What are halogens and why are they dangerous?
Halogens are highly reactive, and they can be harmful or lethal to biological organisms in sufficient quantities. This reactivity is due to high electronegativity and high effective nuclear charge. Halogens can gain an electron by reacting with atoms of other elements. Fluorine is one of the most reactive elements.
What are halogens and where are they located?
The halogens are the elements in group 17 of the periodic table. This is the next-to-last column of elements on the righthand side of the table. The halogen elements are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, and possibly tennessine. The halogens are highly reactive nonmetallic elements.
What elements are in halogens?
- Chlorine . It has been used to make disinfectants and pesticides, given its lethal power. ...
- Fluorine . It is considered excessively toxic, due to its enormous electronegativity. ...
- Bromine . It is relatively less toxic than these two elements. ...
- Iodine . ...
- The astatine . ...
Where are the non metals on the periodic table?
non-metal elements are on the right of the stepped line Metals are on the left of the periodic table, and non-metals are on the right. Atomic structure and the periodic table

Why are 17 called halogens?
The group 17 elements include fluorine(F), chlorine(Cl), bromine(Br), iodine(I) and astatine(At) from the top to the bottom. They are called “halogens” because they give salts when they react with metals.
Why is the 7th group called halogens?
Group 7 elements form salts when they react with metals. The term 'halogen' means 'salt former', which is why Group 7 elements are called halogens.
Where is Group 7 on the periodic table?
The Group 7 elements are called the halogens. They are placed in the vertical column, second from the right, in the periodic table . Chlorine, bromine and iodine are the three common Group 7 elements.
Are halogens Group 7 or Group 17?
Group 7A (or VIIA) of the periodic table are the halogens: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At).
What is Group 17 called?
halogenhalogen, any of the six nonmetallic elements that constitute Group 17 (Group VIIa) of the periodic table. The halogen elements are fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts).
What are the group 7 metals?
Group 7, numbered by IUPAC nomenclature, is a group of elements in the periodic table. They are manganese (Mn), technetium (Tc), rhenium (Re), and bohrium (Bh). All known elements of group 7 are transition metals.
What are the elements in group 8 called?
Group 8A (or VIIIA) of the periodic table are the noble gases or inert gases: helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn).
What is 7 on the periodic table?
N NitrogenThe Elements, sorted by Atomic NumberAtomic NumberSymbolName6CCarbon7NNitrogen8OOxygen9FFluorine76 more rows
Why are elements of group BIA called halogens?
The name halogens are from Greek halo (sea salt) and gens (producing formation) and thus means 'sea salt former'. Group 17 contains fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine which form salts. Hence they are called halogens.
What are the properties of Group 7 elements?
The halogens have low melting points and low boiling points. This is a typical property of non-metals. Fluorine has the lowest melting and boiling points. The melting and boiling points then increase as you go down the group.
Why is the first group called alkali metals?
All the Group 1 elements are very reactive . They must be stored under oil to keep air and water away from them. Group 1 elements form alkaline solutions when they react with water, which is why they are called alkali metals.
What type of bonds do Group 7 elements form?
Group 7 elements are all non-metals and exist as diatomic molecules. In each molecule, two atoms of the element are held together by a single covalent bond.
What are the physical properties of the halogens?
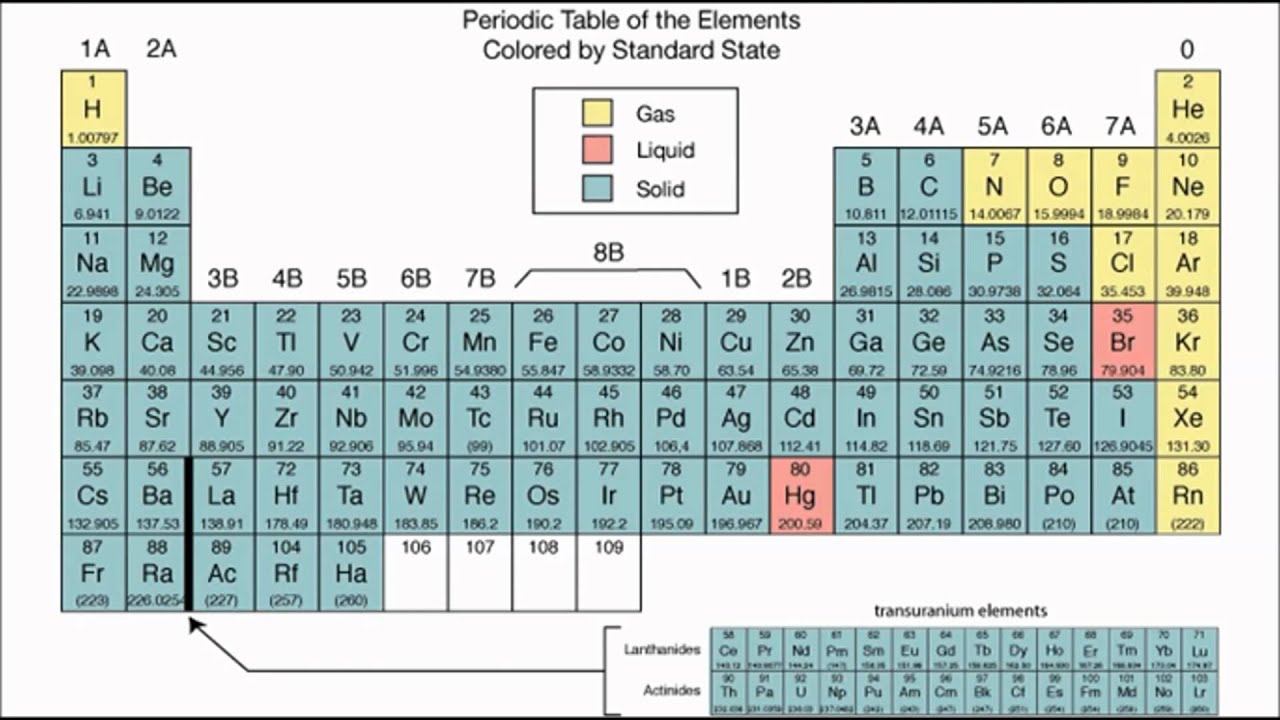
