
What caused the extinction of the Jurassic period?
The Triassic-Jurassic extinction happened between 199 million and 214 million years ago and as in other mass extinctions, it is believed there were several phases of species loss. The blame has been placed on an asteroid impact, climate change, and flood basalt eruptions. During the beginning of this era, mammals outnumbered dinosaurs.
What organisms disappeared during the Jurassic period?
There was a minor mass extinction toward the end of the Jurassic period. During this extinction, most of the stegosaurid and enormous sauropod dinosaurs died out, as did many genera of ammonoids, marine reptiles, and bivalves. What period dinosaurs became extinct?
What important events happened in the Jurassic period?
What major events happened in the Jurassic period? A Shifting Climate and Developing Oceans At the start of the period, the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea continued and accelerated. Laurasia, the northern half, broke up into North America and Eurasia. Gondwana, the southern half, began to break up by the mid-Jurassic.
When did the Proterozoic era start and end?
When did the proterozoic era start? end? Dawned 2.5 Billion years ago and ended 542 million years ago. 3 parts of the proterozoic? 1. early paleoproterozoic (2.5-1.6 GA) 2. middle mesoproterozoic (1.6 - 1.0 GA) 3. new neoproterozoic (1.0 GA - 542 MA)-neoproterozoic = tonian, cryogenian, ediacaran.
See more
When did the Jurassic Period end and why?
We do know that the end of the Jurassic was marked by the Tithonian–early Barremian cool interval, which began 150 million years ago and continued well into the Early Cretaceous (Ogg et al., 2012a).
Why did the Jurassic era end?
The cause of this extinction is unknown, but there is some speculation (by sedimentologist Stephen P. Hesselbo et al.) that it was triggered by the release of huge methane deposits from within the Earth (these deposits formed beneath the seabed as surface algae dies and sinks to the sea floor).
How long did Jurassic Period last?
The Jurassic Period was a golden time for dinosaurs, which flourished for 180 million years.
What happened to the Jurassic Period?
During the Jurassic period, the supercontinent Pangaea split apart. The northern half, known as Laurentia, was splitting into landmasses that would eventually form North America and Eurasia, opening basins for the central Atlantic and the Gulf of Mexico.
Did it snow in the Jurassic period?
“There would have been ice and snow in the three-month-long, dark winters,” Rich says. Still, a variety of dinosaurs thrived here, including small, feathery predators, parrot-like oviraptors and Leaellynasaura, a small herbivore that walked on two legs and had one of the longest tails for its body size of any dinosaur.
How hot was it in the Jurassic period?
Climate. The climate of the Jurassic was generally warmer than that of present, by around 5 °C to 10 °C, with atmospheric carbon dioxide likely four times higher.
Was the T Rex in the Jurassic period?
T. rex lived about 66–68 million years ago during the Cretaceous Period in the western United States, including Montana and Wyoming.
When did dinosaurs go extinct?
about 65 million years agoDinosaurs went extinct about 65 million years ago (at the end of the Cretaceous Period), after living on Earth for about 165 million years.
What did Earth look like in the Jurassic period?
The Jurassic period (199.6 million to 145.5 million years ago) was characterized by a warm, wet climate that gave rise to lush vegetation and abundant life. Many new dinosaurs emerged—in great numbers. Among them were stegosaurs, brachiosaurs, allosaurs, and many others.
What was Earth like when dinosaurs lived?
The climate was relatively hot and dry, and much of the land was covered with large deserts. Unlike today, there were no polar ice caps. It was in this environment that the reptiles known as dinosaurs first evolved.
What are 3 interesting facts about the Jurassic period?
Top Jurassic Period Facts Rocks in this region were formed during the Jurassic Period. The Jurassic Period began 201.3 million years ago (Mya) and ended 145 Mya. It lasted 56 million years, and was the second-longest period of the Mesozoic Era. The Jurassic is the second of the three periods of the Mesozoic Era.
Did dinosaurs live in the Jurassic period?
The 'Age of Dinosaurs' (the Mesozoic Era) included three consecutive geologic time periods (the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous Periods). Different dinosaur species lived during each of these three periods.
What came after the Jurassic era?
