Ionization Energy Trend in the Periodic Table
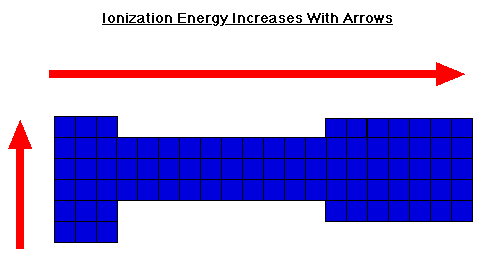
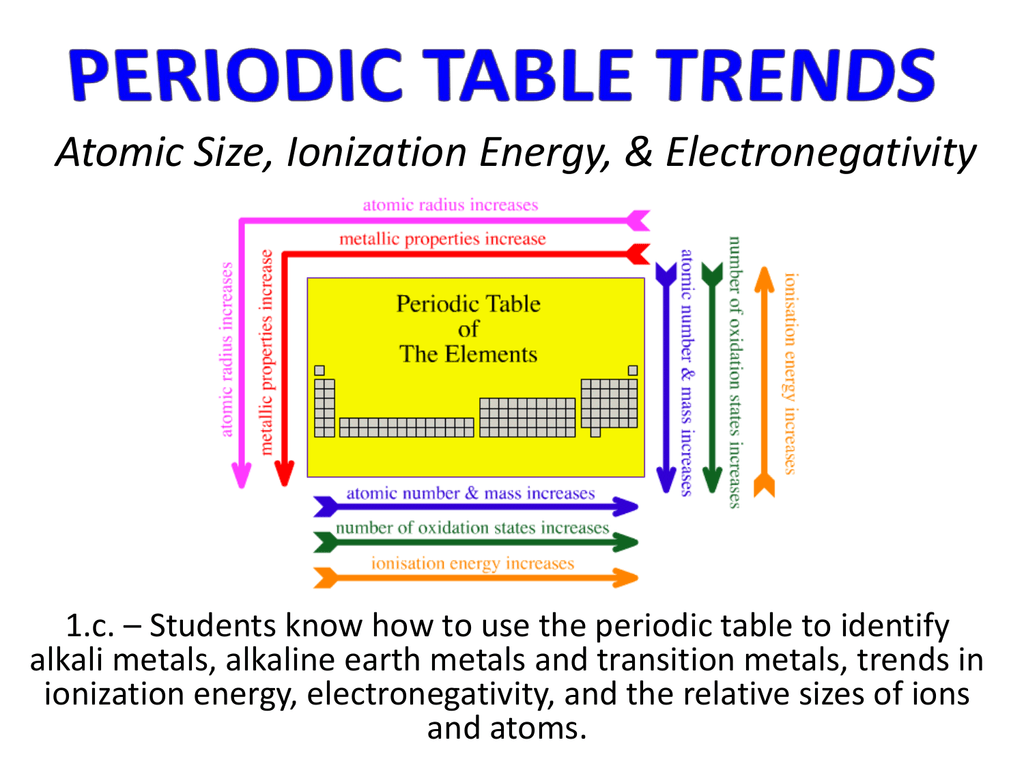
- Ionization energy generally increases moving from left to right across an element period (row). This is because the atomic radius generally decreases moving across a period, so there is a greater effective attraction between the negatively charged electrons and positively-charged nucleus. ...
- Ionization decreases moving top to bottom down an element group (column). ...
How to calculate the first ionization energy?
How to Calculate Ionization Energy. Ionization potential for hydrogen can be calculated using the following equation: E = hcRH (1/n 2 ), where. E is energy of the electron (or the amount of energy it takes to remove the electron, ionization energy) h is Planck’s constant = 6.626 * 10 -34 Js (joules*seconds)
How do you calculate second ionization energy?
∴ Order of second ionization enthalpy is O>F>N>C. How do you calculate second ionization energy? Second ionisation energy is defined by the equation: It is the energy needed to remove a second electron from each ion in 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions to give gaseous 2+ ions.
What trend in ionization energy occurs across a period on the periodic table?
Ionization energy exhibits periodicity on the periodic table. The general trend is for ionization energy to increase moving from left to right across an element period. Moving left to right across a period, atomic radius decreases, so electrons are more attracted to the (closer) nucleus.
What trend does the first ionization energy follow?
What is the trend in first ionization energy down a group? On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally decreases as you move down a group. This is because the outermost electron is, on average, farther from the nucleus, meaning it is held less tightly and requires less energy to remove.
What is the periodic trend for ionization energy Why?
The ionization energy of the elements within a period generally increases from left to right. This is due to valence shell stability. The ionization energy of the elements within a group generally decreases from top to bottom. This is due to electron shielding.
What is the periodic trend for ionization energy for a period?
In general, ionization energy increases across a period and decreases down a group. Across a period, effective nuclear charge increases as electron shielding remains constant.
What is the trend in first ionization energy across a period down a group?
