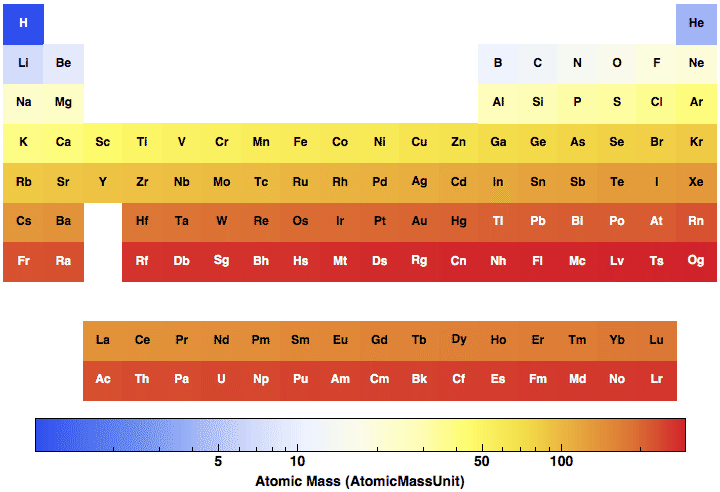
What is atomic mass and how is it determined?
The atomic mass of the atom is the mass of the protons plus the mass of the neutrons, 6 + 7, or 13. 3) Weighted Average for All Atoms of an Element The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average of all the element's isotopes based on their natural abundance. It is simple to calculate the atomic mass of an element with these steps.
Where is the atomic number located on the periodic chart?
The atomic number or proton number (symbol Z) of a chemical element is the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of that element. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element. It is identical to the charge number of the nucleus.
How do atomic masses vary throughout periodic table?
The atomic mass is the total number of nucleons (neutrons and protons) in an atom. The mass varies within an element based on the number of neutrons. Each variety of an atom within an element based on a different number of neutrons is called an isotope of that element.
What is 46 on the periodic table?
Palladium is a chemical element with atomic number 46 which means there are 46 protons and 46 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Palladium is Pd. Palladium, platinum, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium form a group of elements referred to as the platinum group metals (PGMs).
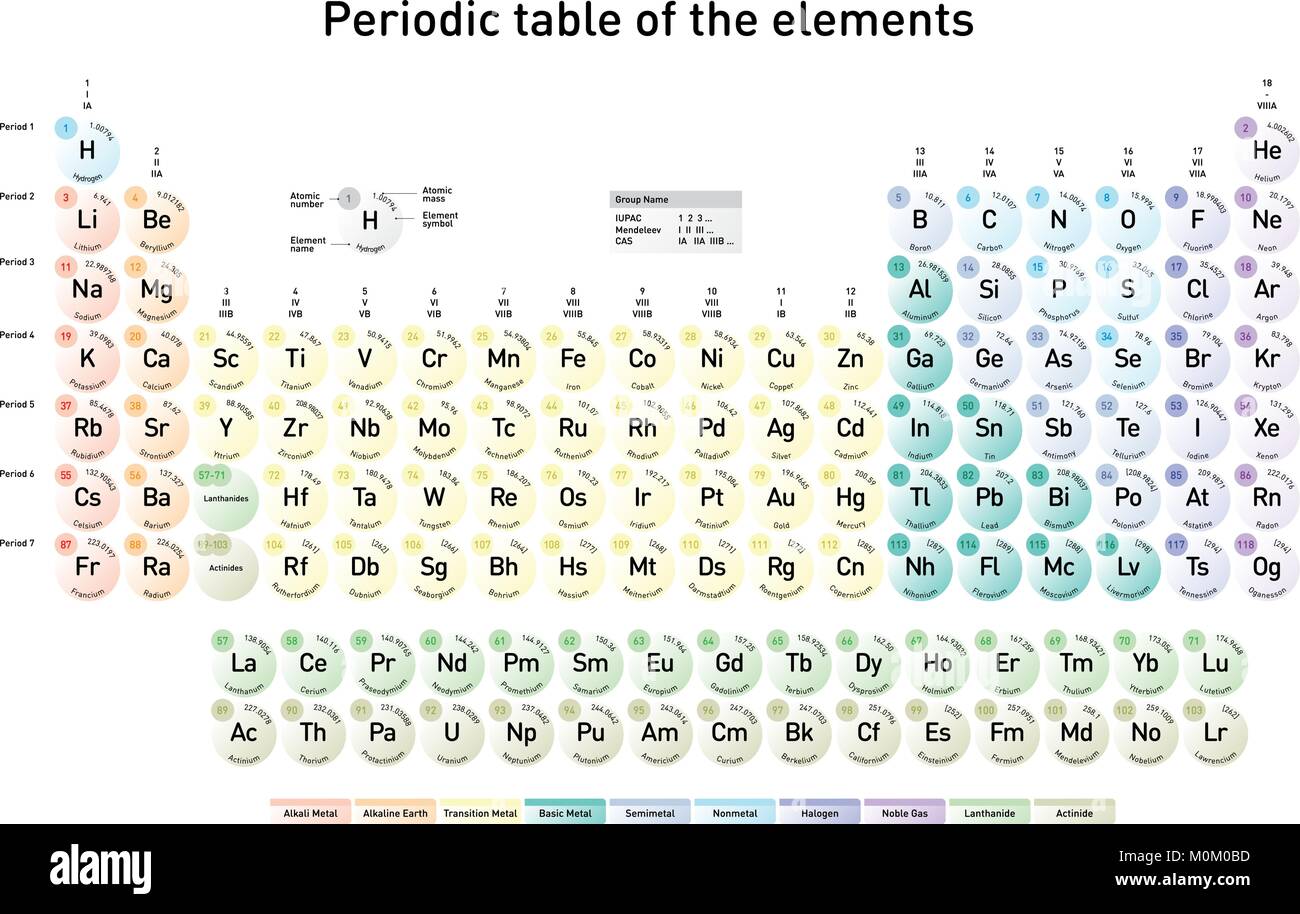
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).
Where is the mass number of an element?
The mass number is written either after the element name or as a superscript to the left of an element’s symbol . For example, the most common isotope of carbon is carbon-12, or 12 C.
What is the mass of a proton?
The mass of a proton is 1.00728 u and a neutron is 1.00867 u.
How do neutrons stabilize the nucleus?
Neutrons stabilize the nucleus, because they attract each other and protons , which helps offset the electrical repulsion between protons. As a result, as the number of protons increases, an increasing ratio of neutrons to protons is needed to form a stable nucleus. If there are too many or too few neutrons for a given number of protons, the