What happens when you go down on the periodic table?
When going down a group in the periodic table the ionization energy decreases, increasing the atomic radius and makes it easier to pull away from the atom/nucleus. When going down a group the smaller atomic radii will be at the top of the group and the larger atomic radii will be at the bottom.
What year did Henry Moseley create the current periodic table?
Using atomic number instead of atomic mass as the organizing principle was first proposed by the British chemist Henry Moseley in 1913, and it solved anomalies like this one. What did Mendeleev contribute to the periodic table?
What year did Mendeleev create the periodic table?
Dmitri Mendeleev & the Periodic Table
- Dmitri Medeleev Biography. Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev was born on February 8th, 1834, in the Russian province of Siberia. ...
- Mendeleev's Contribution to the Periodic Table. In 1869, Mendeleev contributed to the world of periodic tables by creating his version of the periodic table listing the most known elements at ...
- The Mendeleev Periodic Table. ...
How did they make the periodic table?
The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869: he formulated the periodic law as a dependence of chemical properties on atomic mass. Because not all elements were then known, there were gaps in his periodic table, and Mendeleev successfully used the periodic law to predict properties of some of the missing elements.

When was the 1st periodic table made?
1869In 1869, Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev created the framework that became the modern periodic table, leaving gaps for elements that were yet to be discovered.
Who created the 1st periodic table?
Dmitri MendeleevAlbert GhiorsoPeriodic table/Inventors
How the periodic table was created?
In 1863 English chemist John Newlands divided the then discovered 56 elements into 11 groups, based on characteristics. In 1869 Russian chemist Dimitri Mendeleev started the development of the periodic table, arranging chemical elements by atomic mass.
What year was the periodic table finished?
1869Yet historians typically consider one event as marking the formal birth of the modern periodic table: on February 17, 1869, a Russian professor of chemistry, Dimitri Ivanovich Mendeleev, completed the first of his numerous periodic charts.
Who invented 118 elements?
Oganesson is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Og and atomic number 118. It was first synthesized in 2002 at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) in Dubna, near Moscow, Russia, by a joint team of Russian and American scientists.
Why is it called the periodic table?
Why is the periodic table called the periodic table? It is called the periodic table because of the way the elements are arranged. You'll notice they're in rows and columns. The horizontal rows (which go from left to right) are called 'periods' and the vertical columns (going from up to down) are called 'groups'.
What is the oldest element?
PhosphorusThe oldest chemical element is Phosphorus and the newest element is Hassium. Please note that the elements do not show their natural relation towards each other as in the Periodic system.
Who discovered all the elements?
John Newlands, an English chemist, wrote a paper in 1863 which classified the 56 established elements into 11 groups based on similar physical properties, noting that many pairs of similar elements existed which differed by some multiple of eight in atomic weight.
WHO classified elements first?
-The first attempt to classify elements systematically was made by Dobereiner. -In 1817, Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner's observations of the alkaline earths, namely that of strontium had properties that were immediate to those of calcium and barium.
Is the periodic table final?
The periodic table could be considered to end at the largest stable element, lead (atomic number 82). All elements with higher atomic numbers have unstable nuclei, because the assembled protons become too large for the strong nuclear force to hold together.
What was the last element ever discovered?
Element 118, the final element in our International Year of the Periodic Table series, is oganesson. Oganesson was discovered in 2002 and its properties defy our expectations based on trends in the periodic table.
When were the last elements named?
The periodic table was last updated in 2016 with four new chemical elements. What is a chemical element? What is the atomic structure of the newest chemical elements? How did they get their names?
Why is the periodic table not finished?
Though scientists have discovered the elements up to number 118, no one can be sure of whether or not there are remaining elements to add to the periodic table. In modern science, elements are measured by weight, and it's believed that there's a maximum atomic number or atomic weight possible for atoms.
What happened to the periodic table in 1864?
In 1864, with about 50 elements known, the British chemist John Newlands noticed a pattern when he arranged the elements in order of atomic mass, or weight. He found that the properties of the elements seemed to repeat every eighth element. He called this the Law of Octaves, comparing it to musical scales.
Has the periodic table changed since 1869?
Since its conception by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, the periodic table has grown and evolved.
