
What do the years of the Warring States refer to?
What do the years of the Warring States refer to? The period of the Warring States (Zhanguo or Chan-Kuo) refers to the era of about 475 BCE to 221 BCE. It commenced at a time of when the numerous petty city-state kingdoms of the Spring and Autumn period had been consolidated into seven major contenders and a few minor enclaves.
How did the period of Warring States change Chinese society?
How did Chinese society change during the Warring States Period? Confucianism, Legalism, and Daoism all each played a role during the Warring States Period. These three philosophies influenced the styles of Chinese governance throughout the Qin ascendancy, the Han dynasty, and beyond, becoming more or less influential depending on which dynasty was in power. What ]
What was the total death toll in WW1?
What was the total death toll in WW1? The total number of military and civilian casualties in World War I was about 40 million: estimates range from around 15 to 22 million deaths and about 23 million wounded military personnel, ranking it among the deadliest conflicts in human history.
What period was after the Civil War?
The period after the Civil War, 1865 - 1877, was called the Reconstruction period. Abraham Lincoln started planning for the reconstruction of the South during the Civil War as Union soldiers occupied huge areas of the South.

What is the Warring States period?
The Warring States period (481/403 BCE - 221 BCE) describes the three centuries when various rival Chinese states battled viciously for territorial advantage and dominance. Ultimately the Qin state was victorious and established the first unified Chinese state. Besides incessant warfare, and probably because of it, ...
Who were the main thinkers of the Warring States?
There were no actual formal schools at the time but rather a wide spectrum of individual thinkers who included Mencius (Pacifist and Confucianist philosopher), Sun Tzu (military strategist), Mo Ti (aka Mozi, military engineer and philosopher), Hui Shi (Logician) and Gongsun Longzi (Logician). The Warring States Period, in many ways, then, set ...
What was the most important aspect of social life during the Warring States period?
During the Warring States period, warfare was the most important aspect of social life, the principle of the state, and the compass that directed government policies. It is no exaggeration that by the late Warring States period (3rd century BCE), war had escalated to the level that the entire state was organised for the very purpose of war, and this was true for all states (197).
What weapons were used in the Warring States?
Cavalry of mounted archers on sturdy Mongolian steeds, large infantry armies based on universal conscription, and the diffusion of new iron weapons such as swords and crossbows ( which led to new armour), made warfare during the Warring States Period much more deadly than in previous eras. The slower and more organised battles of yesteryear where chariots were used in large numbers and infantry were deployed in a more predictable manner now gave way to a much more dynamic battlefield. Warfare also became more sophisticated with more subtle and disciplined troop deployments, subterfuge and espionage playing their part in victories.
What did the huge numbers involved mean in the war?
The huge numbers involved meant that soldiers were relatively untrained and warfare became less a matter of fighting skill and more about having such a numerical supremacy that a commander could overwhelm his opponent in the field. Remove Ads. Advertisement. Warring States Period Swords.
How many wars were there between 535 and 286 BCE?
Between 535 and 286 BCE there were 358 wars between states. Huge armies were led by commanders who abandoned the chivalrous etiquette of warfare in previous times (if, indeed, there had ever been such a thing) and ruthlessly campaigned to destroy the enemy - both soldiers and non-combatants.
How many states were there in the 4th century?
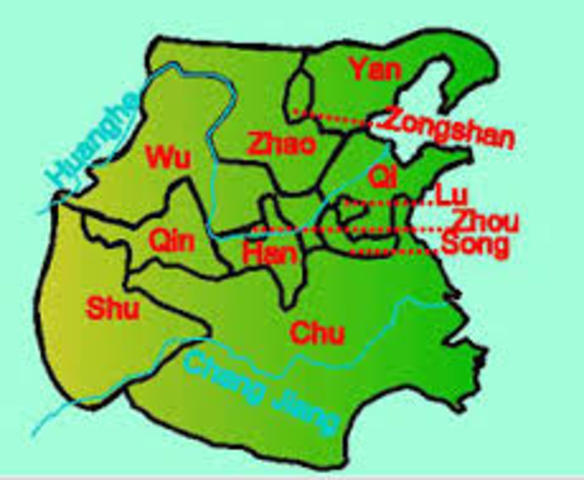
By the early 4th century BCE nearly 100 small states had been consolidated by conquest into seven major states: the Chu, Han, Qi, Qin, Wei, Yan, and Zhao. Sandwiched between these were several smaller states but the big seven had by now become so large and consolidated that it became difficult for one to absorb another.
What was the Warring States period?
The Warring States Period (475–221 BC) was an era of division in ancient China. After the relatively peaceful and philosophical Spring and Autumn Period, various states were at war before the Qin state conquered them all, and China was reunited under the Qin Dynasty.
How many stages are there in the Warring States Period?
The timeline of the Warring States Period could be divided into seven stages:
How many warring states were there in 334 BC?
States declared independence from the Zhou Dynasty, and kingdoms fought for territory, during this period. By 334 BC there were 7 warring states: Qin, Chu, Zhao, Wei, Han, Yan, and Qi. The Warring States Period ended with Qin's conquest of the other states. It was succeeded by the Qin Dynasty in 221 BC, ...
Why did the Vassal States gain independence?
The independence of vassal states was caused by the Zhou Dynasty’s system of enfeoffment: in order to strengthen the Zhou king’s power, nobles who contributed to the dynasty were awarded land.
Which dynasty was the largest in the Warring States?
