The Triassic (/ traɪˈæs.ɪk / try-ASS-ik) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period
Permian
The Permian is a geologic period and system which extends from 298.9 to 252.17 million years ago. It is the last period of the Paleozoic, following the Carboniferous and preceding the Triassic of the Mesozoic. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the ancient kingdom of Permia.
Jurassic
The Jurassic period is a geologic period and system that spanned 56 million years from the end of the Triassic Period 201.3 million years ago to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period 145 Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic Era, also known as the Age of Reptiles. The start of the period was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. Two other extinction events occ…
Full Answer
When was the Proterozoic era start and end?
The Proterozoic Eon. The period of Earth's history that began 2.5 billion years ago and ended 542.0 million years ago is known as the Proterozoic, which is subdivided into three eras: the Paleoproterozoic (2.5 to 1.6 billion years ago), Mesoproterozoic (1.6 to 1 billion years ago), and Neoproterozoic (1 billion to 542.0 million years ago).*.
When did the Triassic extinction start?
The Triassic-Jurassic Extinction. The Triassic-Jurassic extinction event was the fourth major global extinction of the Phanerozoic eon. The event occurred around 201 million years ago at the end of the Triassic Period (a period that lasted from 252-201 million years ago).
What caused the Jurassic period to end?
What caused the end of the Jurassic period? The cause of the end-Triassic extinction is a matter of considerable debate. Many scientists contend that this event was caused by climate change and rising sea levels resulting from the sudden release of large amounts of carbon dioxide.
When did the Silurian Period End and began?
Silurian Period, in geologic time, the third period of the Paleozoic Era. It began 443.8 million years ago and ended 419.2 million years ago, extending from the close of the Ordovician Period to the beginning of the Devonian Period. During the Silurian, continental elevations were generally much
What was the Triassic period?
What was the most important event of the Triassic period?
What are the islands that are located within 30° of the Triassic equator?
What was the result of the Triassic extinction?
What were the major changes that occurred during the Triassic period?
What happened at the end of the Permian?
What was the climate during the Triassic period?
See 4 more
About this website
Triassic Period—251.9 to 201.3 MYA - National Park Service
Triassic age trace fossil of a horseshoe crab (Kouphichnium isp.), Petrified Forest National Park, Arizona.NPS image. Introduction. In 1834 Fredrich von Alberti, a longtime official in the German salt-mining industry, introduced “Triassic” as a descriptive term for a sequence of rocks within a striking threefold division: red beds, topped by chalk, followed by black shale.
Where is the Triassic?
The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek triás meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone), the middle Muschelkalk (shell-bearing limestone) and the upper Keuper (coloured clay).
How high was the sea level in the Triassic period?
The beginning of the Triassic was around present sea level, rising to about 10–20 m above sea level during the Early and Middle Triassic. Beginning in the Ladinan, the sea level began to rise, culminating with the sea level being up to 50 metres above present during the Carnian.
What was the climate like during the Triassic period?
The global climate during the Triassic was mostly hot and dry, with deserts spanning much of Pangaea's interior. However, the climate shifted and became more humid as Pangaea began to drift apart. The end of the period was marked by yet another major mass extinction, the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, that wiped out many groups and allowed dinosaurs to assume dominance in the Jurassic.
What is the shortest period of the Mesozoic era?
The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic , Middle Triassic and Late Triassic .
Why are Triassic deposits rare?
Because a super-continental mass has less shoreline compared to one broken up , Triassic marine deposits are globally relatively rare, despite their prominence in Western Europe, where the Triassic was first studied. In North America, for example, marine deposits are limited to a few exposures in the west.
Which supercontinent was rifting during the Triassic period?
The supercontinent Pangaea was rifting during the Triassic—especially late in that period—but had not yet separated. The first nonmarine sediments in the rift that marks the initial break-up of Pangaea, which separated New Jersey from Morocco, are of Late Triassic age; in the U.S., these thick sediments comprise the Newark Group.
How long did it take for the Permian Triassic extinction to reestablish?
Diverse communities with complex food-web structures took 30 million years to reestablish .
