What is refractory period caused by?
The refractory periods are due to the inactivation property of voltage-gated sodium channels and the lag of potassium channels in closing.
What causes the refractory?
Refractory periods are caused by the inactivation gate of the Na+ channel. Once inactivated, the Na+ channel cannot respond to another stimulus until the gates are reset.
What is relative refractory period?
The relative refractory period is the period of time where voltage gated potassium channels are open and the neuron is hyperpolarized. This means t...
What happens during the refractory period?
During the refractory period, neurons are less likely to send an action potential. During the absolute refractory period, a neuron cannot send anot...
What is the absolute refractory period and what causes it?
The absolute refractory period is a period of time when the neuron is not able to send additional action potentials. It is caused by the voltage ga...
What is the refractory period?
The refractory period occurs right after you reach your sexual climax. It refers to the time between an orgasm and when you feel ready to be sexually aroused again. It’s also called the “resolution” stage.
What happens when you have a vagina?
If you have a vagina, your clitoris retracts under the clitoral hood. Orgasm. Your muscles contract and release tension, and your body gets flushed and red. If you have a penis, your pelvic muscles contract to help release ejaculate. Resolution.
How to get back in the sack faster?
can help you get back in the sack quicker by relaxing penis muscles and improving blood flow. However, individual results may vary, and in some cases ED medications can be counterproductive. It’s best to consult with a therapist or physician who specializes in sexual health. To boost overall health. Stay active.
How much higher is prolactin after PVI?
The researchers found that prolactin, a key hormone in the refractory period, levels are over 400 percent higher after PVI than after masturbation.
What happens when your body is refractory?
Resolution. Your muscles start to relax, your blood pressure and heart rate go down, and your body becomes less responsive to sexual stimulation. This is where the refractory period begins.
What happens when your heart rate goes up?
Excitement. Your heart rate goes up, your breathing gets faster, and your muscles get tense. Blood starts heading toward your genitalia.
How long does it take for a man to become aroused?
For males, there’s a lot more variance. It may take a few minutes, an hour, several hours, a day, or even longer. As you get older, 12 to 24 hours may pass before your body is able to become aroused again. A 2005 analysis suggests that sexual function most noticeably changes — for both sexes — at age 40.
What is Refractory Period?
To understand the refractory period, you need to know about how electrical messages are transferred from nerve cell to nerve cell or from nerve cell to other tissue cells.
Why is the relative refractory period important?
The relative refractory period is extremely important in terms of stimulus strength. The rate at which a neuron transmits action potentials decides how important that stimulus is. There is no such thing as a weak or strong action potential as all require the same level of electrical or chemical stimulus to occur.
What are the components of a neuron?
There are many different types of nerve cell; a generic neuron receives chemical signals via neurotransmitters arriving at the dendrites and forwards these signals down the axon to the next cell by way of electrical impulses.
Why do multiple action potentials not occur in the same neuron at exactly the same time?
This is because a neuron experiences two different situations in which it is either impossible or difficult to initiate a second action potential. These two situations describe the two types of refractory periods.
What is the name of the change in the direction of the target cell?
When stimulated, the voltage along the cell membrane changes one section at a time in the direction of the target cell. When a neuron is stimulated, the subsequent voltage change moves along the axon. This voltage change is called an action potential.
How does alcohol affect your reaction speed?
For example, when drinking alcohol, our reactions and reflexes are impaired. The presence of alcohol together with another task affects our reaction speed. If you drive a car under the influence and the car in front of you brakes suddenly, your reflex to brake will be slower than if not drinking. If, as the car in front brakes, a passenger in the car asks a question, the driver may not hear it. Alternatively, the driver may hear the question very clearly but not see the car in front suddenly stop. Their psychological refractory period prevents us from processing two tasks at once.
How many action potentials are there in a second?
In theory, each action potential requires around one millisecond to be transmitted. This means we could expect a single axon to forward at least one thousand action potentials every second; in reality, this number is much lower. The absolute refractory period lasts for approximately one millisecond; the relative refractory period takes approximately two milliseconds.
What are some activities that increase dopamine levels?
Other pleasurable activities may also boost dopamine, such as doing something new, enjoyable conversation, or mastering a new challenge. Scientists do not completely understand the connection between dopamine levels and the refractory period.