Who made the final periodic table?
Dmitri MendeleevAlbert GhiorsoPeriodic table/Inventors
Who published the periodic table?
Main table of the periodic table published by Australian chemist David Orme Masson in 1895
Who added elements to the periodic table?
Mendeleev himself added these elements to the table as group 0 in 1902, without disturbing the basic concept of the periodic table. In 1905, Swiss chemist Alfred Werner resolved the dead zone of Mendeleev 's table. He determined that the rare-earth elements ( lanthanides ), 13 of which were known, lay within that gap.
What did Mendeleev think of the elements?
Mendeleev noticed that there was a significant difference in atomic mass between cerium and tantalum with no element between them; his consideration was that between them, there was a row of yet undiscovered elements, which would display similar properties to those elements which were to be found above and below them: for instance, an eka-molybdenum would behave as a heavier homolog of molybdenum and a lighter homolog of wolfram (the name under which Mendeleev knew tungsten ). This row would begin with a trivalent lanthanum, a tetravalent cerium, and a pentavalent didymium. However, the higher valency for didymium had not been established, and Mendeleev tried to do that himself. Having had no success in that, he abandoned his attempts to incorporate the rare-earth metals in late 1871 and embarked on his grand idea of luminiferous ether. His idea was carried on by Austrian-Hungarian chemist Bohuslav Brauner, who sought to find a place in the periodic table for the rare-earth metals; Mendeleev later referred to him as to "one of the true consolidators of the periodic law".
What elements did Mendeleev predict?
In 1870, he first tried to characterize the yet undiscovered elements, and he gave detailed predictions for three elements, which he termed eka-boron, eka-aluminium, and eka-silicium, as well as more briefly noted a few other expectations. It has been proposed that the prefixes eka, dvi, and tri, Sanskrit for one, two, and three, respectively, are a tribute to Pāṇini and other ancient Sanskrit grammar ians for their invention of a periodic alphabet. In 1871, Mendeleev expanded his predictions further.
What are the four elements that are considered elements?
The four roots, which were later renamed as elements by Plato, were earth, water, air and fire. Similar ideas about these four elements also existed in other ancient traditions, such as Indian philosophy . A few extra elements were known in the age of alchemy ( zinc, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth ).
What are the elements that are found in ancient times?
Early history. Further information: Classical element. A number of physical elements ( carbon, sulfur, iron, copper, silver, tin, gold, mercury, and lead) have been known from antiquity, as they are found in their native form and are relatively simple to mine with primitive tools.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is an arrangement of the chemical elements, structured by their atomic number, electron configuration and recurring chemical properties. In the basic form, elements are presented in order of increasing atomic number, in the reading sequence.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table of elements is a common sight in classrooms, campus hallways and libraries, but it is more than a tabular organization of pure substances . Scientists can use the table to analyze reactivity among elements, predict chemical reactions, understand trends in periodic properties among different elements and speculate on ...
What is the periodic table of chemical elements?
On its website marking the celebration, UNESCO wrote, “The Periodic Table of Chemical Elements is more than just a guide or catalogue of the entire known atoms in the universe; it is essentially a window on the universe, helping to expand our understanding of the world around us.”.
What elements did Mendeleev predict?
The later discovery of elements predicted by Mendeleev, including gallium (1875), scandium (1879) and germanium (1886), verified his predictions and his periodic table won universal recognition. In 1955 the 101st element was named mendelevium in his honor. The 1869 periodic table by Mendeleev in Russian, with a title that translates "An experiment ...
Why is the periodic table important?
The periodic table provides information about the atomic structure of the elements and the chemical similarities or dissimilarities between them. Scientists use the table to study chemicals and design experiments. It is used to develop chemicals used in the pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries and batteries used in technological devices.
What are the horizontal rows in the periodic table called?
In the periodic table, the horizontal rows are called periods, with metals in the extreme left and nonmetals on the right. The vertical columns, called groups, consist of elements with similar chemical properties. The periodic table provides information about the atomic structure of the elements and the chemical similarities or dissimilarities ...
Why is the periodic table celebrated in 2019?