The physical properties of halogens are as follows. The halogens may exist as solid, liquid, or gas at room temperatures. They dissolve in water...
Where are the halogens found?
They are found in group 17 of the Periodic Table, on the extreme right, close to the noble gases. Their valence electron configuration is the reaso...
Why are Group 7 elements called halogens?
They are called halogens as they form salts with metals. The term "halogen" is derived from the Greek language and means salt producers.
What are halogen elements?
The halogen elements are the six elements in Group 17 of the periodic table. Group 17 occupies the second column from the right in the periodic tab...
What are the major properties of the halogen elements?
Halogen elements are very reactive. With sodium, they produce salts, of which table salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) is the most well known. Each halog...
What are some uses of halogen elements?
Chlorine is used to purify water. In addition, chlorine is part of table salt, sodium chloride, which is one of the most widely used chemical compo...
Why are these elements called halogens?
When these elements react with sodium, they produce salts. The most well known of these is sodium chloride, or common table salt (also called halit...
Where Are Halogens on the Periodic Table?
It places elements with similar chemical properties in groups. The halogens are located in group 17 on the periodic table.
Which column of the periodic table contains halogens?
The halogens' immediate neighbor to the right is the column of noble gases whose atoms have a full complement of electrons. To the left of the column of halogens, there are other non-metal groups, groups 16 and 15. The left part of the periodic table comprises metals.
What are Halogens?
Halogens is the collective name given to a group of non-metallic elements. The name "halogens" owes its origin to the Greek language. "Halogens" means "salt formers". Halogens can be defined as elements that form salts when they react with metals. There are six halogens- fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, and tennessine. Tennessine is the latest addition to the halogen family and is named after the state of Tennessee, US; but it is still not considered a true halogen because it is a synthetic element.
Why are halogens always found in the combined form?
The reactive nature of halogens is the reason why they are always found in the combined form.
What is the boiling point of iodine?
Boiling points: The boiling points of the halogens show a regular gradation. The boiling points from fluorine to iodine are 85.01K, 239.18K, 331.93K, and 457.5K. The boiling point of astatine is not known. This trend in the halogens' property is due to the van der Waal's forces existing in the halogen molecules. These forces are stronger when the atoms have a large number of electrons. More energy is required to overcome these forces. This results in a graded increase in boiling points.
Why are halogens reactive?
To the question, " are halogens reactive", the answer is yes and the reason lies in their electron configuration. Atoms of all the halogens have seven valence electrons. The halogen atoms are very close to a stable electron configuration. This explains why halogens are reactive.
Why are halogens found only as compounds?
Halogens are never found in nature as elements; they are found only as compounds because of their reactive nature.
What is the halogen family?
The halogens, aka halogen family, are a group of reactive elements in group 17 of the periodic table, to the right of the chalcogens, and to the left of the noble gases. Fluorine and chlorine are the “poster children” of the halogens. They are non-metals that consist of diatomic molecules.
Why are halogens so reactive?
Halogens are so reactive, because they have 7 valence electrons, and are very close to having a complete shell of 8 electrons. The halogens will rip an electron from another atom, in order to achieve a very stable state of 8 electrons in their outer shell.