The Cretaceous is defined as the period between 145.5 and 65.5 million years ago,* the last period of the Mesozoic Era, following the Jurassic and ending with the extinction of the dinosaurs (except birds).
Why did the Mesozoic Era end?
This era includes the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous Periods, names that may be familiar to you. It ended with a massive meteorite impact that caused a mass extinction, wiping out the dinosaurs and up to 80% of life on Earth.
When did the dinosaurs go extinct?
about 65 million years agoDinosaurs went extinct about 65 million years ago (at the end of the Cretaceous Period), after living on Earth for about 165 million years.
What comes after the Jurassic period?
Cretaceous Period, in geologic time, the last of the three periods of the Mesozoic Era. The Cretaceous began 145.0 million years ago and ended 66 million years ago; it followed the Jurassic Period and was succeeded by the Paleogene Period (the first of the two periods into which the Tertiary Period was divided).
What dinosaurs lived in the Jurassic Period?
The Jurassic Period was a golden time for dinosaurs, which flourished for 180 million years. Huge sauropod herbivores (such as 87-foot [27-meter] long Diplodocus) and carnivores (such as 35-foot [11-meter] long Allosaurus) emerged. To get a sense of how large these animals were, imagine sprinting as fast as you can.
Who coined the term "Jurassic"?
Alexander von Humboldt, a German pioneer geologist, first coined this term “Jurassic” in 1795 for the strata of the Jura Mountains in northern Switzerland. In 1839 Leopold von Buch redefined the Jurassic as a system in its own right (Eicher 1976).
What are the two major groups of Dinosauria?
With the discovery of many new species since the 1840s, scientists have divided the Dinosauria into two major groups: the Ornithischia and the Saurischia, with the distinction based on the construction of the pelvis. The ornithischians were “bird hipped” as well as being herbivores, including both bipedal and quadrupedal forms. The saurischians or “lizard hipped,” including carnivorous bipedal forms (e.g., theropods such as Tyrannosaurus) and herbivorous bipedal and quadrupedal forms (e.g., sauropods). Some of the quadrupedal saurischians developed into the largest land animals in history, including Diplodocus ( perhaps reaching lengths of 100 feet [30 m] or more) and Brachiosaurus ( perhaps weighing as much as 130,000 pounds [60,000 kg]).
How fast can dinosaurs sprint?
To get a sense of how large these animals were, imagine sprinting as fast as you can. Let’s say you can do the 100-meter dash in 14 seconds. To do the “ Diplodocus dash” (head to foot) would take you four seconds. Good thing they weren’t carnivores! However, carnivorous dinosaurs also diversified during the Jurassic.
What is the difference between a dinosaur and a theropoda?
Theropoda consists of the carnivorous dinosaurs. The Theropoda includes some extinct dinosaurs such as Tyrannosaurus rex and Dilophosaurus. Birds descended from Theropoda.
What dinosaurs are in Thyreophora?
Thyreophora includes the various armored dinosaurs such as Stegosaurus and Ankylosaurus.
Why did dinosaurs wade in swamps?
Modern research has disproved the old concept that dinosaurs were slow-moving, dim-witted, solitary creatures, forced to wade about in swamps because their great bulk could not be supported on land. In fact, many dinosaurs were very agile (even the large ones).
When was the Jurassic period?
The Jurassic ( / dʒʊˈræs.sɪk / juu-RASS-ik) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period 201.3 million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 145 Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified.
What was the beginning of the Jurassic?
The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago, and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated the temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and is the only boundary between geological periods to remain formally undefined.
What was the climate like in the Jurassic period?
The climate of the Jurassic was generally warmer than that of present, by around 5 °C to 10 °C, with atmospheric carbon dioxide likely four times higher. Forests likely grew near the poles, where they experienced warm summers and cold, sometimes snowy winters; there were unlikely to have been ice sheets given the high summer temperatures that prevented the accumulation of snow, though there may have been mountain glaciers. Dropstones and glendonites in northeastern Siberia during the Early to Middle Jurassic indicate cold winters. The ocean depths were likely 8 °C warmer than present, and coral reefs grew 10° of latitude further north and south. The Intertropical Convergence Zone likely existed over the oceans, resulting in large areas of desert in the lower latitudes.