What is a physiological refractory period?
This type of response is a physiological refractory period, meaning a person is physically unable to have sex again. Unlike males, many females can have multiple orgasms, suggesting they do not usually experience a physiological refractory period.
How long does a refractory period last?
The length of the refractory period varies greatly from person to person, from a few minutes to 24 hours, or longer.
What factors can influence the length of a refractory period?
Many factors can influence the length of the refractory period, including: a person’s overall health. relationship quality. quality of sex. frequency of sex. Dopamine plays a key role during sex. A review. Trusted Source. of the research suggests that dopamine levels may influence whether a male can get an erection.
What is a refractory period?
Summary. The refractory period is the span of time after having an orgasm during which a person is not sexually responsive. The refractory period can have both mental and physiological effects. During the refractory period, a person might lose interest in sex, or they might not be able to have sex. It may not be possible for a person ...
How to try PFMT?
To try PFMT, a person should tense the muscles they use to urinate, hold for a few seconds, release, and repeat. Some research has found that erectile dysfunction medication might shorten the refractory period for males. A small, older 2003. Trusted Source.
What is the cycle of sexual desire?
Brain imaging studies suggest that the cycle of a sexual response follows a similar pattern to other pleasurable activities. It begins with intensifying desire, culminates in satisfying that desire, and concludes with decreased desire.
What is Absolute Refractory Period?
Absolute refractory period refers to the period in which the Sodium ion channels are completely inactive. This takes place very rapidly and spontaneously after the opening of the Sodium ion channels. When the sodium ion channels undergo inactivation, they cannot get back to the active state immediately. Thus the initial recovery time required to activate the sodium ions channels is described as the absolute refractory period. This process is a voltage-dependent process. The Absolute refractory period can last for 1-2 milliseconds, whereas the total recovery period spans for about 3-4 milliseconds.
What are the Similarities Between Absolute and Relative Refractory Period?
Both absolute refractory period and the relative refractory period are components of the refractory period that takes place during nerve impulse transmission.
What happens to sodium ion channels during the absolute refractory period?
During the relative refractory period, the stimulus must be stronger than the usual to produce the action potential. The sodium ion channels are completely inactive during the absolute refractory period.
What is the initial recovery time required to activate the sodium ions channels?
Thus the initial recovery time required to activate the sodium ions channels is described as the absolute refractory period. This process is a voltage-dependent process.
Why is the second action potential not initiated during the absolute refractory period?
During the absolute refractory period, a second action potential is not initiated because the sodium ion channels are fully inactivated. Therefore, any additional depolarization stimuli do not take place during this period. The neurons are not excited during this period. Thus, the neuron excitability is null during the Absolute refractory period.
What is the action potential of a nerve impulse?
Action potential of a nerve impulse refers to the phenomenon in which a nerve impulse is transmitted across a neuron. It is a resultant of the difference in concentration of Sodium (Na +) ions and Potassium (K +) ions across the membrane. There are three main phases of action potential; depolarization, repolarization and hyperpolarization.
Which ion channels are dependent on the absolute refractory period?
Both absolute refractory period and the relative refractory period are dependent on the sodium and potassium ion channels.

Definition
What Is Refractory period?
- To understand the refractory period, you need to know about how electrical messages are transferred from nerve cell to nerve cell or from nerve cell to other tissue cells.
Absolute vs Relative Refractory Period
- With the above information, it is now possible to understand the difference between the absolute refractory period and relative refractory period. In terms of an action potential, refractory periods prevent the overlapping of stimuli. In theory, each action potential requires around one millisecond to be transmitted. This means we could expect a single axon to forward at least one thousand a…
Effective Refractory Period
- In heart pacemaker cells that act very similarly to neurons, another type of refractory period exists – the effective refractory period or ERP. This timespan occurs at the same time as the ARP but ends immediately before the RRP. It is often ignored in textbooks, as is the case in the above image. We should imagine the absolute refractory period ending a millimeter or two before the r…
Refractory Period in Psychology
- The word refractory means stubborn or resistant to a process. In terms of action potentials and neurons, this is self-explanatory. A neuron is resistant to a second action potential during refractory periods. In psychology, refractory period means a delay in response. This is not something to do with our intelligence but our reaction times – this refractory period is, therefore…