Full Answer
How to eliminate a refractory period?
- Reduce waistline / excess stomach fat
- Sleep 8 hours a night
- Reduce stress (cortisol production)
- Lift weights
- Eat a balanced diet of protein, fats and carbs (don’t cut out fats and carbs, they are essential)
- Absorb some sunlight / Vitamin D supplementation
What causes absolute refractory period?
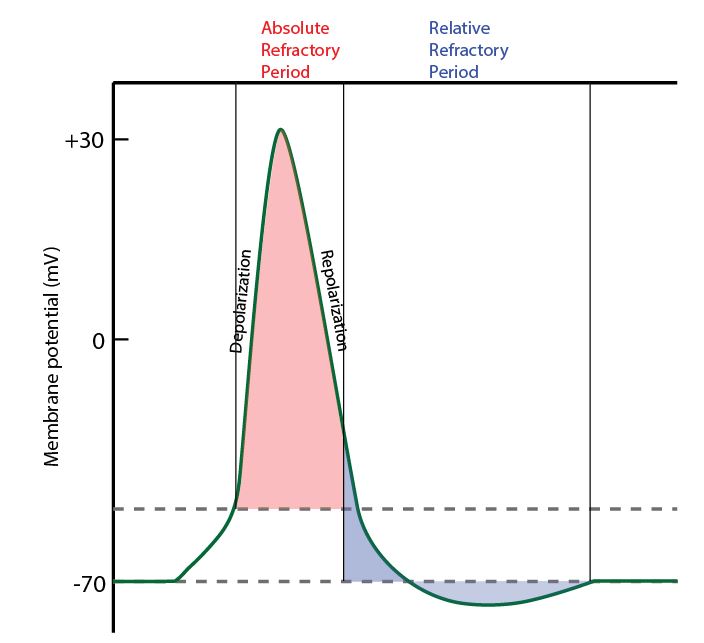
What causes the absolute refractory period? The refractory periods are due to the inactivation property of voltage-gated sodium channels and the lag of potassium channels in closing.
What is the difference between absolute and relative refractory period?
What is the difference between absolute and relative refractory period? Absolute: Is the period of time during which a second action potential ABSOLUTELY cannot be initiated, no matter how large the applied stimulus is. Relative: Is the interval immediately following the Absolute Refractory Period during which initiation of a second action ...
What is an example of refractory period?
When two stimuli occur in close succession, the time it takes us to react to the second stimulus will be longer than it normally would. This is referred to as the refractory period in psychology. An example of the refractory period is when talking on the phone while driving causes you to react slower to seeing a stopped car in front of you.

What is refractory period in a neuron?
By definition, the refractory period is a period of time during which a cell is incapable of repeating an action potential. In terms of action potentials, it refers to the amount of time it takes for an excitable membrane to be ready to respond to a second stimulus once it returns to a resting state.
What is the refractory period in simple terms?
: the brief period immediately following the response especially of a muscle or nerve before it recovers the capacity to make a second response.
What is the refractory period and why is it important?
The refractory period limits the rate at which action potentials can be generated, which is an important aspect of neuronal signaling. Additionally, the refractory period facilitates unidirectional propagation of the action potential along the axon.
What is the refractory period of a neuron quizlet?
a brief time period after an action potential has been initiated during which an axon is either incapable of generating another action potential. The excitable plasma membrane recovers at this time and becomes ready to respond to another stimulus.
What is the best description of the absolute refractory period?
Definition: The absolute refractory period refers to a period during the action potential. This is the time during which another stimulus given to the neuron (no matter how strong) will not lead to a second action potential.
Which answer best describes the relative refractory period in the neuron?
Which answer best describes the relative refractory period in the neuron? The resting membrane potential is restored, but concentrations of sodium and potassium are not restored to their original state.
What happens during the refractory period?
The refractory period is the span of time after having an orgasm during which a person is not sexually responsive. The refractory period can have both mental and physiological effects. During the refractory period, a person might lose interest in sex, or they might not be able to have sex.
Why can't I get hard after the first round?
After sex. After orgasm, every man goes through a recovery cycle, called the refractory period, which is when it is not possible to get another erection. This resolution stage can take anything from minutes to days and varies from man to man, generally extending as you get older.
What does the refractory period prevent?
It is initiated by paced or sensed events; after a sensed event, the refractory period prevents double counting the same event, whereas after a paced event, it prevents sensing the pacing stimulus, its after-potential, or the evoked response. Events within the refractory period do not reset the LRI.
What is the refractory period of an action potential quizlet?
The period of time following the initiation of an action potential during which it is difficult or impossible to initiate a second action potential.
What happens during the absolute refractory period quizlet?