UNESCO named 2019 the International Year of the Periodic Table to mark the 150 th anniversary of Mendeleev’s publication. Researchers and teachers worldwide took this opportunity to reflect on the importance of the periodic table and spread awareness about it in classrooms and beyond.
Who was the first to arrange the elements into a periodic table with increasing order of atomic masses?
Dmitri Mendeleev. Lothar Meyer. British chemist John Newlands was the first to arrange the elements into a periodic table with increasing order of atomic masses. He found that every eight elements had similar properties and called this the law of octaves.
When was the periodic table first discovered?
It was not until a more accurate list of the atomic mass of the elements became available at a conference in Karlsruhe, Germany in 1860 that real progress was made towards the discovery of the modern periodic table.
Who discovered the periodic table?
Ask most chemists who discovered the periodic table and you will almost certainly get the answer Dmitri Mendeleev. Certainly Mendeleev was the first to publish a version of the table that we would recognise today, but does he deserve all the credit?#N#A number of other chemists before Mendeleev were investigating patterns in the properties of the elements that were known at the time. The earliest attempt to classify the elements was in 1789, when Antoine Lavoisier grouped the elements based on their properties into gases, non-metals, metals and earths. Several other attempts were made to group elements together over the coming decades. In 1829, Johann Döbereiner recognised triads of elements with chemically similar properties, such as lithium, sodium and potassium, and showed that the properties of the middle element could be predicted from the properties of the other two.#N#It was not until a more accurate list of the atomic mass of the elements became available at a conference in Karlsruhe, Germany in 1860 that real progress was made towards the discovery of the modern periodic table.#N#This area of the website celebrates the work of many famous scientists whose quest to learn more about the world we live in and the atoms that make up the things around us led to the periodic table as we know it today.
What did Newlands discover about the periodic table?
Just four years before Mendeleev announced his periodic table, Newlands noticed that there were similarities between elements with atomic weights that differed by seven. He called this The Law of Octaves, drawing a comparison with the octaves of music.
What is the name of the three-dimensional arrangement of the elements that is used to determine the atomic weights of?
His principal contribution to chemistry was the 'vis tellurique' (telluric screw), a three-dimensional arrangement of the elements constituting an early form of the periodic classification, published in 1862. The telluric screw plotted the atomic weights of the elements on the outside of a cylinder, so that one complete turn corresponded ...
How is the periodic table arranged?
It wasn’t until 1913, six years after Mendeleev’s death that the final piece of the puzzle fell into place. The periodic table was arranged by atomic mass, and this nearly always gives the same order as the atomic number. However, there were some exceptions (like iodine and tellurium, see above), which didn’t work. Mendeleev had seen that they needed to be swapped around, but it was Moseley that finally determined why.
Which scientist used a periodic arrangement of all known elements?
Although the telluric screw did not correctly display all the trends that were known at the time, de Chancourtois was the first to use a periodic arrangement of all of the known elements, showing that similar elements appear at periodic atom weights.
When was the first attempt to classify elements?
The earliest attempt to classify the elements was in 1789, when Antoine Lavoisier grouped the elements based on their properties into gases, non-metals, metals and earths. Several other attempts were made ...
Who discovered the periodic system?
Important forward steps were the formulation of the general rules of the old quantum theory by William Wilson and Arnold Sommerfeld in 1916, the discovery of the exclusion principle by Wolfgang Pauli in 1925, the discovery of the spin of the electron by George E. Uhlenbeck and Samuel Goudsmit in 1925, and the development of quantum mechanics by Werner Heisenberg and Erwin Schrödinger during the same year. The development of the electronic theory of valence and molecular structure, beginning with the postulate of the shared electron pair by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1916, also played a very important part in explaining the periodic law ( see chemical bonding ).
How many elements are in the periodic table?
Based on an earlier (1882) model of T. Bayley, J. Thomsen in 1895 devised a new table. This was interpreted in terms of the electronic structure of atoms by Niels Bohr in 1922. In this table there are periods of increasing length between the noble gases; the table thus contains a period of 2 elements, two of 8 elements, two of 18 elements, one of 32 elements, and an incomplete period. The elements in each period may be connected by tie lines with one or more elements in the following period. The principal disadvantage of this table is the large space required by the period of 32 elements and the difficulty of tracing a sequence of closely similar elements. A useful compromise is to compress the period of 32 elements into 18 spaces by listing the 14 lanthanoids (also called lanthanides) and the 14 actinoids (also called actinides) in a special double row below the other periods.