What was the Triassic period?
Triassic Period. Learn about the time period that took place 251 to 199 million years ago. The start of the Triassic period (and the Mesozoic era) was a desolate time in Earth's history. Something—a bout of violent volcanic eruptions, climate change, or perhaps a fatal run-in with a comet or asteroid—had triggered the extinction ...
How long ago did the Triassic extinction occur?
It showed up about 225 million years ago. A few million years later came the 27.5-foot-long (8-meter-long) herbivore called Plateosaurus. The Triassic closed in the same way it began. Something—perhaps a volcanic belch or an asteroid collision—caused another mass extinction.
What supercontinent formed at the end of the Triassic period?
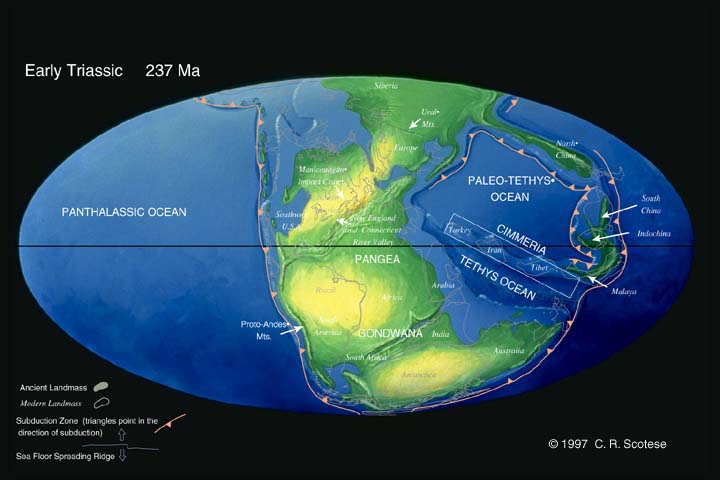
By the start of the Triassic, all the Earth's landmasses had coalesced to form Pangaea , a supercontinent shaped like a giant C that straddled the Equator and extended toward the Poles. Almost as soon as the supercontinent formed, it started to come undone. By the end of the period 199 million years ago, tectonic forces had slowly begun to split the supercontinent in two: Laurasia in the north and Gondwana in the south.
What was the first reptile to go to the sea?
Nothosaurs lived during the mid- and late Triassic period and were among the earliest reptiles to take to the sea. Because nothosaurs may have had to come ashore to lay eggs, the eggs and hatchlings would have been vulnerable to Ticinosuchus. Yet once the hatchlings reached deeper waters, they were safe—for the moment.
What ocean filled the C and was the zipper upon which Pangaea began to split apart?
Even the Poles were ice-free. The Tethys Ocean filled the C and was the zipper upon which Pangaea began to split apart. Earlier failed attempts at the split formed rift valleys in North America and Africa filled with red sediments that today contain the best preserved fossils of Triassic life.
Which two supercontinents split?
By the end of the period 199 million years ago, tectonic forces had slowly begun to split the supercontinent in two: Laurasia in the north and Gondwana in the south. The giant ocean called Panthalassa surrounded Pangaea.
When did dinosaurs evolve?
But perhaps the biggest changes came with the evolution of dinosaurs and the first mammals in the late Triassic, starting around 230 million years ago .
What is the triassic rock?
In 1834 Fredrich von Alberti, a longtime official in the German salt-mining industry, introduced “Triassic” as a descriptive term for a sequence of rocks within a striking threefold division: red beds, topped by chalk, followed by black shale. The term is thus essentially descriptive.
What reptiles were extinct during the Triassic?
Other now-extinct reptiles first appeared during the Triassic: the fish-like ichthyosaurs and plesiosaurs with their long limbs and necks and small heads. On the tectonic side of things, Pangaea began to break apart, a process that continued into the Cenozoic Era.
What continents did Pangaea break up into?
The breakup of Pangaea can be separated into three phases. The first phase formed two resultant continents: Gondwana (South America, Africa, India, Antarctica, and Australia) in the south and Laurasia (North America and Eurasia) in the north. When Pangaea broke up, the re-formed Gondwana continent was not precisely the same as before Pangaea formed; for example, areas that had been part of Gondwana remained attached to North America, such as the land that became Florida.