Why is halogen considered a salt?
Halogen means “salt-producing”. They are salt-producing, because when they react with metals (often violently), they produce ionic compounds known as salts. In 1811 John Schweigger wanted to name the element chlorine “halogen”, but he failed. In 1826, Swedish chemist Jons Berzelius coined the term halogen for the entire group of elements. The Greek word “hal”, meaning salt, also appears in the name of the mineral halite, aka sodium chloride.
What is the weakest bond in the elemental state?
In the elemental state, they form diatomic molecules, joined by nonpolar covalent bonds. The fluorine-to-fluorine bond is the weakest
What is the name of the reaction in which bromide and bromate ions are key ions?
Bromide and bromate ions are key ions in a famous and beautiful oscillating reaction known as the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction
Which element is the most reactive?
Fluorine is the most reactive of all elements, and can only be stored in metals that form passivation layers of the fluoride salt. These unique properties are because of the 7 electrons in their valence shell. Because of their reactivity, there are almost never found in nature in their elemental form.
Is halogen a toxic substance?
The halogens are highly reactive and highly toxic. Breathing in vapors of any of the halogens is very dangerous, and they have distinctive, unpleasant odors (although the author finds a faint smell of bromine oddly interesting).
What are the elements in the halogen group?
The halogen elements are fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). Learn more about the properties of halogens in this article.
Where does the word "halogen" come from?
The word halogen comes from the Greek roots hal- meaning “salt” and -gen meaning “to produce.”. Because of their great reactivity, the free halogen elements are not found in nature. In combined form, fluorine is the most abundant of the halogens in Earth ’s crust.
What are the elements in Group 17?
Group 17 is the second column from the right in the periodic table and contains six elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (As), and tennessine (Ts). Astatine and tennessine are radioactive elements with very short half-lives ...
What is the difference between chlorine and fluorine?
Chlorine is used to purify water. Chlorine also is part of salt, sodium chloride, which is one of the most widely used chemical compounds. Fluorine is used in fluorides, which are added to water supplies to prevent tooth decay. Iodine is used as an antiseptic.
Which element has the greatest difficulty in oxidizing?
The oxidizing strength of the halogens increases in the same order—i.e., from astatine to fluorine. Therefore, of the halogen elements, elemental fluorine is prepared with the greatest difficulty and iodine with the least. As a class, the halogen elements are nonmetals, but astatine shows certain properties resembling those of the metals.
Which element is the most reactive?
Fluorine is the most reactive of the halogens and, in fact, of all elements, and it has certain other properties that set it apart from the other halogens. Chlorine is the best known of the halogen elements. The free element is widely used as a water-purification agent, and it is employed in a number of chemical processes.
How many valence electrons does a halogen have?
They produce salts with sodium, of which table salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) is the most well-known. The halogen elements have seven valence electrons in their outermost electron shell. Therefore, when these elements can receive an electron from another atom, they form very stable compounds since their outermost shell is full.
About Halogen
Halogens elements located in group seventeen of the periodic table. Halogen word is coming from Greek word Hal (salt) and gen (to produce) because they all produce sodium salts of similar properties. They are Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Iodine (I), Astatine (As) and Tennessine (Ts).
Properties of Halogen
Halogens are highly reactive in nature thus, they do not found freely in nature.
Uses of Halogens
Fluorine is used in toothpastes, hydrofluoric acid (HF), mineral water.
Where are halogens found in the periodic table?
The halogen elements are located in group VIIA of the periodic table, which is the second-to-last column of the chart. This is a list of elements that belong to the halogen group and the properties that they share in common:
How many electrons are in a halogen atom?
They are highly reactive nonmetals. Atoms of belonging to the halogen group have 7 electrons in their outermost (valence) shell.
What are halogens used for?
Their high reactivity also makes these elements important components of some types of bleach. Halogens are used in incandescent lamps to make them glow at a higher temperature and with a white color. The halogen elements are important drug components, as they aid drug penetration into tissues.
What color is halogen?
The halogens are colorful, even as gases. Fluorine is the palest element, but even as a gas it has a distinct yellow color.
Why do halogens need more electrons?
These atoms need one more electron in order to have a stable octet. Halogens are highly electronegative, with high electron affinities. The melting and boiling points of the halogens increase as you increase atomic number (as you move down the periodic table).
What is the element Br?
Bromine is element 35 with symbol Br. It is a liquid at room temperature and pressure.
Is chlorine a halogen?
Fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine definitely are halogens. Element 117, which has the placeholder name of ununseptium, might have some properties in common with the other elements. Even though it is in the same column or group of the periodic table with the other halogens, most scientists believe element 117 will behave more like ...