What is the Jurassic stratigraphy?
Jurassic stratigraphy is primarily based on the use of ammonites as index fossils. The first appearance datum of specific ammonite taxa is used to mark the beginnings of stages, as well as smaller timespans within stages, referred to as "ammonite zones"; these, in turn, are also sometimes subdivided further into subzones. Global stratigraphy is based on standard European ammonite zones, with other regions being calibrated to the European successions.
How many epochs were there in the Jurassic period?
The Jurassic period is divided into three epochs: Early, Middle, and Late. Similarly, in stratigraphy, the Jurassic is divided into the Lower Jurassic, Middle Jurassic, and Upper Jurassic series of rock formations. Geologists divide the rocks of the Jurassic into a stratigraphic set of smaller rock units called stages, each formed during corresponding time intervals called ages.
Which dinosaurs were morphologically aberrant?
Chilesaurus, a morphologically aberrant herbivorous dinosaur from the Late Jurassic of South America, has uncertain relationships to the three main groups of dinosaurs, having been recovered as a member of all three in different analyses.
Which group of tree ferns are most common in the Jurassic period?
The Cyatheales, the group containing most modern tree ferns, appeared during the Late Jurassic, represented by members of the genus Cyathocaulis, which are suggested to be early members of Cyatheaceae on the basis of cladistic analysis. Only a handful of possible records exist of the Hymenophyllaceae from the Jurassic, including Hymenophyllites macrosporangiatus from the Russian Jurassic.
What is the Jurassic period?
The Jurassic Period was the second of three geologic time periods of the Mesozoic Era. The Jurassic began about 201 million years ago at the end of the Triassic Period and ended 145 million years ago at the start of the Cretaceous Period. The Jurassic was named for the Jura Mountains between France and Switzerland, where rocks of the period were first studied. The Morrison Formation of the United States and the Solnhofen Limestone of Germany, both famous for their exceptionally well-preserved fossils, are geologic features that were formed during the Jurassic.
What was the impact of the Jurassic period on the Earth?
The Jurassic was a time of significant change in the arrangement of Earth’s continents and oceans. During this period the supercontinent Pangea split apart. That allowed for the eventual development of what are now the central Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico. Increased plate tectonic movement led to significant volcanic activity and mountain building. As the continents separated, sea levels rose. Shallow inland seas formed in the separated landmasses.
What animals were found in the Jurassic period?
By the mid-Jurassic the seafloor teemed with coral-reef builders and, especially, mollusks. Both shelled ammonoids and squidlike belemnoids with internal skeletons were very common, as were bivalves (such as scallops and oysters) and snails.
What is the effect of carbon dioxide on the climate during the Jurassic period?
Analyses of oxygen isotopes in marine fossils suggest that Jurassic global temperatures were generally quite warm. Some evidence suggests that increased volcanic and seafloor-spreading activity during the Jurassic released large amounts of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. The higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere would have led to higher global temperatures. Temperatures increased across the period, with the warmest temperatures occurring in the late Jurassic. That was followed by a cooling trend, with a distinct drop in temperatures at the close of the period.
What were the dominant plants in the early Jurassic period?
On land a new set of plants had become dominant by the early Jurassic. Gymnosperms (“naked-seed” plants) replaced the seed ferns that had dominated older ecosystems. Cycads and ginkgoes were especially prominent. By the late Jurassic almost all the modern forms of conifers had evolved.
What was the name of the event that followed the end of the Triassic era?
The Jurassic Period followed the end-Triassic extinction, one of the five largest mass extinctions in Earth’s history. Roughly half of the major marine invertebrate groups went extinct during the event. It is unclear whether land plants and terrestrial vertebrates suffered a similar extinction at that time.
Did the Jurassic Period end with mass extinction?
Unlike many other major geologic periods, the Jurassic Period did not end with a mass extinction event or a burst of diversity. Some prominent species became extinct before the period ended, including Stegosaurus. However, the distinction between the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods is marked more by several key differences in life-forms, such as the appearance of angiosperms (flowering plants) in the Cretaceous, than by dramatic changes in the environment.