How did the formation of Pangaea affect the Mesozoic era?
Pangaea began to break apart during the Triassic but dispersed mostly during the Jurassic. Just as the formation of Pangaea influenced geologic and biologic events during the Paleozoic Era, the breakup of this supercontinent profoundly affected geologic and biologic events during the Mesozoic Era. The movement of continents affected ocean circulation and climatic regimes. Populations became isolated and were brought into contact with other populations, leading to evolutionary changes in the biota.
What caused the movement of the two continents?
Seafloor spreading at divergent plate boundaries along the mid-ocean ridge of the Tethys Ocean, the body of water between Gondwana and Laurasia, caused the movement of the two continents. Moreover, rifting separated North America (part of Laurasia) and Africa (part of Gondwana), which were sutured together at the time, initiating the opening of the Atlantic Ocean, continuing westward into the Gulf of Mexico. The rifting was accompanied by igneous activity along the new margins, producing features like the Palisades of New Jersey and New York. The rifting also caused the Tethys Ocean to close, though the final closing did not occur until about 35 million years ago when India collided with Asia, forming the Himalayan orogeny.
How did the movement of continents affect ocean circulation and climatic regimes?
The movement of continents affected ocean circulation and climatic regimes. Populations became isolated and were brought into contact with other populations, leading to evolutionary changes in the biota. The breakup of Pangaea can be separated into three phases.
What era was the Mesozoic era?
The Mesozoic Era begins with the Triassic Period. This era is popularly known as the “Age of Reptiles” and for good reason: reptiles, and particularly dinosaurs, were the dominant land-dwelling vertebrate animals at the time.
What is the Triassic period?
Geologically and climatically the Triassic is a time of relative quiet in Earth history. An apparent catastrophic loss of plant life may have lead to global warming and a transition from meandering to braided rivers (charecteristic of distrurbed environments) during th eearly Triassic. There are no known glaciations during this Period on the supercontinent of Pangea.
What happened to dinosaurs at the end of the Triassic?
As we approach the end of the Triassic, dinosaurs began their dominance of terrestrial ecosystems. The Triassic ended in a significant extinction event with about 25% of all animal families disappearing. Ammonites were reduced to a single genus dispite their rapid and extensive diversification in the early Triassic.
How are the Permian and Triassic biota different?
The differences in Permian and Triassic biota are so great that they also mark the transition between the Paleozoic and the Mesozoic Eras. The Permian extinctions were so extensive and deep that the early Triassic saw a return to a Precambrian-like ecology. Microbes dominated these early ecologies, with microbial reefs occuring in the earliest Triassic. Stromatolites became widespread for the first time in 400 million years. Both in the sea and on land the early Triassic biota are dominated by limited diversity opportunistic fauna and flora. As an example, vast beds of a near monoculture of the scallop Claria were deposited in the seas of what is now Utah. On land lycopsids dominanted the low-diversity flora, with other opportunistic species such as quilworts unusually common. It took nearly four million years for ocean biotic diversity to recover, while on land it was not until the middle Triassic that conifer dominated forests finally displaced the lycopsids. As we approach the end of the Triassic, dinosaurs began their dominance of terrestrial ecosystems.
When did stromatolites become widespread?
Stromatolites became widespread for the first time in 400 million years. Both in the sea and on land the early Triassic biota are dominated by limited diversity opportunistic fauna and flora. As an example, vast beds of a near monoculture of the scallop Claria were deposited in the seas of what is now Utah.
When did phytosaurs become extinct?
Phytosaurs had a crocodilian appearance, but were not closely related. They appear in the Late Triassic and become extinct with the end of the Triassic.
Which family of corals was the first to be found in the Middle Triassic?
Cnidarians (corals): The extinction of the Paleozoic coral families resulted in a slow recovery of this group during the Triassic. The Scleractinian family, the first modern corals, appear in the Middle Triassic. Moderrn corals represent new newly skeletonized groups, apparently evolving from soft-bodied organisms during the early Triassic.
