Where are the coinage metals on the periodic table?
coinage metals are low reactive metals which are present in the d-block,1B group which are Copper (Cu),Silver (Ag) and Gold (Au), also it is an interesting thing to note that all these elements have the latin names and symbols which are Cuprum,Argentinum,Aurum respectively thank you. 182 views
Where are heavy metals located on the periodic table?
Heavy metals and their effects on the environment and biosphere It is crucial to note that several trace elements in the heavy metal family are required for many biological activities; they are mostly found in Period 4 of the periodic table of elements. The term "heavy metal" refers to any chemical element with a density greater than 5 g/cm3.
Where are semi metals on the periodic table?
- metals are found on the left hand side of the table;
- non-metals are found on the far right hand side of the table; and
- semi-metals are found in the region between the metals and non-metals.
What are all the metals on the periodic table?
Types of metals on the Periodic table
- Alkali metals. Alkali metals are located on the left most side of the Periodic table in group 1. ...
- Alkaline earth metals. Alkaline earth metals are located on the left side of the Periodic table in group 2. ...
- Transition metals. ...
- Inner transition metals. ...
- Post transition metals. ...
- Rare earth metals. ...
- Heavy metals. ...
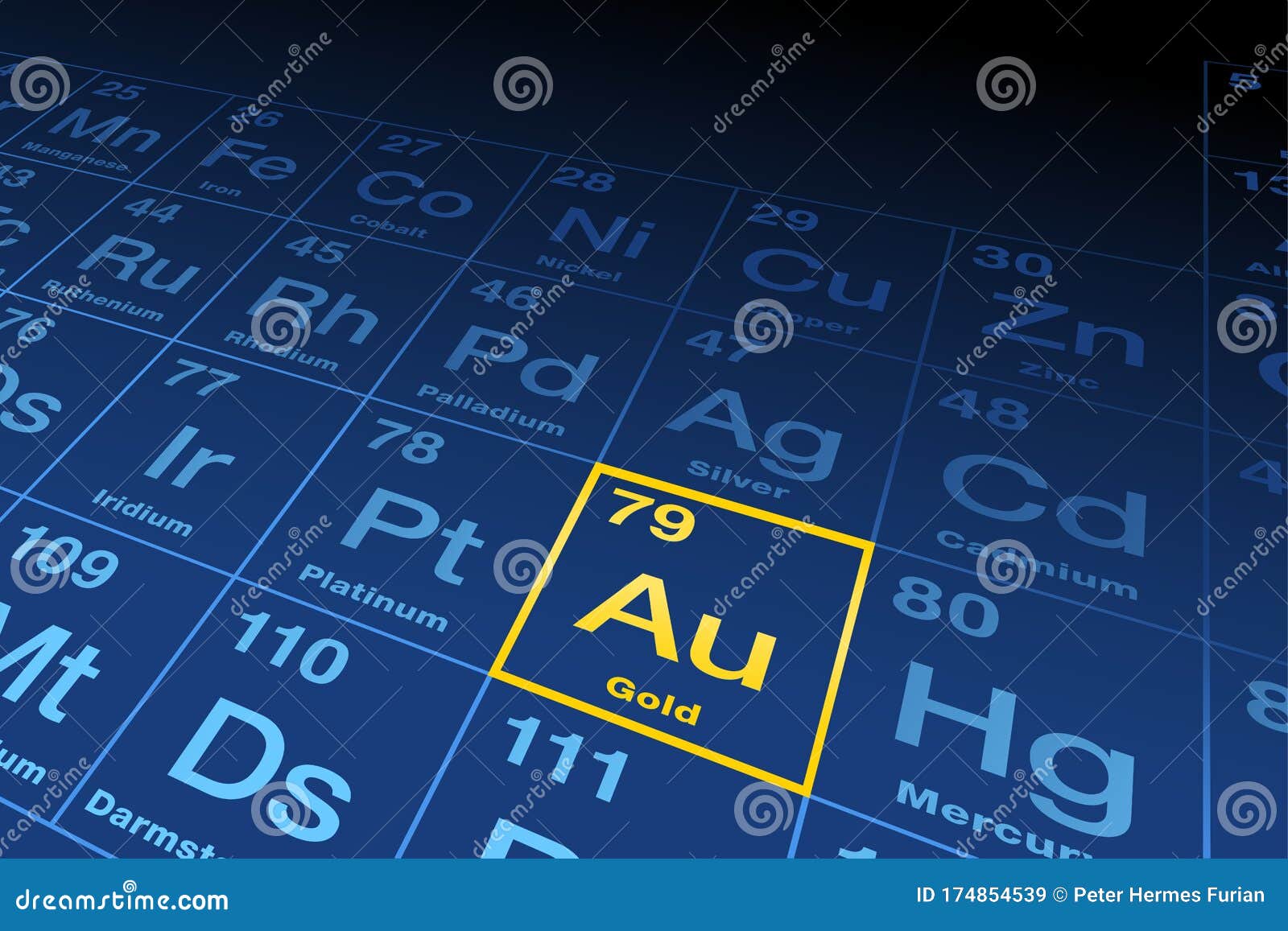
What periodic group is gold?
gold (Au), chemical element, a dense lustrous yellow precious metal of Group 11 (Ib), Period 6, of the periodic table of the elements.
What is Group 11 on the periodic table called?
Group 11: Transition Metals.
Where is gold and silver on the periodic table?
Group 11Group 11, by modern IUPAC numbering, is a group of chemical elements in the periodic table, consisting of copper (Cu), silver (Ag), and gold (Au).