As we move from left to right across a period, the ionization energy of elements increases. This is due to the decrease in the size of atoms across a period. The valence electrons get closer to the nucleus of an atom as we move from left to right due to increased nuclear charge.
Why does first ionization energy decrease down a group?
On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally decreases as you move down a group. This is because the outermost electron is, on average, farther from the nucleus, meaning it is held less tightly and requires less energy to remove.
What is the trend for second ionization energy?
Second ionization energy decreases as you go down the group. Third ionization energy decreases as you go down the group. For each element in the Group, the first ionization energy is less than the second ionization energy which is less than the third ionization energy.
Which is the correct order of ionization energies?
Correct Answer: Option B. Explanation: Since it is easier to take out an electron from a negatively charged ion than from a neutral atom, the ionization energies for anions will be lesser than the corresponding neutral atoms. So the order of ionisation energy is F>F− and Cl>Cl−.
Which gives the correct order for first ionization energies?
The answer is b) Ar > Cl > S > Si > Al. Ionization energy increases from left to right of the periodic table since the effective...
Why does the first ionisation energy increase across Period 3?
General increase in first IE Effective nuclear charge increases hence attraction between nucleus and valence electron is stronger. More energy is required to remove the valence electron hence first IE increases across Period 3.
What is the trend across a period?
The atomic radius across a period in the periodic table tends to decrease from left to right. As you move across a period the number of electrons from one element to the next increases by one.
How ionization energy varies in groups and periods?
Ionization energy increases from left to right in a period and decreases from top to bottom in a group.
Why does ionization energy increase from bottom to top?
This is because the valence electrons do not screen each other very well, allowing the effective nuclear charge to increase steadily across the row. The valence electrons are therefore attracted more strongly to the nucleus, so atomic sizes decrease and ionization energies increase.
Why does ionization energy decrease from BE to B?
Boron has higher nuclear charge.
Which element has the highest ionization energy?
In general, (first) ionization energies increase toward the top right corner of the periodic table, with helium having the highest ionization energy. Before we break down the trend into its period and group trends, let’s talk about a major contributing factor to this trend: the octet rule.
What is Ionization Energy?
So what is the definition of ionization energy? It is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom, which forms an ion. It is usually measured in kJ/mol, and the measurement is based on an isolated atom in its gaseous phase. Let’s learn how to calculate it, what is meant by first and second ionization energy, and how it trends on the periodic table.
Why does ionization decrease when you go down a group?
This is because as you go down a group, electrons are located in successively higher energy levels, farther away from the attraction of the nucleus. Furthermore, down a group, there are more electrons between the outside valence electrons and the nucleus. These middle electrons help “shield” the outer electrons from the attractive forces of the nucleus. Therefore, it is easier to remove an electron from lower in a group.
Why does a group 1 element have very low ionization energies?
Thus, group 1 elements have very low ionization energies. It takes very little energy to remove an electron because the atom can be more stable without it.
How do ions get their charge?
An ion is a positively or negatively charged atom—it gets the charge by having a number of electrons unequal to that of its protons. For example, the sodium ion, also written as Na +, has 11 protons and 10 electrons. There is one more proton than there are electrons, making the ion positively charged. The number of protons for any atom or ion is always constant (the number of protons determines the atomic number).
What is the energy of an electron?
E is energy of the electron (or the amount of energy it takes to remove the electron, ionization energy)
Which group of gases has the highest ionization potential?
As you can see on the graph, the noble gases have the highest ionization energies, and the alkali metals have the lowest ionization energies. Between groups 1 and 18, ionization potentials generally increase across a period.
What is the trend of ionization?
Ionization, together with atomic and ionic radius, electronegativity, electron affinity, and metallicity, follows a trend on the periodic table of elements. Ionization energy generally increases moving from left to right across an element period ( row). This is because the atomic radius generally decreases moving across a period, ...
What is the trend for ionization energy to decrease moving from top to bottom down a periodic table group?
The general trend is for ionization energy to decrease moving from top to bottom down a periodic table group. Moving down a group, a valence shell is added. The outermost electrons are further from the positive-charged nucleus, so they are easier to remove.
Why does ionization decrease as electrons move down the group?
This is because the principal quantum number of the outermost electron increases moving down a group. There are more protons in atoms moving down a group (greater positive charge), yet the effect is to pull in the electron shells, making them smaller and screening outer electrons from the attractive force of the nucleus. More electron shells are added moving down a group, so the outermost electron becomes increasingly distance from the nucleus.
What is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom?
Updated July 03, 2019. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion. The first or initial ionization energy or E i of an atom or molecule is the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of isolated gaseous atoms or ions.
What is ionization energy?
Ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion in the gas phase. The most common units of ionization energy are kilojoules per mole (kJ/M) or electron volts (eV). Ionization energy exhibits periodicity on the periodic table. The general trend is for ionization energy to increase moving from left ...
What are the exceptions to the ionization energy trend?