resulting nucleus is not stable and it undergoes radioactive decay . Unstable isotopes decay through various radioactive decay pathways, most commonly alpha decay, beta decay, or electron capture. Many other rare types of decay, such as spontaneous fission or neutron emission are known. It should be noted that all of these decay pathways may be accompanied by the subsequent emission of gamma radiation. Pure alpha or beta decays are very rare.
What is the sum of the baryon number of all incoming particles?
The sum of the baryon number of all incoming particles is the same as the sum of the baryon numbers of all particles resulting from the reaction.
What is the nucleus of an atom?
The atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic mass number (or the mass number) of the atom and is given the symbol A.
Which is heavier, a proton or a neutron?
The neutron is slightly heavier than the proton. This increases the mass of nuclei with more neutrons than protons relative to the atomic mass unit scale based on 12 C with equal numbers of protons and neutrons.
How much is one unified atomic mass unit?
One unified atomic mass unit is approximately the mass of one nucleon (either a single proton or neutron) and is numerically equivalent to 1 g/mol.
What is Atomic Mass?
Atoms are the smallest units of elements, or the simplest substances that cannot be broken down further chemically. Both atoms and elements are organized onto a display called the periodic table of elements.
How to find the mass of an atom?
Another way to find the atomic mass of an atom is to add up the total mass of protons, neutrons, and electrons. But, because electrons are 1/1865th the mass of a proton or neutron, it is okay to simply add up the number of protons and the number of neutrons to get atomic mass. Adding up the masses of an atom's electrons when determining the mass is mostly only relevant when measuring the exact atomic mass differences between ions of the same element. Ions are atoms that are missing or have additional electrons when comparing them to the number of protons in the atom. To find the atomic mass of an element, one can look at the average atomic mass of an atom on the periodic table of elements.