What is the long period form of the periodic system?
Long-period form of periodic system of elements. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. With the discovery of the noble gases helium, neon, argon, krypton, radon, and xenon by Lord Rayleigh (John William Strutt) and Sir William Ramsay in 1894 and the following years, Mendeleyev and others proposed that a new “zero” group to accommodate them be added to ...
What elements did Mendeleyev predict?
Mendeleyev was also able to predict the existence, and many of the properties, of the then undiscovered elements eka-boron, eka-aluminum, and eka-silicon, now identified with the elements scandium, gallium, and germanium, respectively. Similarly, after the discovery of helium and argon, the periodic law permitted the prediction of the existence ...
How does the atomic weight of an element show its position in the periodic system?
That the exact atomic weight of an element is of small significance for its position in the periodic system is shown by the existence of isotopes of every element —atoms with the same atomic number but different atomic weights. The chemical properties of the isotopes of an element are essentially the same, and all the isotopes of an element occupy the same place in the periodic system in spite of their differences in atomic weight.
Which elements were put in positions out of the order of atomic weights?
In the pairs argon and potassium, cobalt and nickel, and tellurium and iodine, for example, the first element had the greater atomic weight but the earlier position in the periodic system. The solution to this difficulty was found only when the structure of the atom was better understood.
How many spaces are there in a period of 32?
A useful compromise is to compress the period of 32 elements into 18 spaces by listing the 14 lanthanoids (also called lanthanides) and the 14 actinoids (also called actinides) in a special double row below the other periods.
When did the periodic table start?
I’ll tell you the complete History of Periodic table starting from 1789 to 1913.
Who invented the periodic table?
But it was the combined efforts of many chemists for the invention of Periodic table. The chemists who invented Periodic table are listed below. Antoine Lavoisier (1789) Johann Dobereiner (1829) Alexandre Beguyer de Chancourtois (1862) ...
Why Periodic table was invented?
The Periodic table was invented in order to classify all the known elements according to the similarities in their properties.
How did Johann Dobereiner classify the elements?
He classified the known elements by knowing their properties. After few years of this classification, several attempts were also made by other chemists. But some important work was given by Johann Dobereiner after few years. Let us see how Johann Dobereiner contributed to the development of Periodic table.
What did the king prepare for each known element?
He prepared the cards of each known element with their properties and details written on them.
How many elements are there in the universe?
Till today there are total 118 known elements like hydrogen, helium, lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, and so on…
Who was the first person to publish the periodic table?
Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) Henry Moseley (1913) And many more…. Many of you might think that Mendeleev was the person who discovered the Periodic table. But this is not completely true. Yes, he was the first to publish the Periodic table with 63 elements which were discovered during his time.
When was the periodic table updated?
The online version of the Periodic Table has been updated to the most recent printed version, which is dated September 2010. There was also a September 2009 version. Since version 4, elements have been added such that there are no "missing elements" from 1 to 118. Several official names have been added for high Z elements.
What is the atomic weight of ytterbium?
Redesign of the Periodic Table. Several numerical values have been updated. The standard atomic weight of ytterbium has been revised from 173.054 to 173.045. The values of the fundamental physical constants have been updated to the 2014 CODATA recommended values. For elements 103, 107, 108, 109, 111, 113, 115, the mass number of the longest-lived isotope has been updated.
What is the periodic table?
periodic table, in full periodic table of the elements, in chemistry, the organized array of all the chemical elements in order of increasing atomic number —i.e., the total number of protons in the atomic nucleus. When the chemical elements are thus arranged, there is a recurring pattern called the “periodic law” in their properties, ...
Who proposed the periodic law?
Then in 1869, as a result of an extensive correlation of the properties and the atomic weights of the elements, with special attention to valency (that is, the number of single bonds the element can form), Mendeleyev proposed the periodic law, by which “the elements arranged according to the magnitude of atomic weights show a periodic change of properties.” Lothar Meyer had independently reached a similar conclusion, published after the appearance of Mendeleyev ’s paper.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element . Hydrogen has 1 proton, and oganesson has ...
