Full Answer
How can I calculate the period of a pendulum?
The period of a pendulum is proportional to to the square root of its length and is described by the equation: P = 2π × √ L / g where pi is 3.1415 and g is the force of gravity.
How can you determine the period of pendulum?
for calculating the period of any such pendulum is the distance from the pivot to the center of oscillation. This point is located under the center of mass at a distance from the pivot traditionally called the radius of oscillation, which depends on the mass distribution of the pendulum.
What does the period of a pendulum depend on?
The period of a pendulum does not depend on the mass of the ball, but only on the length of the string. Two pendula with different masses but the same length will have the same period. Two pendula with different lengths will different periods; the pendulum with the longer string will have the longer period.
How does length affect the period of a pendulum?
Time period of a pendulum can be increased or decreased by changing th elength of the string of pendulum. The time period of the pendulum decreases as the length of the string increases and it increases as the length of the string decreases, hence time period is inversely proportional to the length of the string.

What is meant by the period of a pendulum?
The time period of a simple pendulum: It is defined as the time taken by the pendulum to finish one full oscillation and is denoted by “T”. The amplitude of simple pendulum: It is defined as the distance travelled by the pendulum from the equilibrium position to one side.
How do you find the period of a pendulum?
each complete oscillation, called the period, is constant. The formula for the period T of a pendulum is T = 2π Square root of√L/g, where L is the length of the pendulum and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
How do you calculate the period?
Starting on the first day of your period, start counting. The day before your next period is the last day of your menstrual cycle. That's when you stop counting. That's how many days you had in your menstrual cycle that month.
How do u calculate period?
To calculate your menstrual cycle, count the days between your last few periods. Begin counting on the first day of your period to the day before your next period.Do this for a few cycles, and add up the total number of days, dividing it by the number of cycles.
What is a pendulum?
A pendulum is a body suspended from a fixed point so that it can swing back and forth under the influence of gravity. The time interval of a pendul...
What are pendulums used for?
Different types of pendulums have different applications. Examples of simple pendulums are found in clocks, swing sets, and even the natural mechan...
How are pendulum clocks powered?
Pendulum clocks are powered by mechanisms that trigger the pendulum to swing with a constant period. Traditionally, weight or spring mechanisms ful...
When was the pendulum clock invented?
Some authorities ascribe the invention of the pendulum clock to Galileo, while others credit Christiaan Huygens. This disagreement arises because G...
How does a pendulum make its period longer?
A simple pendulum consists of a bob suspended at the end of a thread that is so light as to be considered massless. The period of such a device can be made longer by increasing its length, as measured from the point of suspension to the middle of the bob. A change in the mass of the bob, however, does not affect the period, ...
Why does the pendulum have a shorter period?
Because the strength of Earth’s gravitational field is not uniform everywhere, a given pendulum swings faster , and thus has a shorter period, at low altitudes and at Earth’s poles than it does at high altitudes and at the Equator.
What is a pendulum with an extended mass called?
There are various other kinds of pendulums. A compound pendulum has an extended mass, like a swinging bar, and is free to oscillate about a horizontal axis. A special reversible compound pendulum called Kater’s pendulum is designed to measure the value of g, the acceleration of gravity.
What are some examples of pendulums?
Examples of simple pendulums are found in clocks, swing sets, and even the natural mechanics of swinging legs. Tetherballs are examples of spherical pendulums. Schuler pendulums are used in some inertial guidance systems, while certain compound pendulums have applications in measuring the acceleration of gravity.
Why is a pendulum suspended?
A pendulum is a body suspended from a fixed point so that it can swing back and forth under the influence of gravity . The time interval of a pendulum’s complete back-and-forth movement is constant.
How does a pendulum swing?