What is a polished slab of dinosaur bone?
polished slab of dinosaur bone. chunk of dinosaur bone. Gastroliths, stones used by dinosaurs to help grind their food. Both dinosaurs and birds, their modern descendants, used a crop filled with stones to help break down their food into small particles to aid digestion. Gastroliths.
What is the name of the dinosaur that has a skull?
Dinosaurs (Dinosauria [Birds and Dinosaurs]<Reptilia) Of the two major dinosaur groups, the ornithicians are represented by a skull cast (a Hypsilophodont Othniella rex also known as “ Nannosaurus rex ”). Othniella rex life reconstruction.
What were the arthopods in the Permian extinction?
Although the trilobites had vanished in the Permian extinction event, the arthopods were well represented in the oceans by crustaceans. These included shrimp, lobsters, and crabs such as Eryon.
What were the plants that covered much of the land?
Forests covered much of the land, with trees such as conifers, gingko, and an under story of plants such as ferns, cycads and horsetail rushes. Flowering plants had yet to evolve and there were no grasses so the open plains of modern Earth did not exist making it a very different world than today.
What animals were found in the Jurassic?
Jurassic* ammonites and dinosaurs made a huge comeback after their near extinction at the end of the Triassic. Oysters, crabs, lobsters, and teleost (modern) fish appear . Plesiosaurs and marine crocodiles first appeared, joining icthyosaurs, sharks, bony fish, cephalopods and many other marine predators. Reef ecosystems built on coral and sponge backbones flourished, providing homes for gastropods and the remaining lower numbers of the declining members of the Paleozoic fauna such as brachiopods and sea lilies. Reptiles remain the dominant land animals even after their massive losses to extinction at the end of the Triassic. Dinosaurs grow larger, with the largest saurichians appearing in the Upper Jurassic. The other main dinosaur group, the ornithicians, makes their first appearance in the Jurassic. The first birds show up in the fossil record, but flying pterosaurs of all sizes rule the air. Theropod dinosaurs, which gave rise to birds, continue to evolve in parallel—both groups are covered in colorful feathers. Insect diversify, evolving many modern forms such as wasps and beetles. The first lizards appear, probably feeding on the new insect diversity. Conifers dominate coal-producing forests. Forests covered much of the land, with trees such as conifers, gingko, and an under story of plants such as ferns, cycads and horsetail rushes. Flowering plants had yet to evolve and there were no grasses so the open plains of modern Earth did not exist making it a very different world than today.
What are the major tectonic elements?
These maps of major tectonic elements (plates, oceans, ridges, subduction zones, mountain belts ) are used with permission from Dr. Ron Blakey at Northern Arizona University. The positions of mid-ocean ridges before 200 Ma are speculative. Explanation of map symbols.
How long is the neck of an Othniella Rex?
This dinosaur had the longest neck (about 41 ft) of known dinosaurs, to give a animal with a total length of 70–80 ft.
How long ago was the Jurassic period?
Please be respectful of copyright. Unauthorized use is prohibited. <p>The Jurassic period (199.6 million to 145.5 million years ago) was characterized by a warm, wet climate that gave rise to lush vegetation and abundant life. Many new dinosaurs emerged—in great numbers.
What was the Jurassic period?
The Jurassic period (199.6 million to 145.5 million years ago) was characterized by a warm, wet climate that gave rise to lush vegetation and abundant life. Many new dinosaurs emerged—in great numbers. Among them were stegosaurs, brachiosaurs, allosaurs, and many others. Artwork by Publiphoto/Photo Researchers Inc. Science.
How long was Diplodocus?
Diplodocus, another sauropod, was 90 feet (27 meters) long. These dinosaurs' sheer size may have deterred attack from Allosaurus, a bulky, meat-eating dinosaur that walked on two powerful legs. But Allosaurus and other fleet-footed carnivores, such as the coelurosaurs, must have had occasional success.
What was the climate like during the Jurassic period?
Jurassic Period. During this period, Earth's climate changed from hot and dry to humid and subtropical. Dinosaurs, birds, and rodents. Crumbling landmasses and inland seas. Sea monsters, sharks, and blood-red plankton. Forests of ferns, cycads, and conifers. Warm, moist, tropical breezes.
