Where do you find #electrons?
0:004:23How to find the Protons Neutrons and Electrons of an element ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWelcome to moomoomath and science in this video let's learn to use the periodic table in order toMoreWelcome to moomoomath and science in this video let's learn to use the periodic table in order to find an elements name symbol number of protons neutrons. And electrons take a look at this chart.
Where are the protons on a periodic table?
The letter(s) in the middle is the symbol of the element. The number on the bottom left corner is the atomic number, which tells you the number of protons. The number on the upper left corner is the mass number, which is equal to the neutrons and protons added together.
Are neutrons and electrons the same?
Electrons are a type of subatomic particle with a negative charge. Protons are a type of subatomic particle with a positive charge. Protons are bound together in an atom's nucleus as a result of the strong nuclear force. Neutrons are a type of subatomic particle with no charge (they are neutral).
How do you find the protons electrons and neutrons?
To calculate the numbers of subatomic particles in an atom, use its atomic number and mass number: number of protons = atomic number. number of electrons = atomic number. number of neutrons = mass number - atomic number.
Are neutrons and protons the same number?
For most of the 16 lightest elements (up to oxygen) the number of neutrons is equal to the number of protons.
How do you find neutrons?
To find the number of neutrons, subtract the number of protons from the mass number. number of neutrons=40−19=21.
Are protons and electrons equal?
The number of electrons on a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. This is known as the atomic number, Z. The removal or addition of electrons to a neutral atom creates ions that have a net negative or positive charge.
How many protons are in an atom?
By definition, atoms have no overall electrical charge. That means that there must be a balance between the positively charged protons and the negatively charged electrons. Atoms must have equal numbers of protons and electrons. In our example, an atom of krypton must contain 36 electrons since it contains 36 protons.
What is the color of electrons in an orbital?
The 2, 2 and 6 (in red color ) are the number of electrons present in that particular orbitals. Here, 2 electrons are in s-orbitals of 1st energy shell. Similarly, other 2 electrons are in s-orbitals of the 2nd energy shell, and. 6 electrons are in p-orbitals.
What is electron configuration?
What exactly is the Electron Configuration? Electron configuration is the structure which describes the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus of an atom. This is how the electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom. In simple words, if we know the electron configuration of an element, then we can easily get the idea ...
What are orbitals?
There are few regions around the nucleus where the probability of finding electrons is maximum. Such regions are known as orbitals.
Why is electronic configuration important?
Electronic configuration is important in the following ways. Electron configuration is very important to know where the electrons are located around the atoms. Number of electrons present in s, p, d and f orbitals can be found using electron configuration. Through electronic configuration, the chemical properties of elements can be predicted by ...
How can chemical properties be predicted?
Through electronic configuration, the chemical properties of elements can be predicted by knowing their valence electrons.
Can you find every detail of an interactive periodic table?
You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table.
How are electrons arranged around the nucleus of an atom?
Just like the moon revolving around the earth, the electrons also revolve around the nucleus.
How many electrons can a shell hold?
1st shell can hold 2 electrons. 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons. 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons. 4th shell can hold 32 electrons. Now I’ll show you the complete list of elements with electrons per shell.
Can you find every detail of an interactive periodic table?
You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table.
Is the Interactive Periodic Table free?
Checkout Interactive Periodic table and download it’s high resolution image now ( It’s FREE)
How many elements are there in the periodic table?
