What are some reasons for no period?
Some of the causes of missed periods, besides pregnancy, are as follows:
- Stress: This is one of the most common reasons for a missed period. ...
- Low body weight: Low body weight is another potential reason for a missed period. ...
- Obesity: Similarly to low body weight, obesity can also result in hormonal changes, leading to an absence of menstruation.
What happens during the latent period of muscle contraction?
There is a delay, or latent period, of about 2 milliseconds (msec) between the onset of the stimulus and the onset of the twitch. This is the time required for excitation, excitation-contraction coupling, and tensing of the series-elastic components of the muscle. The force generated during this time is called internal tension.
How long is the latent period of muscle contraction?
The time between a stimulus to the motor nerve and the subsequent contraction of the innervated muscle is called the latent period, which usually takes about 10 ms and is caused by the time taken for nerve action potential to propagate, the time for chemical transmission at the neuromuscular junction, then the subsequent steps in excitation-contraction coupling.
Why is my period late calculator?
The most common causes for your period to be late are: stress, pregnancy, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), peri-menopause, menopause, recently stopping hormonal birth control and thyroid conditions. How much delay is normal in periods? The amount of time your period can be late varies depending on your normal cycle length.

What is the latent period?
The latent period, rather than the incubation period, has more influence on the spreading dynamics of an infectious disease or epidemic. The time interval during which the host is infectious, i.e. the pathogens can be transmitted directly or indirectly from the infected host to another individual, is called the infectious period ...
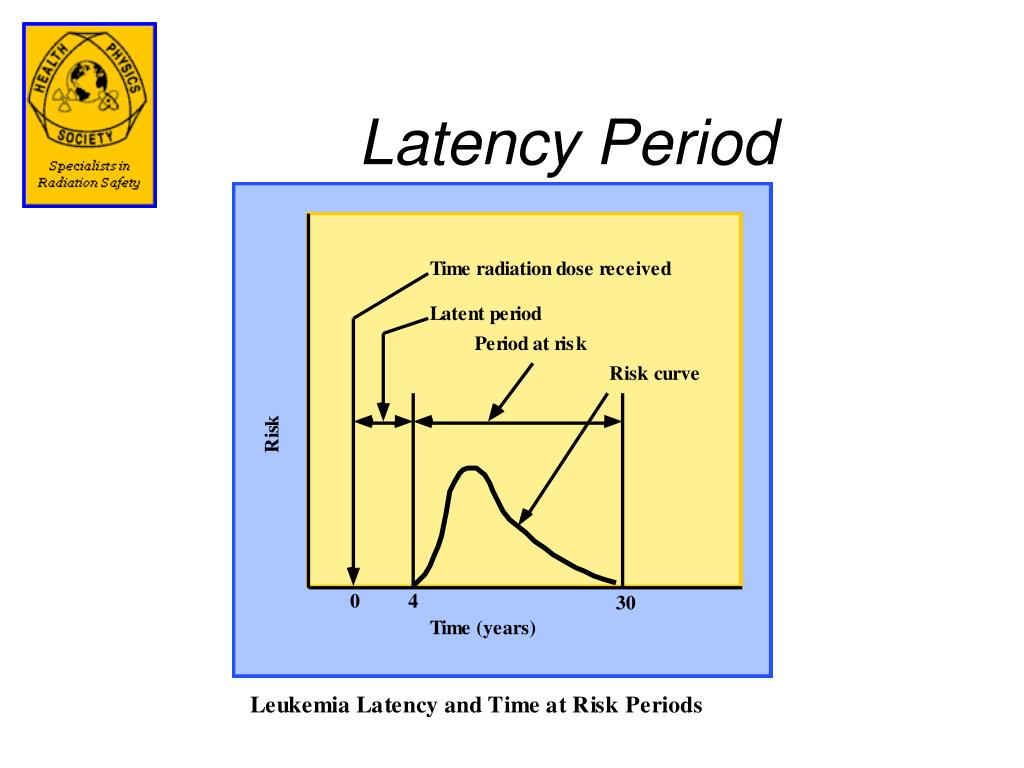
What is the latency period in cancer?
In the discussion of cancers (a non-infectious disease ), the term "latency period" is used to indicate the time that passes between being exposed to something that can cause disease (such as radiation or a virus) and having symptoms.
What is the term for an early or mild stage of infection that lasts years longer than the latent period?
For example, in HIV/AIDS, the incubation period lasts years longer than the latent period.
What is the incubation period?