Which family of ammonoids survived the Permian extinction?
(Cephalopoda): The single family of ammonoids surviving the Permian extinction appears to be the first group to recover in the Triassic. They quickly diversified to about 400 genera. Ammonites on display include:
What was the period before the Triassic?
The period of time before the Triassic was called the Permian. This was a time when a wide variety of animals lived, including a group of animals called the synapsids, which would later evolve into mammals.
What is the Triassic period?
The Triassic period stands out in Earth’s history as the time when dinosaurs first evolved. It was followed by the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods – at the end of the latter, the dinosaurs were wiped out in a mass extinction event along with the majority of all other life. As a period of geologic time, the boundaries of ...
How did the Triassic differ from the Jurassic?
It was only in the next geologic period, the Jurassic, that the powerful pseudosuchians died back and the dinosaurs really took over , evolving into huge animals like the stegosaurus and the long-necked diplodocus. It’s always been a major mystery how the dinosaurs went from pipsqueaks to rulers.
What was the first dinosaur?
Alongside these terrestrial vertebrates, the first dinosaurs began to appear. They were mostly much smaller and meeker creatures, many not much bigger than a cow. One example is Tanystropheus, which had an extraordinary neck that was twice as long as its body.
What era did the Permian end?
This not only marked the end of the Permian period and the start of the Triassic, it was such a serious catastrophe that it is used as the marker of the end of a geologic era, the palaeozoic era.
What group of reptiles evolved in the Triassic period?
Out of the ashes of this extinction, several new groups of reptiles began to evolve in the Triassic. One particularly successful group was called the pseudosuchians. This is the lineage to which present-day crocodiles and alligators belong. They are a paltry bunch today, about 25 species all told.
When did the Triassic extinction end?
The end Triassic extinction event. About 200 million years ago , during a period known as the Triassic-Jurassic boundary, Pangaea started to crack. North America separated from Europe; South America from Africa. As they parted, Earth haemorrhaged lava from volcanoes in what is now the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean.
What dinosaurs lived during the Triassic period?
The dinosaur <i>Batrachotomus</i> lived during the Triassic period. (Image credit: Shutterstock) The Triassic Period was the first period of the Mesozoic Era and occurred between 251 million and 199 million years ago. It followed the great mass extinction at the end of the Permian Period and was a time when life outside ...
What was the climate like in the Triassic period?
At the beginning of the Triassic, most of the continents were concentrated in the giant C-shaped supercontinent known as Pangaea. Climate was generally very dry over much of Pangaea with very hot summers and cold winters in the continental interior. A highly seasonal monsoon climate prevailed nearer to the coastal regions.
How are rauisuchians differentiated from dinosaurs?
Unlike their close relatives the crocodilians, Rauisuchians had an upright stance but are differentiated from true dinosaurs by the way that the pelvis and femur were arranged. Another lineage of Archosaurs evolved into true dinosaurs by the mid-Triassic. One genus, Coelophysis, was bipedal.
Which dinosaurs were extinct by the mid-Triassic?
However, by the mid-Triassic, most of the Therapsids had become extinct and the more reptilian Archosaurs were clearly dominant. Archosaurs had two temporal openings in the skull and teeth that were more firmly set in the jaw than those of their Therapsid contemporaries.
How did the Permian Extinction affect the oceans?
The oceans had been massively depopulated by the Permian Extinction when as many as 95 percent of extant marine genera were wiped out by high carbon dioxide levels. Fossil fish from the Triassic Period are very uniform, which indicates that few families survived the extinction. The mid- to late Triassic Period shows the first development of modern stony corals and a time of modest reef building activity in the shallower waters of the Tethys near the coasts of Pangaea.
What were the mammals of the late Jurassic?
Early mammals of the late Triassic and early Jurassic were very small, rarely more than a few inches in length. They were mainly herbivores or insectivores and therefore were not in direct competition with the Archosaurs or later dinosaurs. Many of them were probably at least partially arboreal and nocturnal as well.
What did ichthyosaurs do in the Triassic?