Exceptions to the Ionization Energy Trend. If you look at a chart of first ionization energies, two exceptions to the trend are readily apparent. The first ionization energy of boron is less than that of beryllium and the first ionization energy of oxygen is less than that of nitrogen.
Why is ionization energy important?
Ionization energy is important because it can be used to help predict the strength of chemical bonds. Also Known As: ionization potential, IE, IP, ΔH°. Units: Ionization energy is reported in units of kilojoule per mole (kJ/mol) or electron volts (eV).
What is Ionization Energy?
Ionization energy is the minimum amount of energy required to remove the outermost, or most loosely bound, electron in the electron cloud of an atom of a certain element. The outermost electron (s) in an atom are valence electrons. Because valence electrons are the furthest from the nucleus of the atom, they are influenced by the atom's positively charged nucleus the least. Therefore, valence electrons would be the first to be stripped away by nuclei from another atom that has a greater positively charged influence on the electrons. Additionally, more than one electron can be removed from an atom; as electrons are stripped away it becomes increasingly difficult and requires more energy to remove electrons. Ionization energy is measured in kilojoules per mole. The formula for ionization energy is as follows:
How do protons affect ionization energy?
The reason why the number of protons affects ionization energy is that they are positively charged and pull on negatively charged electrons. Therefore, atoms with more protons have a greater influence on their outermost electrons, and their orbits are more tightly packed around their nuclei. However, atoms that have a greater number of electrons, and electron orbitals between them, decrease the positively charged influence the protons have on their outermost electrons or valence electrons. More electrons tend to cloud, or neutralize, the positively charged nucleus so that it is felt less by valence electrons. Lastly, the increase in the number of electron orbits around a nucleus means that the outermost electrons are further away from the positively charged nucleus of the atom. Increasing the distance between valence electrons and the nucleus they surround, decreases the nucleus' influence on the valence electrons. This results in a trend of decreasing ionization energy going down a group.
How many protons does lithium have?
For example, both lithium and fluorine have the same amount of electron shells but differ in their number of protons. Lithium has 3 protons, and fluorine has 9. The nucleus of fluorine has more protons and therefore has a stronger positively charged force that pulls the electron shells in tighter around the nucleus. This causes the outermost electrons of fluorine to require more energy to strip them from the nuclei that they tightly surround.
Why does ionization energy decrease when moving from top to bottom?
Ionization energy decreases moving from top to bottom in a group. The reason for this is because moving down a group increases the period number and therefore the number of electron orbits. An increase in electron orbits results in a decrease in ionization energy because the distance between the nucleus and its outermost electrons increases, which decreases the influence the nucleus has on its outermost electrons.
How is ionization energy determined?
Ionization energy, or the minimum amount of energy required to strip a valence electron, is contingent on the number of electron orbits around the nuclei and the number of protons in the nuclei of a given element. The periodic table of elements is organized in a way that creates an ionization energy trend. The periodic table is organized into groups and periods. Groups are the columns on the table, and periods are the rows. Excluding group 8a or 18, elements in the same group contain the same amount of valence electrons. Elements in the same period or row contain the same amount of electron orbitals in their atoms.
Why do elements move down a group?
The reason for this pattern is because moving down in a group is increasing the period number or the number of electron orbitals that surround the nuclei of that element. Increasing the number of electron orbitals, or shells, increases the size of the atom and the distance between the outermost electrons and the nucleus. Because the distance between them is greater, the nucleus has a lesser influence on the electrons. The electrons are therefore held less tightly around the nucleus in atoms of elements going down a group.
What does it mean when the atomic radius increases?
An increase in atomic radius is a decrease in ionization energy.
What Is Ionization Energy?
the amount of energy required by an isolated gaseous atom to lose an electron in its ground state.
What happens to the second ionization energy?
Whenever an electron is removed from an atom, a specific amount of energy is required to remove it, hence the ionization enthalpies of chemical elements are always positive. The second most outer electron will be more attracted by the nucleus than the first outer electron. Therefore, the second ionization energy will be greater than the first ionization energy. In the same way, third ionization enthalpy will be greater than the second one.
What is the energy needed to remove the second electron from its valence shell?
In the same way, second ionization energy is described as the energy needed to remove the second electron from its valence shell. It can be explained by the equation given below: A + (g) → A 2+ (g) + e –. Whenever an electron is removed from an atom, a specific amount of energy is required to remove it, hence the ionization enthalpies ...
What is the force of attraction between electrons and the nucleus?
The force of attraction between electrons and the nucleus. The force of repulsion between electrons. The effective nuclear charge felt by the outermost electrons will be less than the actual nuclear charge. This is because the inner electrons will shield the outermost electrons by hindering the path of nuclear charge.
Why do electrons move closer to the nucleus?
The valence electrons get closer to the nucleus of an atom as we move from left to right due to increased nuclear charge. The force of attraction between the nucleus and the electrons increases and hence more energy is required to remove an electron from the valence shell. ...