A simple pendulum consists of a bob suspended at the end of a thread that is so light as to be considered massless. The period of such a device can be made longer by increasing its length, as measured from the point of suspension to the middle of the bob. A change in the mass of the bob, however, does not affect the period, provided the length is not thereby affected. The period, on the other hand, is influenced by the position of the pendulum in relation to Earth. Because the strength of Earth’s gravitational field is not uniform everywhere, a given pendulum swings faster, and thus has a shorter period, at low altitudes and at Earth’s poles than it does at high altitudes and at the Equator.
What is the purpose of a Schuler pendulum?
This principle of the Schuler pendulum is applied in some inertial guidance systems to maintain a correct internal vertical reference, even during rapid acceleration.
What is the period of a pendulum?
Formula: the period of a pendulum is defined as the time taken to complete a cycle (swing). It depends on the length of the pendulum and the gravity of the place where it is been measured. It also depends on the amplitude that is the maximum angle that a pendulum can swing form the point zero or the vertical axis.
What is a pendulum?
Definition: A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot that swing with a regular movement. The first scientist that tried to describe the physical phenomenon behind this movement was Galileo Galilei, which in 1602, after he became interested from a chandelier in Pisa Cathedral. He discovered that this movement could be useful to be used as a timekeeper because the time in which a pendulum completes a whole movement from one side to the opposite side is independent on the mass of the pendulum or the width of the swing.
Why was the pendulum used as a timekeeper?
He discovered that this movement could be useful to be used as a timekeeper because the time in which a pendulum completes a whole movement from one side to the opposite side is independent on the mass of the pendulum or the width of the swing.
What is the unit of period?
The unit of period is always in time units: seconds, minutes, hours, etc.
What is the period of a pendulum?
The time for one complete cycle, a left swing and a right swing, is called the period. The period depends on the length of the pendulum and also to a slight degree on the amplitude, the width of the pendulum's swing.
What is a pendulum?
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position. When released, the restoring force acting on the pendulum's mass causes it ...
How did Huygens make the clock period isochronous?
To make its period isochronous, Huygens mounted cycloidal-shaped metal 'chops' next to the pivots in his clocks, that constrained the suspension cord and forced the pendulum to follow a cycloid arc (see cycloidal pendulum ). This solution didn't prove as practical as simply limiting the pendulum's swing to small angles of a few degrees. The realization that only small swings were isochronous motivated the development of the anchor escapement around 1670, which reduced the pendulum swing in clocks to 4°–6°.
Why did pendulums change length?
The largest source of error in early pendulums was slight changes in length due to thermal expansion and contraction of the pendulum rod with changes in ambient temperature. This was discovered when people noticed that pendulum clocks ran slower in summer, by as much as a minute per week (one of the first was Godefroy Wendelin, as reported by Huygens in 1658). Thermal expansion of pendulum rods was first studied by Jean Picard in 1669. A pendulum with a steel rod will expand by about 11.3 parts per million (ppm) with each degree Celsius increase, causing it to lose about 0.27 seconds per day for every degree Celsius increase in temperature, or 9 seconds per day for a 33 °C (59 °F) change. Wood rods expand less, losing only about 6 seconds per day for a 33 °C (59 °F) change, which is why quality clocks often had wooden pendulum rods. The wood had to be varnished to prevent water vapor from getting in, because changes in humidity also affected the length.
Why do pendulums have to be recalibrated?
Pendulums are affected by changes in gravitational acceleration, which varies by as much as 0.5% at different locations on Earth, so precision pendulum clocks have to be recalibrated after a move. Even moving a pendulum clock to the top of a tall building can cause it to lose measurable time from the reduction in gravity.
How does a clock pendulum work?
Each time the pendulum swings through its centre position, it releases one tooth of the escape wheel (g). The force of the clock's mainspring or a driving weight hanging from a pulley, transmitted through the clock's gear train, causes the wheel to turn, and a tooth presses against one of the pallets (h), giving the pendulum a short push. The clock's wheels, geared to the escape wheel, move forward a fixed amount with each pendulum swing, advancing the clock's hands at a steady rate.