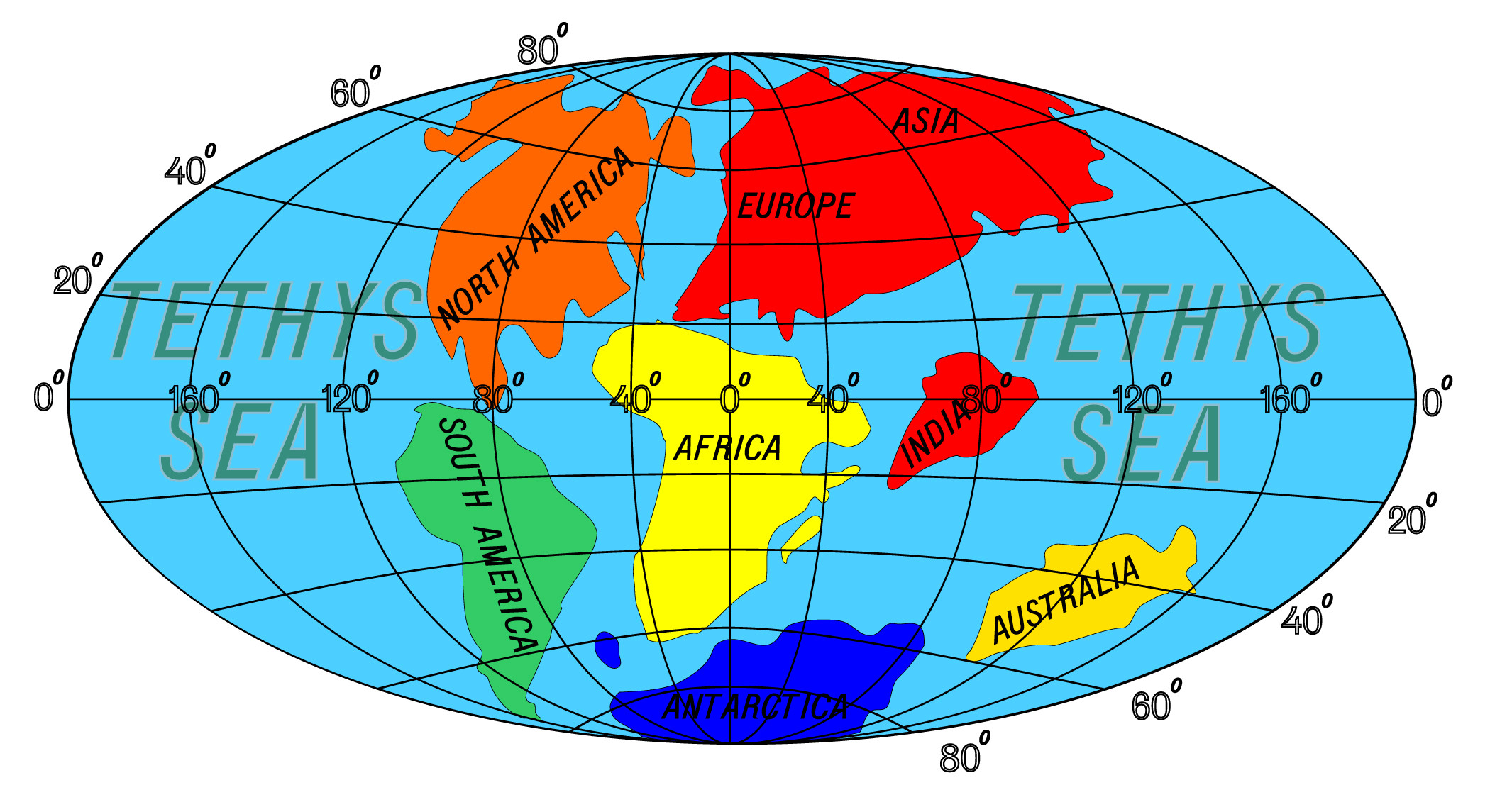
Which continents split from the western half of the world?
The eastern portion—Antarctica, Madagascar, India, and Australia —split from the western half, Africa and South America. New oceans flooded the spaces in between. Mountains rose on the seafloor, pushing sea levels higher and onto the continents.