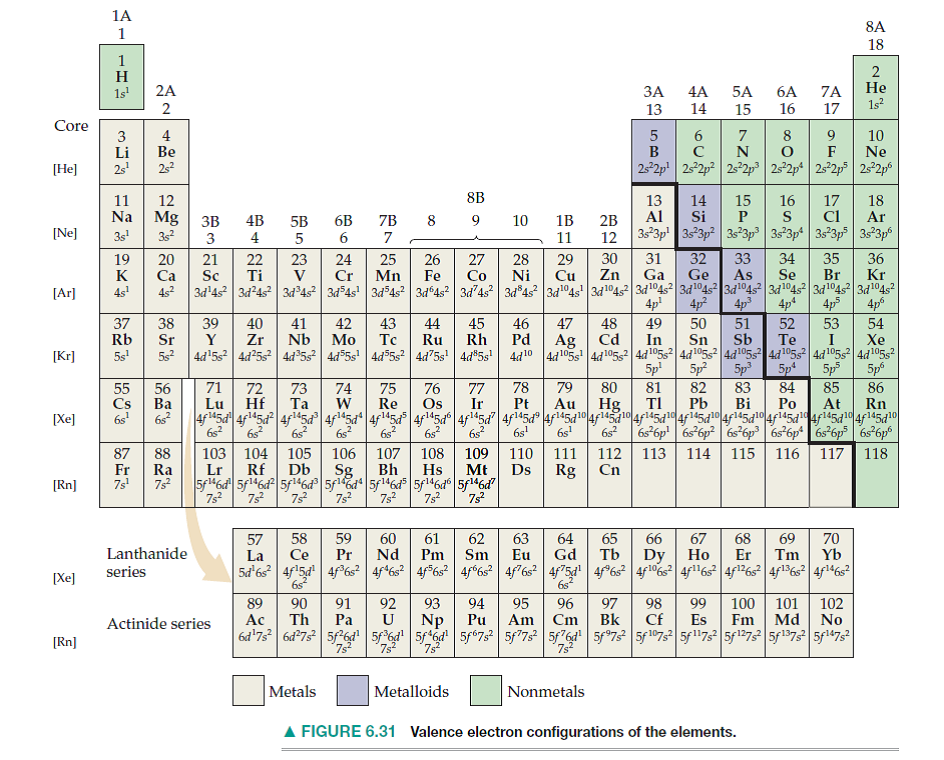
There are 118 elements in the periodic table. Each element has a unique atomic structure that is influenced by its electronic configuration, which is the distribution of electrons across different orbitals of an atom. This article provides you with an electronic configuration chart for all these elements.
How many electrons does the M shell carry?
The M shell contains 3s, 3p, and 3d, and can carry 18 electrons. The N shell containing 4s, 4d, 4p and 4f, can carry 32 electrons. Such an arrangement helps explain the periodicity and periodic trends observed across the elements of the periodic table.
What are the shells of an atom?
This model has been widely accepted, and according to it, each atom has shells, which further have subshells. The shells are labeled K, L, M, N , and so on, from the innermost to the outermost shell. Each shell has subshells that are named for the type of emission lines produced from different states of angular momentum.
What is electronic configuration?
The concept of electronic configuration has replaced the older concept of valency and valence electrons. It involves the specific arrangement of electrons in shells and sub-shells of Bohr’s atomic model. This model has been widely accepted, and according to it, each atom has shells, which further have subshells.
How are elements placed in order on the periodic table?
Elements are placed in order on the periodic table based on their atomic number, how many protons they have. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons will equal the number of protons, so we can easily determine electron number from atomic number.
What does the periodic table show?
In addition to listing the atomic number for each element, the periodic table also displays the element’s relative atomic mass, the weighted average for its naturally occurring isotopes on earth. Looking at hydrogen, for example, its symbol, and name appear, as well as its atomic number of one—in the upper left-hand corner—and its relative atomic mass of 1.01.
How many electrons are in the outermost shell of an atom?
The number of electrons in the outermost shell of a particular atom determines its reactivity, or tendency to form chemical bonds with other atoms. This outermost shell is known as the valence shell, and the electrons found in it are called valence electrons. In general, atoms are most stable, least reactive, when their outermost electron shell is full. Most of the elements important in biology need eight electrons in their outermost shell in order to be stable, and this rule of thumb is known as the octet rule. Some atoms can be stable with an octet even though their valence shell is the 3n shell, which can hold up to 18 electrons. We will explore the reason for this when we discuss electron orbitals below.
How do the orbitals fit in with the electron shells?
So, how do these mathematically defined orbitals fit in with the electron shells we saw in the Bohr model? We can break each electron shell down into one or more subshells, which are simply sets of one or more orbitals . Subshells are designated by the letters , , , and , and each letter indicates a different shape. For instance, subshells have a single, spherical orbital, while subshells contain three dumbbell-shaped orbitals at right angles to each other. Most of organic chemistry—the chemistry of carbon-containing compounds, which are central to biology—involves interactions between electrons in and subshells, so these are the most important subshell types to be familiar with. However, atoms with many electrons may place some of their electrons in and subshells. Subshells and have more complex shapes and contain five and seven orbitals, respectively.
How do electrons travel around the nucleus?