What elements are triads?
Döbereiner in 1817 showed that the combining weight, meaning atomic weight, of strontium lies midway between those of calcium and barium, and some years later he showed that other such “ triads ” exist (chlorine, bromine, and iodine [halogens] and lithium, sodium, and potassium [alkali metals]). J.-B.-A. Dumas, L. Gmelin, E. Lenssen, Max von Pettenkofer, and J.P. Cooke expanded Döbereiner’s suggestions between 1827 and 1858 by showing that similar relationships extended further than the triads of elements, fluorine being added to the halogens and magnesium to the alkaline-earth metals, while oxygen, sulfur, selenium, and tellurium were classed as one family and nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth as another family of elements.
Why do the elements in the periodic table have different orbits?
The arrangement of the elements in the periodic table comes from the electronic configuration of the elements. Because of the Pauli exclusion principle, no more than two electrons can fill the same orbital. The first row of the periodic table consists of just two elements, hydrogen and helium. As atoms have more electrons, they have more orbits available to fill, and thus the rows contain more elements farther down in the table.
What are the elements that are related to the first seven?
Newlands proposed classifying the elements in the order of increasing atomic weights, the elements being assigned ordinal numbers from unity upward and divided into seven groups having properties closely related to the first seven of the elements then known: hydrogen, lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen . This relationship was termed the law of octaves, by analogy with the seven intervals of the musical scale.
What was the first major development in the 19th century?
The early years of the 19th century witnessed a rapid development in analytical chemistry—the art of distinguishing different chemical substances —and the consequent building up of a vast body of knowledge of the chemical and physical properties of both elements and compounds.
Who invented the periodic table?
In the year 1869, a Russian chemist Dimitri Mendeleev started to develop the periodic table by arranging the chemical elements by atomic mass. He predicted the discovery of several other elements and left spaces open in his periodic table for them to accommodate. He is the one who invented the first periodic table and is the periodic table founder.
Who discovered the modern periodic table?
However, as the development of the periodic table was gradually done, the modern periodic table was discovered by Henry Moseley. Share this with your friends.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table refers to an arrangement of the chemical elements that are organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, their electron configurations and their recurring chemical properties. Elements are presented in the periodic table in the order of the increasing atomic number. The standard form of the table contains a grid ...
What was the actual development of the periodic table?
The actual development in the periodic table happened after the development of Mendeleev’s periodic table. He introduced a law which stated that the properties of a given element are the periodic function of their atomic masses. He then arranged elements in periods or horizontal rows and groups or vertical columns in the increasing order according ...
What is the symbol of chemistry?
The periodic table is for many people the symbol of chemistry. It is a single image in a tabular form which contains all the known elements in the universe that are combined into an easily readable table. There are many different patterns present in the table as well. All of these elements seem to fit together and connect to each other to form a readable table and, in turn, the image of chemistry. The thought of elements first came around in 3000 B.C. The Greek philosopher Aristotle had an idea that everything on the Earth was made up of these elements. In the ancient times, elements like gold and silver were easily accessible, however, the elements which Aristotle chose were Earth, Water, Fire, and Air.
How are elements arranged in order?
According to him, the elements can be arranged in an ascending order according to their atomic weights. He also admitted that in this arrangement every eighth element in a row had the same properties to that of the first element of the same row, which depicts the octaves of music.
What elements did Aristotle choose?
In the ancient times, elements like gold and silver were easily accessible, however, the elements which Aristotle chose were Earth, Water, Fire, and Air.
Who invented the periodic table?
Most people think Mendeleev invented the modern periodic table. Dmitri Mendeleev presented his periodic table of the elements based on increasing atomic weight on March 6, 1869, in a presentation to the Russian Chemical Society.
Who published the first periodic table?
A year earlier (1864) Lothar Meyer published a periodic table that described the placement of 28 elements. Meyer's periodic table ordered the elements into groups arranged in order of their atomic weights. His periodic table arranged the elements into six families according to their valence, which was the first attempt to classify the elements according to this property.
How did Mendeleev and De Chancourtois organize elements?