How does a mass spectrometer work?
In more detail, a mass spectrometer first vaporizes a sample so that all the atoms float freely, then ionizes the sample or changes the charge of each atom by adding or taking away electrons. Next, the now charged atoms are sent through a chamber that influences the sample with an electromagnet. Because each atom is charged the electromagnet will affect and move each atom. Additionally, because the sample might be made up of different atoms of different masses, each atom will be influenced by the electromagnet based on their masses and inertia - so that each atom ends up in a stream of other atoms of the same mass. Once the atoms are separated into streams, they are captured and detected by a system that then measures the mass of the stream and calculates what percentage of the sample is made of which elements and isotopes. Being able to measure the atomic mass of atoms and therefore identify the atoms that make up a substance or sample has become extremely useful among many disciplines in science. By identifying the atoms that make up a sample, scientists can consequently use a mass spectrometer to date samples by using a method called radiometric dating. One of the most accurate radiometric dating methods is uranium-lead dating.
How to find the average atomic mass of an element?
When looking at a periodic table of elements, there is a number under each element that has decimal places. This is the average atomic mass of that element. Atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons but can vary in their number of neutrons. So, each element will have different isotopes, or atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. When looking at carbon on the periodic table, it says carbon has an average atomic mass of 12.011 amu. This number is determined by the fact that in any sample of carbon there are some atoms of carbon that have masses of 13 amu and 14 amu because carbon-13 atoms have 7 neutrons and carbon-14 atoms have 8 neutrons.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is equal to the amount of protons that are contained in one atom of that element. Each element is made up of atoms that all have the same number of protons. For example, all carbon atoms have 6 protons, so carbon's atomic number is '6.'
How is the age of the Earth determined?
The age of the earth was determined by using uranium-lead dating. Zircons were sent through a mass spectrometer to determine the uranium-lead ratio inside their crystalline structures. Zircons are commonly used in radiometric dating because they are a mineral made of uranium and thorium, but they strongly reject lead while they are forming. Therefore, if any lead is found in a zircon, the lead formed from the decay of uranium atoms. That is, zircons are like little atomic clocks that that decay at a predictable rate. So, when Clair Patterson, a geophysicist, was hired to calculate the age of the earth, he was given zircons that were found in a meteorite because most meteorites likely formed near the beginning of our solar system.
Why are hydrogen isotopes different in atomic mass?
Examples of hydrogen isotopes which differ in atomic mass because they differ in numbers of neutrons.
How to find the mass of an element?
The number of protons and the number of neutrons shall determine the mass number of an element. Since the isotopes of an element have slightly different mass numbers, it calculates the atomic mass by obtaining the mean of the mass numbers for its isotopes.
What is the name of the tabular arrangement of all the elements on the basis of their respective atomic numbers?
The periodic table is the tabular arrangement of all the chemical elements on the basis of their respective atomic numbers. In the periodic table , the vertical columns are called ‘groups’ and the horizontal rows are called ‘periods’.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is equal to the total number of protons in the nucleus of the atoms of that element. The atomic number can provide insight into the electronic configuration of the element. For example, carbon has an electron configuration of [He] 2s 2 2p 2, since its atomic number is 6.
What is the number of protons in the nucleus called?
The number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number. The atomic number of each element is unique.
Why is the atomic number of each element unique?
While the atomic number always stays the same some elements have atoms with different atomic mass numbers. This is because some elements have a different number of neutrons in the nucleus.
How can periodic trends be observed?
Periodic trends in the properties of the elements can be observed down the groups and across the periods of the modern periodic table. Every chemical element has a specific atomic number, which provides insight into the number of protons present within its nucleus.
Why is the atomic number important?
This number is very important, because it is unique to a given element’s atoms. An element’s atoms all have the same number of protons and each element has a different number of protons in its atoms. Test your knowledge on periodic table elements.