Why are pendulums useful?
This property, called isochronism, is the reason pendulums are so useful for timekeeping. Successive swings of the pendulum, even if changing in amplitude, take the same amount of time. For larger amplitudes, the period increases gradually with amplitude so it is longer than given by equation (1).
What is the time period of a pendulum?
The time period of a simple pendulum: It is defined as the time taken by the pendulum to finish one full oscillation and is denoted by “T”.
What is the point of a simple pendulum?
A simple pendulum can be described as a device where its point mass is attached to a light inextensible string and suspended from a fixed support. The vertical line passing through the fixed support is the mean position of a simple pendulum. The vertical distance between the point of suspension and the centre of mass of the suspended body (when it is in mean position) is called the length of the simple pendulum denoted by L. This form of the pendulum is based on the resonant system having a single resonant frequency.
How does a pendulum work?
The simple pendulum is a mechanical system that sways or moves in an oscillatory motion. This motion occurs in a vertical plane and is mainly driven by the gravitational force. Interestingly, the bob that is suspended at the end of a thread very light somewhat we can say it is even massless. The period of a simple pendulum can be made extended by increasing the length string while taking the measurements from the point of suspension to the middle of the bob. However, it should be noted that if the mass of the bob is changed it will the period remains unchanged. Period is influenced mainly by the position of the pendulum in relation to Earth as the strength of gravitational field is not uniform everywhere.
What is a pendulum used for?
Meanwhile, pendulums are a common system whose usage is seen in various instances. Some are used in clocks to keep track of the time while some are just used for fun in case of a child’s swing. In some cases, it is used in an unconventional manner such as a sinker on a fishing line. In any case, we will explore and learn more about the simple pendulum on this page. We will discover the conditions under which it performs simple harmonic motion as well as derive an interesting expression for its period.
What happens to the time period of a pendulum when the temperature changes?
If the temperature of a system changes then the time period of the simple pendulum changes due to a change in length of the pendulum.
What is the kinetic energy of a pendulum?
Kinetic Energy. The kinetic energy of the pendulum is given as K.E = (1/2) mv 2. At the highest point, the kinetic energy is zero and it is maximum at the lowest point. However, the total energy is constant as the function of time.
When is the pendulum at the lowest point?
When θ = 0 0, the pendulum is at the lowest point. Then cos 0 0 = 1. Therefore h = L (1-1) = 0
What Is a Pendulum?
A pendulum is a weight hung from a stationary point in a way that allows it to swing freely back and forth. A simple pendulum is one where the pendulum bob is treated as a point mass, and the string from which it hangs is of negligible mass. Simple pendulums are interesting from a physics perspective because they are an example of simple harmonic motion, much like springs or rubber bands can be.
How to describe a pendulum?
One equation tells us that the time period of the pendulum, T, is equal to 2pi times the square-root of L over g, where L is the length of the string, and g is the acceleration due to gravity (which is 9.8 on Earth).
Why does a pendulum show harmonic motion?
The pendulum shows simple harmonic motion because as the pendulum is pulled one way, the motion when released is equal but opposite. Over time the pendulum slows down due to air resistance.
What is simple pendulum motion?
Simple harmonic motion is any motion where a restoring force is applied that is proportional to the displacement and in the opposite direction of that displacement.
How many times does a pendulum cycle?
Okay, let's go through an example. A pendulum that is 4 meters in length completes one full cycle 0.25 times every second. The maximum displacement the pendulum bob reaches is 0.1 meters from the center. What is the time period of the oscillation? And what is the displacement after 0.6 seconds?
What is a pendulum in physics?
At its simplest, a pendulum is a weight and a string, or structure, for the weight to hang from. Explore the definition of a pendulum in physics and use an example problem to learn the equations for describing a pendulum. Updated: 11/05/2021
What happens when you lift a pendulum to one side?