Specifically, electrons don’t really circle the nucleus, but rather spend most of their time in sometimes-complex-shaped regions of space around the nucleus, known as electron orbitals. We can’t actually know where an electron is at any given moment in time, but we can mathematically determine the volume of space in which it is most likely to be found—say, the volume of space in which it will spend 90% of its time. This high-probability region makes up an orbital, and each orbital can hold up to two electrons.
What happens to the second electron shell after the orbital is filled?
After the orbital is filled, the second electron shell begins to fill, with electrons going first into the orbital and then into the three orbitals. Elements in the second row of the periodic table place their electrons in the 2n shell as well as the 1n shell.
Why do we need periodic table?
probably not. That’s because the periodic table isn’t just a big bucket that holds all of the elements. Instead, it’s more like a filing system. The position of each element in the table gives important information about its structure, properties, and behavior in chemical reactions. Specifically, an element’s position in the periodic table helps you figure out its electron configuration, how the electrons are organized around the nucleus. Atoms use their electrons to participate in chemical reactions, so knowing an element’s electron configuration allows you to predict its reactivity—whether, and how, it will interact with atoms of other elements.
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).
Electron styles
The easiest way to remember the electron designs is always to brand the Periodic Desk in disables of components.
Atomic variety
The regular kitchen table listings aspects in raising purchase of atomic variety, with a similar components placed into the same top to bottom line. For example, team 1A components are smooth materials that react violently with normal water and provide off 1 fees.
Atomic weight
The atomic weight is actually a simple strategy in biochemistry, where most reactions stick to simple numerical interactions amongst atoms. Chemistry involves calculating and weighing the numbers of reactants and products, and atomic dumbbells are basic to the computation.
Atomic class
The periodic desk is a long list of compound aspects established in increasing get of atomic quantity. Components with similar chemistry are arranged into periods and groups, and those from the very same group of people have the same atomic variety. Components from the same class talk about the identical valence electrons and busy shells.
Atomic configuration
The electron design of an atom describes its placement inside the atom. The easiest way to establish the electron configuration is to try using a periodic dinner table and its element blocks. The factor prevents are arranged to offer the greatest electron orbital. The s, p, and d disables contain components from teams a person to seven.
Atomic layouts
Atoms have a number of electrons and take on various atomic configurations. In atomic science, this is called the digital casing. The electrons of an atom are positioned in a concentric shell round the atomic nucleus. Though these shells are certainly not actual buildings, they do help us envision electrons’ spaces.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a chart that organizes elements by their atomic structure. It is color-coded and assigns each element a unique 1 or 2-letter abbreviation. Other elemental information includes atomic weight and atomic number. You can find a periodic table online or in a chemistry book.
Where is the atomic number located?
The atomic number is located above the element symbol, in the upper left-hand corner of the square. The atomic number will tell you how many protons make up a single atom of an element. For example, boron (B) has an atomic number of 5, therefore it has 5 protons.
Why is an ion positive?
Although the number of protons in the atom remains the same, the number of electrons is altered in an ion. Because an electron has a negative charge, when you remove electrons, the ion becomes positive.
How to find neutrons?
Subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass. To find the number of neutrons, you will need to subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass. Remember that the atomic number is the same as the number of protons, which you have already identified.
Why does an ion become positive when you remove electrons?
Because an electron has a negative charge, when you remove electrons, the ion becomes positive. When you add more electrons, the ion becomes negative.
What are the three groups of elements?
Find your element on the periodic table. The table orders elements by atomic number and separates them into three main groups: metals, non-metals, and metalloids (semi-metals). Further elemental groupings include alkali metals, halogens, and noble gases.
Which type of charge is positively charged?
Protons are positively charged, electrons are negatively charged, and neutrons have no (neutral) charge.
Why we need electrons
We need electrons for so much more than lighting our computer screens. Electrons are the building blocks of atoms. They are what give atoms their positive and negative charges. Without electrons, atoms would not be able to combine to form new chemical compounds. Since just about everything you see is made of chemicals, we really need electrons.
Where are the electrons on the periodic table?
Electrons are found on the far right column of the periodic table. These elements are found in group 2.
Summary
Electrons are everywhere! They’re present throughout nature, and they’re even inside our bodies. Electrons can display some amazing properties, like magnetism, electricity, and more. But where exactly do they come from? The answer to that lies in the periodic table.
Background
There are three different types of electrons. These types are called valence electrons, core electrons, and orbital electrons.