Later in the Triassic, ichthyosaurs evolved into purely marine forms with dol phin-shaped bodies and long-toothed snouts. Their vertebrae indicate they swam more like fish, using their tails for propulsion with strong fin-shaped forelimbs and vestigial hind limbs.
What was the Triassic extinction?
Not the most well-known extinction event, the Triassic/Jurassic extinction was a fizzle compared to the earlier Permian/Triassic extinction and the later Cretaceous/Tertiary (K/T) extinction. The event, nevertheless, witnessed the demise of various genera of marine reptiles, as well as large amphibians and certain branches of archosaurs. We don't know for sure, but this extinction may have been caused by volcanic eruptions, a global cooling trend, a meteor impact, or some combination thereof.
What were the plants that were found in the Triassic period?
The Triassic period wasn't nearly as lush and green as the later Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, but it did see an explosion of various land-dwelling plants, including cycads, ferns, Gingko-like trees, and seed plants.
What was the marine life during the Cretaceous Period?
Marine Life During the Cretaceous Period. Shortly after the beginning of the Cretaceous period, the ichthyosaurs ("fish lizards") disappeared. They were replaced by vicious mosasaurs, gigantic pliosaurs like Kronosaurus, and slightly smaller plesiosaurs like Elasmosaurus.
What was the first continent to form during the Cretaceous?
During the early Cretaceous period, the inexorable breakup of the Pangaean supercontinent continued, with the first outlines of modern North and South America, Europe, Asia and Africa taking shape. North America was bisected by the Western Interior Sea (which has yielded countless fossils of marine reptiles), and India was a giant, floating island in the Tethys Ocean. Conditions were generally as hot and muggy as in the preceding Jurassic period, albeit with intervals of cooling. The era also saw rising sea levels and the spread of endless swamps—yet another ecological niche in which dinosaurs (and other prehistoric animals) could prosper.
What animals were in the Jurassic period?
Mammals: The mouse-sized early mammals of the Jurassic period, only recently evolved from their Triassic ancestors, kept a low profile, scurrying around at night or nesting high up in trees so as not to get squashed under the feet of bigger dinosaurs. Elsewhere, the first feathered dinosaurs began to appear, typified by the extremely bird-like Archaeopteryx and Epidendrosaurus. It's possible that the first true prehistoric birds had evolved by the end of the Jurassic period, though the evidence is still sparse. Most paleontologists believe that modern birds descend from the small, feathered theropods of the Cretaceous period.
What period did dinosaurs live in?
The Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods were marked out by geologists to distinguish among various types of geologic strata (chalk, limestone, etc.) laid down tens of millions of years ago. Since dinosaur fossils are usually found embedded in rock, paleontologists associate dinosaurs with the geologic period in which they lived—for example, "the sauropods of the late Jurassic."
What is the Cretaceous period?
The Cretaceous period is when dinosaurs attained their maximum diversity, as ornithischian and saurischian families branched off into a bewildering array of armored, raptor-clawed, thick-skulled, and/or long-toothed and long-tailed meat- and plant-eaters.
What was the Triassic period?
Triassic Period, in geologic time, the first period of the Mesozoic Era, lasting from 252 million to 201 million years ago. It marked the beginning of major changes that were to take place throughout the Mesozoic Era, particularly in the evolution of life and the distribution of continents and living things.
What was the most important event of the Triassic period?
The Triassic followed on the heels of the largest mass extinctionin the history of the Earth. This event occurred at the end of the Permian, when 85 to 95 percent of marine invertebrate species and 70 percent of terrestrial vertebrate genera died out. During the recovery of life in the Triassic Period, the relative importance of land animals grew. Reptilesincreased in diversityand number, and the first dinosaurs appeared, heralding the great radiation that would characterize this group during the Jurassic and Cretaceousperiods. Finally, the end of the Triassic saw the appearance of the first mammals—tiny, fur-bearing, shrewlike animals derived from reptiles.
What are the islands that are located within 30° of the Triassic equator?
Scattered across Panthalassa within 30° of the Triassic Equator were islands, seamounts, and volcanic archipelagoes, some associated with deposits of reef carbonates now found in western North America and other locations. Paleogeography and paleoceanography of Early Triassic time.