During the Warring States Period, nobles stopped supporting the Zhou Dynasty (1046–221 BC), and Zhou's vassal states declared themselves independent from Zhou, becoming kingdoms or warring states. Chu became the biggest state. It controlled the southern third of the entire region of the Warring States. Qin also controlled about a third of the ...
What was Shang Yang's rule?
Shang Yang espoused rule according to a defined set of strict rules and a clear political philosophy. By 338 BC, although Shang Yang was eventually killed, his reform had made Qin the most powerful and ruthless state, both in military and economic terms.
Which state controlled the southern third of the entire region of the Warring States?
It controlled the southern third of the entire region of the Warring States. Qin also controlled about a third of the territory in the west. The rest of the states comprised the northeastern third of the region of the Warring States.
What is the Warring States period?
The Warring States period was one of the most fertile and influential in Chinese history.
When did Qin establish the Chinese Empire?
Qin finally defeated all the other states and established the first unified Chinese empire in 221 bce. …known as the Zhanguo ( Warring States) period. The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica This article was most recently revised and updated by Adam Augustyn, Managing Editor, Reference Content.
When did the Warring States fight?
The military of the Warring States refers primarily to the military apparatuses of the Seven Warring States which fought from around 475 BC to 221 BC when the state of Qin conquered the other six states, forming China 's first imperial dynasty, the Qin dynasty.
What were the first crossbows used in the Warring States?
Large mounted crossbows known as "bed crossbows" were used as early as the Warring States period. Mozi described them as defensive weapons placed on top the battlements. The Mohist siege crossbow was described as a humongous device with frameworks taller than a man and shooting arrows with cords attached so that they could be pulled back. By the Han dynasty, crossbows were used as mobile field artillery and known as "Military Strong Carts". Around the 5th century AD, multiple bows were combined together to increase draw weight and length, thus creating the double and triple bow crossbows. Tang versions of this weapon are stated to have obtained a range of 1,160 yards, which is supported by Ata-Malik Juvayni on the use of similar weapons by the Mongols in 1256.
What was the rapid growth of Qin's military?
The rapid growth of Qin's military began with the adoption of Shang Yang 's Legalist reforms beginning in 361 BC. Shang Yang was originally a minor official in the state of Wei, but failed to gain recognition there and defected to Qin in 361 BC. Shang Yang personally led the Qin army to wage war on his native homeland and recovered territory previously lost to Wei. This forced Wei to shift its capital eastward to Daliang in 340 BC. Unfortunately, after the death of Duke Xiao of Qin in 338 BC, Shang Yang was accused of treason and killed.
How many km can Wu Qi march in one day?
Wu Qi did not mention the military merits of Wei. Elite armoured soldiers capable of marching 40-50 km in one day while equipped with heavy armour, a helmet, a halberd or pike, swords, a crossbow with 50 bolts, and three days of rations. Qin general, front. Qin general, back.
When did Jin become independent?
In 453 BC, the three houses of Han, Zhao, and Wei defeated their rivals at the Battle of Jinyang and began the tripartite division of the old state of Jin. In 424 BC , they mutually recognized each other's independence; however, it was not until 403 BC when King Weilie of Zhou recognized this political reality and bestowed upon them the title of marquis. In 376 BC, they formally divided the territory of Jin between themselves.
Who was Wu Qi?
Wu Qi (440–381 BC) Wu Qi was a general born in the state of Wei who went on to serve in the state of Chu. He is traditionally credited with the authorship of the Wuzi, one of the Seven Military Classics, in which he described the military merits of six of the Warring States.
Who defeated the Qin army?
Two years later, the Qin army was defeated by relief forces from Wei and Chu at the siege of Handan, the capital of Zhao.
How many states were there in China during the Warring States Period?
During the Warring States Period of Chinese history, from 475 to 221 BCE, what we now think of today as China was divided into seven competing nations. The fiefs that had grown in importance during the end of the Zhou Dynasty had now become states of their own.
Who was the first ruler of China?
One of those seven states was the state of Qin, whose young ruler, King Zheng, would later become Qin Shi Huangdi, the first ruler of the Qin Dynasty, in 221 BCE. The Qin Dynasty is often credited as the first dynasty to unify China. But let's rewind the tape to about a century and a half earlier to understand a key influence on the Qin Dynasty: Legalism.
Time Frame
Background
- In the 5th century BCE the Eastern Zhou (Chou) Dynasty (771-256 BCE) was crumbling. No longer dominant in military terms, the Zhou were forced to rely on armies of other allied states, who on occasion took the opportunity to forward their own territorial claims. For this reason, the Zhou king was compelled to sometimes make the military leader of another state the military leader o…
A New Type of Warfare
- Cavalry of mounted archers on sturdy Mongolian steeds, large infantry armies based on universal conscription, and the diffusion of new iron weapons such as swords and crossbows (which led to new armour), made warfare during the Warring States Period much more deadly than in previous eras. The slower and more organised battles of yesteryear where chariots were used in large nu…
The Rise of Qin
- Rather ironically given future events, the Qin was one one of the few states which remained loyal to the Zhou. For example, the Qin ruler, Duke Xin, was rewarded for protecting Zhou interests with the title of Hegemon in 364 BCE. His successor Xiao, was given the same honour in 343 BCE. Xiao is known for taking on the services of the gifted advisor Shang Yang, poached from the Wei stat…
Cultural Developments
- The period may have been dominated by wars but there were some cultural side effects to all this military activity. The technological necessity to produce weaponry as good as or better than one's opponents led to better tools and craft skills, especially metalworking and the use of iron. Artists, in turn, were able to produce more skilled artworks, notably mastering such difficult and time-co…