The incubation period is also useful to count the number of infected people. The period from the time of infection to the time of becoming infectious is called the pre-infectious period or the latent period. During the pre-infectious or latent period, a host may or may not show symptoms (i.e.
What is the time interval between the time of invasion by an infectious pathogen and the time of onset (first appearance?
The time interval from the time of invasion by an infectious pathogen to the time of onset (first appearance) of symptoms of the disease in question is called the incubation period. After the incubation period is over, the host enters the symptomatic period. Moreover, at a certain point in time after infection, ...
How to determine generation time?
The generation time specifies how fast infections are spreading in the community with the passing of each generation. In contrast, the effective reproductive number determines in what number the infections are spreading in the community with the passing of each generation. The latent period and the infectious period helps determine the generation time of an infection. The mean generation time is equal to the sum of the mean latent period and one-half of the mean infectious period, given that infectiousness is evenly distributed across the infectious period.
Why is serial interval used as a proxy measure?
Therefore the serial interval is often used as a proxy measure to estimate the generation time.
Which model shows that diseases can be infected in the latent period and the infected period?
In this paper, we discuss an SEIR model that the diseases can be infected in the latent period and the infected period.
What is the blanking period?
blanking period a period of time during and after a pacemaker stimulus when the unstimulated chamber is insensitive to avoid sensing the electronic event in the stimulated chamber. effective refractory period absolute refractory period.
What is the definition of incubation period?
1. The duration elapsing between the application of a stimulus and the response, e.g., contraction of a muscle. 2. bioterrorism Interval between exposure to a chemical, toxic, or radiologic agent and the first signs or symptoms. 3. Synonym (s): incubation period (1) .
What is the absolute refractory period?
absolute refractory period the part of the refractory period from phase 0 to approximately −60 mV during phase 3; during this time it is impossible for the myocardium to respond with a propagated action potential, even with a strong stimulus. Called also effective refractory period.
What is the vulnerable period?
vulnerable period that time at the peak of the T wave during which serious arrhythmias are likely to result if a stimulus occurs. Wenckebach's period a usually repetitive sequence seen in partial heart block, marked by progressive lengthening of the P–R interval; see also dropped beat.
What is the supernormal period in electrocardiography?
supernormal period in electrocardiography, a period at the end of phase 3 of the action potential during which activation can be initiated with a milder stimulus than is required at maximal repolarization, because at this time the cell is excitable and closer to threshold than at maximal diastolic potential.
What is the moment in muscular contraction when no deflection of the galvanometer is produced?
isoelectric period the moment in muscular contraction when no deflection of the galvanometer is produced.
What is the latent period?
A latent period allows study of alterations of anatomy and physiology before, during, and after onset of epileptogenesis and the model, therefore, may be ideal for experiments focused on underlying cellular mechanisms and antiepileptogenic strategies.
How long does it take for a pharyngitis to develop latent period?
The latent period is usually 10 to 14 days after pharyngitis/angina or 2 to 3 weeks after pyoderma. One-third of APSGN patients develop discrete microscopic hematuria and/or proteinuria in the latent period. Usually the disease has sudden onset with development of nephritic syndrome (edema, oliguria, azotemia, hematuria, hypertension).
How long does hematuria last?
The urine is described as being smoky, cola colored, tea colored, or rusty. Gross hematuria may last a few hours during the day. Usually it resolves after 1 to 2 weeks and transforms into microscopic hematuria. Once gross hematuria has resolved, relapses may appear after physical exercise or intercurrent infections.
How long is the latent period?
For a contracting muscle the latent period lasts about 0.02 seconds, during which time calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
What is the latent period of a disease?
A "latent period" is the lag time between exposure to a disease-causing agent and the onset of the disease the agent causes. In infectious diseases it is often identical to the incubation period, but not always. A disease may have incubated but remains latent, or dormant, within the body. For instance, the latent period between exposure to HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection and the onset of AIDS ( acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) may be many years, although invasion of the body by HIV does cause a transient primary infection two to three weeks after initial exposure. Transmissable spongiform encephalopathy, caused by infectious prions, may have a latent period of up to twenty years or more.
What Does Latent Period Mean?
A latent period is the duration of time between initial exposure to a carcinogen, contaminant, or toxin and the onset of irreversible symptoms/conditions associated with the exposure such as chronic diseases, cancer, and benign and/or malignant tumors. Prolonged exposure to chemicals can lead to proliferation of cancer cells, targeting primary organs in the body resulting in cellular decomposition. Because many pathological conditions develop at a slow rate (latent period), symptoms can go undetected for years.
What are the symptoms of latent period?
