How many metalloids are on the periodic table?
There are six elements generally accepted to be metalloids. However, based on the classification criteria being used, the exact number may vary, ra...
What are 4 properties of metalloids?
The four major properties of metalloids are as follows: - They are solids - They have a metallic luster - They are brittle - They are semicondu...
What types of properties do metalloids display?
Metalloid element properties include a mixture of properties of both metals and nonmetals. While some characteristics (such as their metallic luste...
Where are the metalloids on the periodic table?
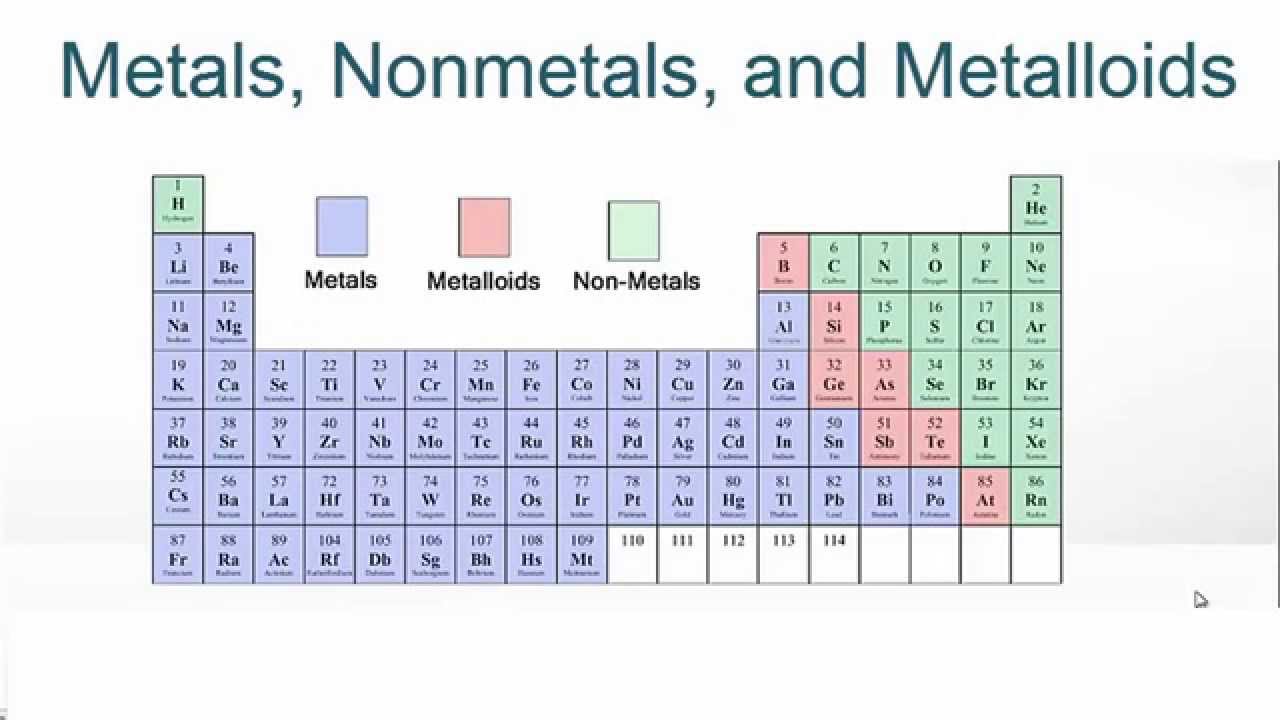
The metalloids are located along a slanted line between the metal elements and nonmetal elements of the periodic table. They span from Group 13 to...
Where are metalloids located?
Location of Metalloids in the Periodic Table. The metalloids, also known as semi-metals, are placed between metals and non-metals in the periodic table of elements. There are seven elements that are classified as metalloids and placed in Group 13, 14, 15, 16, and 17. They are found in a stair step line that helps differentiate metals ...
How many elements are metalloid?
As mentioned above, there are 7 elements in the periodic table that exhibit metalloid behavior. They occur in a diagonal line from boron to astatine through the p-block. The elements in the upper-right portion of the line show increasing non-metallic behavior and the elements at the lower-left of the line show increasing metallic behavior.
What is the line that separates metalloids from non-metals called?
The line that separates metalloids from the metals and non-metals in the periodic table is called amphoteric line.
What are metalloids?
Metalloids are elements from the periodic table with properties that lie between metals and non-metals. The following ScienceStruck article will cover some information related to metalloids. The first person to come up with a periodic table of elements was Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev, a Russian chemist. He came up with the first version of periodic ...
What is the meaning of the term "metalloid"?
The term metalloid comes from the Greek word metallon, which means ‘metal’, and edios, meaning ‘sort.’ The metalloids are often seen forming amphoteric oxides, and they behave as semiconductors. They have properties of both metals and non-metals in the periodic table. They even carry electric charge that makes them suitable for use in computers and calculators. Their ionization energy as well as electronegativity values are between those of metals and non-metals. Their reactivity depends on the metals that they are reacting with.
How do the chemical properties of elements vary?
According to Mendeleev’s law of periodic table, the chemical and physical properties of elements vary in a periodic fashion according to their atomic weights. However, the modern periodic table of elements follow the law that, the properties of elements vary according to their atomic number and not by their weight. The elements of a Mendeleev’s table were arranged in rows called periods and columns called groups. The chemical elements of the same group had similar properties. There are different regions in the periodic table that are called periodic table blocks, as they are named according to the subshell of the last electron of the atom.
Where does the term "metalloid" come from?