Both de Chancourtois and Mendeleev organized elements by increasing atomic weight. This makes sense because the structure of the atom was not understood at the time, so the concepts of protons and isotopes had yet to be described.
How is the periodic table arranged?
While Mendeleev and Chancourtois arranged elements by atomic weight, the modern periodic table is ordered according to increasing atomic number (a concept unknown in the 19th century.)
How does the periodic table order the elements?
The modern periodic table orders the elements according to increasing atomic number rather than increasing atomic weight. For the most part, this doesn't change the order of the elements, but it's an important distinction between older and modern tables.
When did Chancourtois publish his arrangement of elements?
In 1862 (five years before Mendeleev), de Chancourtois presented a paper describing his arrangement of the elements to the French Academy of Sciences. The paper was published in the Academy's journal, Comptes Rendus, but without the actual table.
What elements were discovered in Mendeleev's table?
Some elements were known since ancient times, such as gold, sulfur, and carbon. Alchemists began to discover and identify new elements in the 17th century.
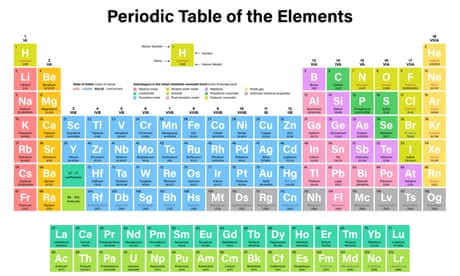
Overview
The periodic table is an arrangement of the chemical elements, structured by their atomic number, electron configuration and recurring chemical properties. In the basic form, elements are presented in order of increasing atomic number, in the reading sequence. Then, rows and columns are created by starting new rows and inserting blank cells, so that rows (periods) and columns (groups) s…
Early history
A number of chemical elements, such as carbon, sulfur, iron, copper, silver, tin, gold, mercury, and lead, have been known since before antiquity, as they are found in their native form and are relatively simple to mine with primitive tools. Around 330 BCE, the Greek philosopher Aristotle proposed that everything is made up of a mixture of one or more roots, an idea originally suggested by the Sicilian philosopher Empedocles. The four roots, which the Athenian philosopher Plato called ele…
First categorizations
The history of the periodic table is also a history of the discovery of the chemical elements. The first person in recorded history to discover a new element was Hennig Brand, a bankrupt German merchant. Brand tried to discover the philosopher's stone—a mythical object that was supposed to turn inexpensive base metals into gold. In 1669, or later, his experiments with distilled human urine resulted …
Comprehensive formalizations
Properties of the elements, and thus properties of light and heavy bodies formed by them, are in a periodic dependence on their atomic weight.— Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev, formulating the periodic law for the first time in his 1871 article "Periodic regularity of the chemical elements"
French geologist Alexandre-Émile Béguyer de Chancourtois noticed that the ele…
Priority dispute and recognition
That person is rightly regarded as the creator of a particular scientific idea who perceives not merely its philosophical, but its real aspect, and who understands so to illustrate the matter so that everyone can become convinced of its truth. Then alone the idea, like matter, becomes indestructible.— Mendeleev in his 1881 article in British journal Chemical News in a correspondence debate with Meyer over priority of the periodic table invention
Inert gases and ether
The great value of Newland's, Mendeleef's, and Lothar Meyer's generalisation, known as the periodic arrangement of the elements, is universally acknowledged. But a study of this arrangement, it must be allowed, is a somewhat tantalising pleasure; for, although the properties of elements do undoubtedly vary qualitatively, and, indeed, show approximate quantitative rela…
Atomic theory and isotopes
In 1907 it was discovered that thorium and radiothorium, products of radioactive decay, were physically different but chemically identical; this led Frederick Soddy to propose in 1910 that they were the same element but with different atomic weights. Soddy later proposed to call these elements with complete chemical identity “isotopes“.
Later expansions and the end of the periodic table
We already feel that we have neared the moment when this [periodic] law begins to change, and change fast.— Russian physicist Yuri Oganessian, co-discoverer of several superheavy elements, in 2019
As early as 1913, Bohr's research on electronic structure led physicists such as Johannes Rydberg to extrapolate the properties of undiscovered elements heavier than uranium. Many agreed that …