The period from the initiation of the action potential to immediately after the peak is referred to as the absolute refractory period (ARP) This is the time during which another stimulus given to the neuron will not lead to a second action potential.
What causes relative refractory period quizlet?
The relative refractory period is caused by hyperpolarization as potassium rushes out of the cell after the action potential.
What is refractory period of muscle?
In physiology, a refractory period is a period of time during which an organ or cell is incapable of repeating a particular action, or (more precisely) the amount of time it takes for an excitable membrane to be ready for a second stimulus once it returns to its resting state following an excitation.
What occurs during the refractory period psychology?
The term psychological refractory period (PRP) refers to the period of time during which the response to a second stimulus is significantly slowed because a first stimulus is still being processed.
What is refractory period in cardiac muscle?
The functional refractory period (FRP) is the shortest interval between two consecutively conducted impulses out of a cardiac tissue resulting from any two consecutive input impulses into that tissue (i.e., the shortest output interval that can occur in response to any input interval in a particular tissue).
What is the refractory period and what does it prevent?
The refractory period is a state of recovery that occurs after a neuron has fired an action potential. During this period, another action potential...
What channels are open during relative refractory period?
During relative refractory, voltage-gated potassium channels are open, allowing positively charged potassium ions to leave the cell. Some voltage-g...
What is relative and absolute refractory period?
The absolute refractory period occurs right after an action potential is produced. During absolute refractory, the neuron cannot fire another actio...
What is the benefit of a relative refractory period?
The relative refractory period requires a much larger stimulus than was previously required in order to produce an action potential. This causes de...
What is the relative refractory period of an action potential?
The relative refractory period of an action potential occurs mostly during the hyperpolarization stage. Here, potassium channels are open, causing...
How long is the refractory period?
Although we have reported the refractory period to be 3-4 ms long, it should be noted that the hyperpolarization phase can last up to 15 ms in some neurons. In these neurons, therefore, the relative refractory period is much longer.
What is the absolute refractory period?
The absolute refractory period is responsible for setting the upper limit on the maximum number of action potentials that can be generated during any given time period. In other words, the absolute refractory period determines the maximum frequency of action potentials that can be generated at any point along the axon plasma membrane. This action potential frequency, in turn, has important physiological implications for how the nervous system can respond to high-frequency stimuli, and also for the ability of the nervous system to send high-frequency signals to effector organs when needed (see Frequency Coding in the Nervous System ).
What happens during the absolute refractory period?
During the absolute refractory period, a second stimulus (no matter how strong) will not excite the neuron. During the relative refractory period, a stronger than normal stimulus is needed to elicit neuronal excitation.
Which channel is responsible for the absolute refractory period?
In summary, inactivation of Na + channels is solely responsible for the absolute refractory period. Both Na + channel inactivation and greater than resting pK value are responsible for the relative refractory period.
How does a stimulus bring a neuron to threshold?
During the relative refractory period, the neuron can be excited with stimuli strong er than that needed to bring a resting neuron to threshold. The strength of of the stimulus required is very high early in the relative refractory period and gradually becomes smaller throughout the relative refractory period as Na + channels recover from inactivation and as K + permeability returns to its resting level (see figure ). At the end of the relative refractory period, when the neuron is back to its resting state, the stimulus strength is at the minimum level required to bring a resting neuron to threshold (dashed line).
What is the absolute refractory period?
In summary, the absolute refractory period is when a neuron can no longer send an action potential. During an action potential, voltage-gated sodium channels open, and sodium rushes into the cell. After a specific period of time, the sodium channels slam shut and no longer let sodium in.
How does the absolute refractory period affect how strongly we can feel a stimulus?
So, there is an upper limit to how strongly we can feel any sensation, or how fast our brain can send signals to our bodies. Thus, the absolute refractory period limits how fast we can respond, and how much we can feel our environment.
Why can't neurons fire action potentials?
At this time, no matter what goes on, the neuron just can't fire an action potential. The reason for this lies in the voltage-gated sodium channels.
What is the time that neurons must rest and not send another impulse called?
The time that they must rest, and not send another impulse, is called the absolute refractory period. Lesson.
How Do Neurons Communicate?
Neurons send messages using electrical and chemical signals. The message starts when a neuron receives chemicals, called neurotransmitters at the dendrites. The neurotransmitters cause the neuron to become more positive inside the cell. This is called depolarizing. If a neuron depolarizes enough, a signal, called an action potential is sent down the axon towards the synaptic terminal, where it will send the signal to the next neuron.
When can a neuron be restimulated?
neuron can be restimulated if stimulus is larger than threshold
Can a neuron be restimulated by stimulus?
neuron cannot be restimulated by stimulus of any strength because voltage-gated sodium channels open and are then inactivated