What was the result of the Triassic extinction?
Though this event was less devastating than its counterpart at the end of the Permian, it did result in drastic reductions of some living populations —particularly of the ammonoids, primitive mollusks that have served as important index fossilsfor assigning relative ages to various strata in the Triassic System of rocks.
What were the major changes that occurred during the Triassic period?
The Triassic Period marked the beginning of major changes that were to take place throughout the Mesozoic Era, particularly in the distribution of continents, the evolution of life, and the geographic distribution of living things. At the beginning of the Triassic, virtually all the major landmasses of the world were collected into the supercontinent of Pangea. Terrestrial climates were predominately warm and dry (though seasonal monsoons occurred over large areas), and the Earth’s crust was relatively quiescent. At the end of the Triassic, however, plate tectonicactivity picked up, and a period of continental rifting began. On the margins of the continents, shallow seas, which had dwindled in area at the end of the Permian, became more extensive; as sea levels gradually rose, the waters of continental shelves were colonized for the first time by large marine reptiles and reef-building corals of modern aspect.
What happened at the end of the Permian?
This event occurred at the end of the Permian, when 85 to 95 percent of marine invertebrate species and 70 percent of terrestrial vertebrate genera died out. During the recovery of life in the Triassic Period, the relative importance of land animals grew. Reptiles increased in diversity and number, and the first dinosaurs appeared, ...
What was the climate during the Triassic period?
Terrestrial climates were predominately warm and dry (though seasonal monsoons occurred over large areas), and the Earth’s crust was relatively quiescent. At the end of the Triassic, however, plate tectonic activity picked up, and a period of continental rifting began.

Overview
The Triassic is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic.
Etymology
The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek triás meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone), the middle Muschelkalk (shell-bearing limestone) and the upper Keuper (coloured clay).
Paleogeography
During the Triassic, almost all the Earth's land mass was concentrated into a single supercontinent, Pangaea (lit. 'entire land'). This supercontinent was more-or-less centered on the equator and extended between the poles, though it did drift northwards as the period progressed. Southern Pangea, also known as Gondwana, was made up by closely-appressed cratons corresponding to mod…
Climate
The Triassic continental interior climate was generally hot and dry, so that typical deposits are red bed sandstones and evaporites. There is no evidence of glaciation at or near either pole; in fact, the polar regions were apparently moist and temperate, providing a climate suitable for forests and vertebrates, including reptiles. Pangaea's large size limited the moderating effect of the global ocean; its continental climate was highly seasonal, with very hot summers and cold winters. The …
Flora
On land, the surviving vascular plants included the lycophytes, the dominant cycadophytes, ginkgophyta (represented in modern times by Ginkgo biloba), ferns, horsetails and glossopterids. The spermatophytes, or seed plants, came to dominate the terrestrial flora: in the northern hemisphere, conifers, ferns and bennettitales flourished. The seed fern genus Dicroidium would dominate Gondw…
Fauna
In marine environments, new modern types of corals appeared in the Early Triassic, forming small patches of reefs of modest extent compared to the great reef systems of Devonian or modern times. Serpulids appeared in the Middle Triassic. Microconchids were abundant. The shelled cephalopods called ammonites recovered, diversifying from a single line that survived the Permian …
Coal
No known coal deposits date from the start of the Triassic Period. This is known as the "coal gap" and can be seen as part of the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Possible explanations for the coal gap include sharp drops in sea level at the time of the Permo-Triassic boundary; acid rain from the Siberian Traps eruptions or from an impact event that overwhelmed acidic swamps; climate s…
Lagerstätten
The Monte San Giorgio lagerstätte, now in the Lake Lugano region of northern Italy and Switzerland, was in Triassic times a lagoon behind reefs with an anoxic bottom layer, so there were no scavengers and little turbulence to disturb fossilization, a situation that can be compared to the better-known Jurassic Solnhofen Limestone lagerstätte.
The remains of fish and various marine reptiles (including the common pachypleurosaur Neustic…