Well, when you lift a pendulum to one side, the force of gravity wants to pull it back down, and the tension in the string wants to pull it left (or right). These combined forces work together to pull it back towards the middle (the equilibrium position).

Overview
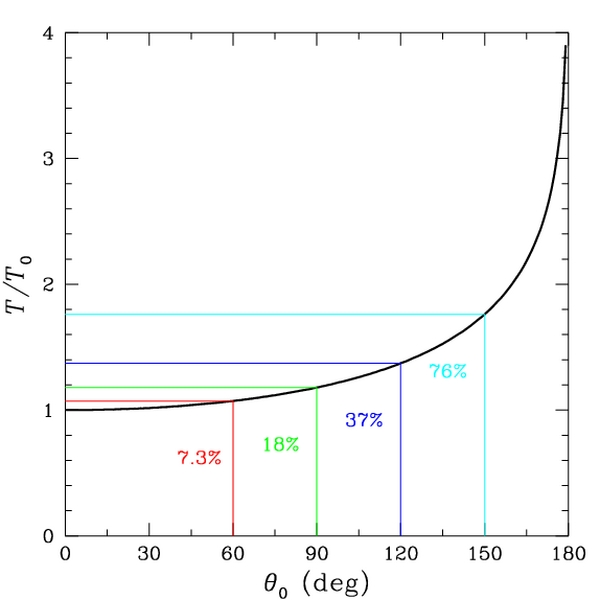
Period of oscillation
The period of swing of a simple gravity pendulum depends on its length, the local strength of gravity, and to a small extent on the maximum angle that the pendulum swings away from vertical, θ0, called the amplitude. It is independent of the mass of the bob. If the amplitude is limited to small swings, the period T of a simple pendulum, the time taken for a complete cycle, is:
where is the length of the pendulum and is the local acceleration of gravity.
Simple gravity pendulum
The simple gravity pendulum is an idealized mathematical model of a pendulum. This is a weight (or bob) on the end of a massless cord suspended from a pivot, without friction. When given an initial push, it will swing back and forth at a constant amplitude. Real pendulums are subject to friction and air drag, so the amplitude of their swings declines.
Compound pendulum
Any swinging rigid body free to rotate about a fixed horizontal axis is called a compound pendulum or physical pendulum. The appropriate equivalent length for calculating the period of any such pendulum is the distance from the pivot to the center of oscillation. This point is located under the center of mass at a distance from the pivot traditionally called the radius of oscillation, which depends on the mass distribution of the pendulum. If most of the mass is concentrated in a rela…
History
One of the earliest known uses of a pendulum was a 1st-century seismometer device of Han Dynasty Chinese scientist Zhang Heng. Its function was to sway and activate one of a series of levers after being disturbed by the tremor of an earthquake far away. Released by a lever, a small ball would fall out of the urn-shaped device into one of eight metal toad's mouths below, at the eight points …
Use for time measurement
For 300 years, from its discovery around 1582 until development of the quartz clock in the 1930s, the pendulum was the world's standard for accurate timekeeping. In addition to clock pendulums, freeswinging seconds pendulums were widely used as precision timers in scientific experiments in the 17th and 18th centuries. Pendulums require great mechanical stability: a length change …
Accuracy of pendulums as timekeepers
The timekeeping elements in all clocks, which include pendulums, balance wheels, the quartz crystals used in quartz watches, and even the vibrating atoms in atomic clocks, are in physics called harmonic oscillators. The reason harmonic oscillators are used in clocks is that they vibrate or oscillate at a specific resonant frequency or period and resist oscillating at other rates. How…
Gravity measurement
The presence of the acceleration of gravity g in the periodicity equation (1) for a pendulum means that the local gravitational acceleration of the Earth can be calculated from the period of a pendulum. A pendulum can therefore be used as a gravimeter to measure the local gravity, which varies by over 0.5% across the surface of the Earth. The pendulum in a clock is disturbed by the pushes it rec…