See more

Is Zn a metal ion?
Zinc ion as the second most abundant transition metal ion in the human body plays key roles in the catalytic function of many enzymes and in gene transcription. Most of the zinc ions in biological systems are tightly bound to proteins for structural and catalytic functions.
Is Zn a metal nonmetal or metalloid?
zinc (Zn), chemical element, a low-melting metal of Group 12 (IIb, or zinc group) of the periodic table, that is essential to life and is one of the most widely used metals.
Why Zn is a metal?
Zinc (Zn) is a soft metal with an electrical structure that is particularly stable (full-filled stable configuration). As a result, the metallic connections in them are weak. They have a high ability to oxidize to the + 2 oxidation state. The electronic configuration = ( Zn ) is [ A r ] 4 s 2 3 d 10.
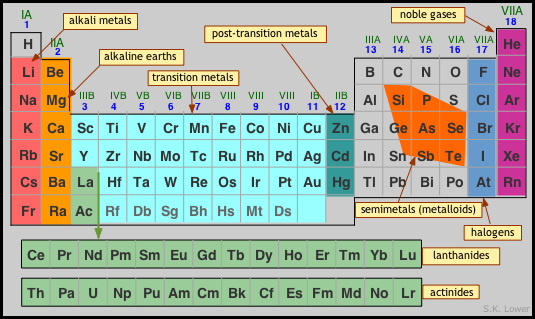
Where is Zn in the periodic table?
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table.
Why is zinc metalloid?
Zinc shows certain properties like non-metals, so it is termed as a metalloid. Zinc makes amphoteric oxides which react with bases also (property of a non-metal).
What is zinc made of?
Zinc is primarily extracted from ore containing zinc sulfide, zinc blende, or sphalerite. The countries mining and producing the most refined zinc, in descending order, are China, Peru, Australia, the United States, and Canada.
Is zinc a strong metal?
Zinc metal in its pure form is a very strong metal. However, when combined with other metals such as copper and nickel-copper, it increases zinc's dimensional and impact strength as well as its stability and corrosion resistance.
What zinc is used for?
Zinc is a trace mineral, meaning that the body only needs small amounts, and yet it is necessary for almost 100 enzymes to carry out vital chemical reactions. It is a major player in the creation of DNA, growth of cells, building proteins, healing damaged tissue, and supporting a healthy immune system.
What is unique about zinc?
Zincs most remarkable quality is its natural capacity to protect. By protecting steel against corrosion, zinc protects buildings, automobiles, ships and steel structures of every kind from corrosion by the atmosphere, water, and soil.
Is Zn a main group element?
Group 12 elements are commonly thought to be transition metals; however, zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), and mercury (Hg) share some properties of both groups, and many scientists believe they should be classified as the main group elements.
Why is zinc called zinc?
Where did zinc get its name? A German alchemist name Paracelsus named the metal zinc. It either comes from the German word "zinke" meaning "spiked" (for the spiked shapes of the zinc crystals) or "zinn" meaning "tin". There are five isotopes of zinc that occur in nature.
Why is zinc reactive?
The reason are: Zinc is a more electropositive element than iron. Zinc has a bigger atomic size than that of iron and thus has more number of electrons. The fact of having more elecetrons and a 'd' sub shell, gives zinc a lot of hybridisation possibilities than that of iron.
Is iron a metal nonmetal or metalloid?
iron (Fe), chemical element, metal of Group 8 (VIIIb) of the periodic table, the most-used and cheapest metal.
Is zinc a strong metal?
Zinc metal in its pure form is a very strong metal. However, when combined with other metals such as copper and nickel-copper, it increases zinc's dimensional and impact strength as well as its stability and corrosion resistance.
Is copper a metal nonmetal or metalloid?
copper (Cu), chemical element, a reddish, extremely ductile metal of Group 11 (Ib) of the periodic table that is an unusually good conductor of electricity and heat. Copper is found in the free metallic state in nature.
Where are metals nonmetals and metalloids?
The metals are to the left of the line (except for hydrogen, which is a nonmetal), the nonmetals are to the right of the line, and the elements immediately adjacent to the line are the metalloids.
How many isotopes does zinc have?
With the middling atomic number 30, it has five stable isotopes of atomic weight from the dominant zinc 64 to zinc 70, plus an extra 25 radioisotopes. Because of its hazy origins, it's difficult to pin down one person as the discoverer of the element.
Who discovered zinc?
Moras de Respour, reported the extraction of metallic zinc from zinc oxide, but as far as Europe was concerned zinc was discovered by the German chemist Andreas Marggraf in 1746, and indeed he was the first to recognise it as a new metal.
What is zinc used for?
Uses. Most zinc is used to galvanise other metals, such as iron, to prevent rusting. Galvanised steel is used for car bodies, street lamp posts, safety barriers and suspension bridges. Large quantities of zinc are used to produce die-castings, which are important in the automobile, electrical and hardware industries.
How much zinc is in the human body?
Zinc is essential for all living things, forming the active site in over 20 metallo-enzymes. The average human body contains about 2.5 grams and takes in about 15 milligrams per day. Some foods have above average levels of zinc, including herring, beef, lamb, sunflower seeds and cheese.
Where was zinc first used?
Zinc was known to the Romans but rarely used. It was first recognised as a metal in its own right in India and the waste from a zinc smelter at Zawar, in Rajasthan, testifies to the large scale on which it was refined during the period 1100 to the 1500.
How are elements organized into blocks?
Elements are organised into blocks by the orbital type in which the outer electrons are found. These blocks are named for the characteristic spectra they produce: sharp (s), principal (p), diffuse (d), and fundamental (f). The number of protons in an atom.
What is a vertical column in the periodic table?
A vertical column in the periodic table. Members of a group typically have similar properties and electron configurations in their outer shell. Period. A horizontal row in the periodic table. The atomic number of each element increases by one, reading from left to right. Block.
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).
Copper in Periodic table
Copper element is in group 11 and period 4 of the Periodic table. Copper is the d-block element and it belongs to transition metals group.
Is Copper a Transition Metal? Why?
Yes, Copper is a transition metal because it has incompletely filled d-orbital in its most common oxidation state (Cu2+).
Properties of Copper
The physical and chemical properties of copper element are mentioned below.
Free Gift for you: Interactive Periodic Table
Let me tell you how this Interactive Periodic Table will help you in your studies.