Which supercontinent broke up into North America and Eurasia?
At the start of the period, the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea continued and accelerated. Laurasia, the northern half, broke up into North America and Eurasia. Gondwana, the southern half, began to break up by the mid-Jurassic.
How big are dinosaurs?
On land, dinosaurs were making their mark in a big way—literally. The plant-eating sauropod Brachiosaurus stood up to 52 feet (16 meters) tall, stretched some 85 feet (26 meters) long, and weighed more than 80 tons. Diplodocus, another sauropod, was 90 feet (27 meters) long. These dinosaurs' sheer size may have deterred attack from Allosaurus, a bulky, meat-eating dinosaur that walked on two powerful legs. But Allosaurus and other fleet-footed carnivores, such as the coelurosaurs, must have had occasional success. Other prey included the heavily armored stegosaurs.
What dinosaurs were extinct during the Jurassic Period?
Sources. The Jurassic Period ended with a minor extinction that included stegosaurid and sauropod dinosaurs and some ammonoids, marine reptiles, and bivalves. No one knows for sure what caused this extinction but scienctists have three ideas of what might have happened.
What type of eruptions have lasted for many years?
The first possibility is a flood basalt eruption, large scale volcanic activity. These type of eruptions may have lasted for many years and lava could have traveled many miles. This could have occurred on land or on the ocean floor.
Is the Earth's climate always the same?
Earth's climate has not always been the same. The Earth has gone through ice ages and extremely hot times. This could have happened at the end of the Jurassic Period. The last theory is meteor crashes on earth. Meteor can cause massive shock waves and debris all around the Earth.

Overview
The Jurassic is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period 201.3 million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 145 Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified.
The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associate…
Etymology and history
The chronostratigraphic term "Jurassic" is linked to the Jura Mountains, a forested mountain range that mainly follows the France–Switzerland border. The name "Jura" is derived from the Celtic root *jor via Gaulish *iuris "wooded mountain", which was borrowed into Latin as a name of a place and evolved into Juria and finally Jura.
During a tour of the region in 1795, German naturalist Alexander von Humboldt recognized carbon…
Geology
The Jurassic Period is divided into three epochs: Early, Middle, and Late. Similarly, in stratigraphy, the Jurassic is divided into the Lower Jurassic, Middle Jurassic, and Upper Jurassic series. Geologists divide the rocks of the Jurassic into a stratigraphic set of units called stages, each formed during corresponding time intervals called ages.
Paleogeography and tectonics
At the beginning of the Jurassic, all of the world's major landmasses were coalesced into the supercontinent Pangaea, which during the Early Jurassic began to break up into northern supercontinent Laurasia and the southern supercontinent Gondwana. The rifting between North America and Africa was the first to initiate, beginning in the early Jurassic, associated with the emplac…
Climate
The climate of the Jurassic was generally warmer than that of present, by around 5 °C to 10 °C, with atmospheric carbon dioxide likely four times higher. Forests likely grew near the poles, where they experienced warm summers and cold, sometimes snowy winters; there were unlikely to have been ice sheets given the high summer temperatures that prevented the accumulation of snow, though there may have been mountain glaciers. Dropstones and glendonites in northeastern Siberi…
Flora
There is no evidence of a mass extinction of plants at the Triassic–Jurassic boundary. At the Triassic–Jurassic boundary in Greenland, the sporomorph (pollen and spores) record suggests a complete floral turnover. An analysis of macrofossil floral communities in Europe suggests that changes were mainly due to local ecological succession. At the end of the Triassic, the Peltaspermac…
Fauna
The Triassic–Jurassic extinction decimated pseudosuchian diversity, with crocodylomorphs, which originated during the early Late Triassic, being the only group of pseudosuchians to survive, with all others, including the herbivorous aetosaurs and carnivorous "rauisuchians" becoming extinct. The morphological diversity of crocodylomorphs during the Early Jurassic was around the same a…
External links
• Examples of Jurassic Fossils
• Jurassic (chronostratigraphy scale)
• Jurassic fossils in Harbury, Warwickshire
• Jurassic Microfossils: 65+ images of Foraminifera