The term metalloid comes from the Greek word metallon, which means ‘metal’, and edios, meaning ‘sort.’. The metalloids are often seen forming amphoteric oxides, and they behave as semiconductors. They have properties of both metals and non-metals in the periodic table.
Where are metalloids on the periodic table?
As previously mentioned, metalloids are a group of elements that occur in a slanted line between the metals and nonmetals on the periodic table. This line of metalloid elements spans between Group 13 to Group 16, 17, or 18 (depending on how many elements are considered to be metalloids truly).
Where are metalloids located?
The metalloids are located along a slanted line between the metal elements and nonmetal elements of the periodic table. They span from Group 13 to Group 16, 17, or 18 based on what criteria of classifying metalloid elements is being used.
What are Metalloid Elements?
Metalloid elements, also known as semimetals, are elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals. The metalloid definition is considered to include between six to nine elements that occur along a slanted line between the metal and nonmetal elements of the periodic table. The six elements that are unanimously considered to be metalloids are the following:
How many types of metalloids are there?
There are three distinct categories of metalloid elements based on the number of valence electrons, and the chemical properties within each category are fairly similar.
What are the elements that are considered metalloids?
The six elements that are unanimously considered to be metalloids are the following: Boron. Silicon. Germanium. Arsenic. Antimony. Tellurium. Apart from these six elements, the definition of metalloid elements sometimes includes the elements bismuth, polonium, and astatine as well.
Why are metalloids ambiguous?
This ambiguity is in large part due to a lack of specific properties that are considered characteristics of all metalloids. Instead, the metalloid elements are simply characterized as having a mix of properties that are in between the properties of metals and nonmetals.
Which element has four valence electrons?
There are also two metalloid elements - silicon and germanium - which have exactly four valence electrons. These elements can act either as a metal (by giving up electrons) or nonmetal (by accepting electrons) depending on the other elements involved in the chemical reaction.
What are metalloids called?
Some metalloids such as silicon and germanium can act as electrical conductors under the specific conditions thus, they are called semiconductors.
What are the properties of metaloids?
8) Atomic properties: Metalloids are very diverse in their atomic characterization. There are some with great atomic weight. Such as polonium, its atomic weight is 127.6 and other elements such as boron weight has 10.81. And silicon has 28.08. Same happens with their densities ranging from 2.37 gram per centimeter cube (Boron) to 9.32 gram per centimeter cube (polonium).
What are semi-metallic materials used for?
10) Utility: Most semi-metallic materials are used to make electronic and semiconductor components such as rectifiers and transistors, even in the case of silicon chips and microprocessors. However, their versatility makes them very versatile. For example, some isotopes of boron are useful in neutron capture in nuclear power plants, which also serve as mechanisms for regulating atomic reactions.
Why do metals react differently?
5) Reactivity: Metals react differently due to their intermediate state depending on the presence of the metal element and then react as a non-metallic and then react as a metal. They are related to different elements depending on the element, which is why they are usually found with minerals such as uranium, lead, Sulphur etc.
What is the most common metal in the Earth's crust?
The most common metal in the earth’s crust is silicon, the second most common element overall ( oxygen is more common).
Can metalloids form alloys?
Similar to metals, metalloids can form alloys with other metals.
Is polonium a radioactive element?
May pose a health risk. Boron or arsenic themselves can be somewhat toxic, and polonium is a highly toxic, radioactive element that gives off harmful alpha particles.

About Metalloids
- Metalloids are actually those materials that have properties could belong to either metals or non-metals. Their properties somewhere similar to metals and non-metals both. Silicon is known as the best example of metalloids. These are located between Post-Transition metals and Non-metals on the periodic table. Many other elements are also included i...
Properties of Metalloids
- They are generally solids like metals, and brittle like non metals.
- Their ability to conduct heat is in between metals and non-metals.
- They conduct electricity at higher temperature.
- Some metalloids such as silicon and germanium can act as electrical conductors under the specific conditions thus, they are called semiconductors.
Characteristics of Metalloids
- 1) Occurrence:it can be found in the periodic table in diameters from boron (B) to statin (At). It is divided into columns 13, 14, 15, 16 and 17. The table is divided into two elements, the elements in the middle on the right are non-metallic and the elements on the left are metallic. 2) Form and coloration: The metalloids are varied in their shape and color. They can be transparent or opaqu…
Uses of Metalloids
- Silicon (SiO2)
- Silicon is a semiconductor and heavily used in electrical industries.
- It is also used in manufacture of water proof material called silicone such as bags, umbrellas, raincoats.
- Sand is the main ingredient in manufacturing of glass.
- Silicon (SiO2)
- Silicon is a semiconductor and heavily used in electrical industries.
- It is also used in manufacture of water proof material called silicone such as bags, umbrellas, raincoats.
- Sand is the main ingredient in manufacturing of glass.
- Other metalloids such as boron, galliumis also used in electrical devices.
Metalloids Interesting Facts
- The most common metal in the earth’s crust is silicon, the second most common element overall (oxygenis more common).
- The least natural mineral is tellurium. Metals are valuable in the electronics industry. For example, silicon is used to manufacture telephone and computer chips.
- Arsenic and poloniumsemimetals are highly toxic. Antimony and tellurium are mainly used in …
- The most common metal in the earth’s crust is silicon, the second most common element overall (oxygenis more common).
- The least natural mineral is tellurium. Metals are valuable in the electronics industry. For example, silicon is used to manufacture telephone and computer chips.
- Arsenic and poloniumsemimetals are highly toxic. Antimony and tellurium are mainly used in metal alloys to add desirable properties.