During the latent period, progression of symptoms can reflect many independent variables such as age, allergic hypersensitivity, compound chemical (s) exposure, drinking/smoking habits, genetics, and concentration of toxic substances. Many individuals can experience discrete biological and/or physiological health concerns such as persistent coughing/wheezing, eye/skin irritation, nausea/vomiting, and diminished sperm count in men and fertility issues in women.
What is the period between exposure and onset of clinical symptoms called?
The period between exposure and onset of clinical symptoms is called 'incubation period'. The host may become infectious (i.e. able to transmit the pathogen to other hosts) at any moment of the infection. This moment will vary per pathogen. The following schematic figure demonstrates these different time periods: ...
What is the period between exposure and infection?
The period between exposure and infection is called ' latent period', since the pathogen is present in a 'latent' stage, without clinical symptoms or signes of infection in the host.
What is the difference between induction and latent period?
Induction and latent periods are distinguishable concepts referring respectively to the period between causal action and disease initiation, and the period between disease initiation and detection. A disease cannot be characterized as having a long or short induction period, except in relation to a specific etiologic component. Inappropriate assumptions, explicit or implicit, about the length of the combined induction and latent period (the "empirical induction period") in an analytic study result in nondifferential misclassification and bias toward the null. Repeated analyses, varying the assumptions about the length of the empirical induction period, can be used to minimize such misclassification, thereby providing estimates for an undiluted measure of effect and the mode of the empirical induction period.
Can a disease have a long induction period?
A disease cannot be characterized as having a long or short induction period, except in relation to a …. Induction and latent periods are distinguishable concepts referring respectively to the period between causal action and disease initiation, and the period between disease initiation and detection. A disease cannot be characterized as having ...
What is the latent period?
In simple words, the latent period is the timing of phage induced host cell lysis. Eclipse period lies within the latent period. During the latent period, the host cell is under the control of the phage protein complex. translocation of the viral nucleic acid into the bacterial cytoplasm from the periplasm.
What is the difference between the latent period and the eclipse period?
The key difference between eclipse and latent period is that eclipse period is the time of synthesizing phage proteins and nucleic acids inside the host cell, while the latent period is the time between injection of the viral genome into the cell and host cell lysis. A bacteriophage (phage) is an obligate intracellular virus particle ...
What is Eclipse Period?
Eclipse period is the time of bacteriophage growth which starts at the beginning of the latent period and ends at the first appearance of the new intracellular viral progeny inside the host cell. During the eclipse period, new nucleic acids and phage proteins are synthesized.
What are the Similarities Between Eclipse and Latent Period?
Eclipse and latent periods are two durations of the phage lytic cycle.
What is the latent period of a bacteriophage?
In a bacteriophage growth, the latent period is the time between injection or uptake of the viral genome into the host cell to release of new viral progeny by host cell lysis. Therefore, the latent period begins with the viral attachment with the bacterial cell wall. Then it extends via different stages and terminates at the point ...
What happens in the lytic cycle?
In the lytic cycle, bacteriophages infect bacteria and rapidly kill the host bacterial cell by lysis. In the lysogenic cycle, viral genetic material integrates with bacterial genome or plasmids and exists within the host cell for many generations without killing the host bacterium.
How long is the latent period of T4?
The latent period varies among the different viral-host systems. The latent period of T4 and E. coli is 20 minutes while it is 50 minutes for λ and E. coli. Likewise, the latent period differs among phage systems, and it is influenced by the host physiology as well.

Overview
In epidemiology, particularly in the discussion of infectious disease dynamics (modeling), the latent period (also known as the latency period or the pre-infectious period) is the time interval between when an individual or host is infected by a pathogen and when they become infectious, i.e. capable of transmitting pathogens to other susceptible individuals.
Relationship with related concepts in infectious disease dynamics
To understand the spreading dynamics of an infectious disease or an epidemic, three important time periods should be carefully distinguished: incubation period, pre-infectious or latent period and infectious period. Two other relevant and important time period concepts are generation time and serial interval.
The infection of a disease begins when a pathogenic (disease-causing) infecti…
Usage of the term outside epidemiology
Outside the confines of epidemiology, the term "latent period" may be defined in some general-purpose dictionaries (e.g. the Collins English Dictionary or Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary ) as being the time interval between infection by a pathogen and the onset of symptoms, i.e., as a synonymous term for the epidemiologically different concept of "incubation period".
In the discussion of cancers (a non-infectious disease), the term "latency period" is used to indicat…
See also
• Incubation period
• Infectious period
• Viral shedding
• Generation time
• Serial interval