Is gold part of metal?
Gold is a soft, yellow metal. Like all other metals, gold is also highly malleable and ductile. Moreover, gold is able to conduct both electricity and heat rather easily. The atomic number of gold is 79, and its elemental abbreviation is Au, from the Latin 'aurum' meaning 'shining dawn'.
What metal is closest to gold?
Pinchbeck is a form of brass, an alloy of copper and zinc mixed in proportions so that it closely resembles gold in appearance. It was invented in the early 18th century by Christopher Pinchbeck (died 1732), a London clock- and watch-maker.
Is gold a main group element?
Examples of main group elements include helium, lithium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. Elements that are not main group elements are the transition metals (such as titanium, copper, and gold), the lanthanides (such as lanthanum and erbium), and the actinides (such as actinium and plutonium).
Are silver and gold found together?
Silver and gold are often found together since they exist in the same base ore material.
Is gold or silver a metal?
Gold and silver have been recognized as valuable metals and were highly coveted by ancient civilizations. Precious metals still have their place in a savvy investor's portfolio in modern times.
What color is gold on the periodic table?
Data ZoneClassification:Gold is a transition metalColor:golden yellowAtomic weight:196.9665State:solidMelting point:1064.18 oC, 1337.33 K7 more rows
What metal is gold called?
Gold is element 79 and its symbol is Au. Though the name is Anglo Saxon, gold originated from the Latin Aurum, or shining dawn, and previously from the Greek. It's abundance in the earth's crust is 0.004 ppm. 100% of gold found naturally is isotope Au-197.
What is pure gold made of?
WHAT IS PURE GOLD? It's simply gold made with 100% gold, without any other metals or alloys mixed in. That means it's the most precious and expensive type of gold jewelry you can buy.
What metal is gold?
transition metalChemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions.
What does 11 mean in the periodic table?
We know that the atomic number of sodium is 11.
What is 11th periodic table?
Sodium - Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table.
What is an element Class 11?
Element is a pure substance made up of only one kind of atom which can't be split up into two or more substance. compound is a pure substance made up of two or more substance combined in fixed proportion by mass.
Is group 11 an alkali metal?
The alkali metals make up Group 1 of the periodic table. This family consists of the elements lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and Fr, respectively). Group one elements share common characteristics.
Where Is Gold Found On The Periodic Table?
Gold is the 79 th element on the periodic table. It is located in period 6 and group 11.
What is the only metal with a yellow metallic appearance?
Like other transition metals, gold is in the middle of the periodic table. It is the only metal that has a distinctive yellow metallic appearance in pure form, although there are other elements that oxidize to develop a golden tint.
Is gold a hard metal?
While most metals are hard, pure gold is actually quite soft. The metal is easily drawn into a wire (ductile), hammered (malleable), and is one of the best conductors of heat and electricity. Cite this Article. Format. mla apa chicago. Your Citation.
Gold in Periodic table
Gold element is in group 11 and period 6 of the Periodic table. Gold is the d-block element and it belongs to transition metals group.
Is Gold a Transition Metal? Why?
Yes, Gold is a transition metal because it has incompletely filled d-orbital in its common oxidation state (Au3+).
Properties of Gold
The physical and chemical properties of gold element are mentioned below.
Free Gift for you: Interactive Periodic Table
Let me tell you how this Interactive Periodic Table will help you in your studies.
What is the oxidation state of an atom?
The oxidation state of an atom is a measure of the degree of oxidation of an atom. It is defined as being the charge that an atom would have if all bonds were ionic. Uncombined elements have an oxidation state of 0. The sum of the oxidation states within a compound or ion must equal the overall charge.
What is density in science?
Density is the mass of a substance that would fill 1 cm 3 at room temperature. Relative atomic mass. The mass of an atom relative to that of carbon-12. This is approximately the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
What is the vertical column in the periodic table?
A vertical column in the periodic table. Members of a group typically have similar properties and electron configurations in their outer shell. A horizontal row in the periodic table. The atomic number of each element increases by one, reading from left to right.
What is the difference between 24 carat and 9 carat gold?
The term ‘carat’ indicates the amount of gold present in an alloy. 24-carat is pure gold, but it is very soft. 18- and 9-carat gold alloys are commonly used because they are more durable.
What is gold used for in dentistry?
Dentists sometimes use gold alloys in fillings, and a gold compound is used to treat some cases of arthritis.
What is gold used for?
The metal is also used for coinage, and has been used as standard for monetary systems in some countries. Gold can be beaten into very thin sheets (gold leaf) to be used in art, for decoration and as architectural ornament. Electroplating can be used to cover another metal with a very thin layer of gold.
Why does gold fall to the bottom?
Because it is found in it's natural state and does not naturally alloy with anything else and because it is the heaviest metal, by sifting rock in water, the gold always falls to the bottom and all less dense impurities are washed away.
Where is gold found on Earth?
Gold is widely present in the Earth’s crust (0.3 ppm by weight). It is also present in river beds as rock bound gold is released by erosion of rock by running water. Gold also exists in the form of alloy, such as amalgam (with mercury) or with silver. Gold is found in association of pyrites deposits and from quarts and gravels. Naturally, most of the gold present in the Earth’s crust is in combination with silver. The term “electrum” is used for gold ore that have silver content of more than 20%. The biggest producer of gold is China from around two third of the gold (around 455 tons) in world is produced. The other countries where gold is being mined include USA, Canada and Russia. The annual production of gold in the world is 2500 tons per year. Oceans, including the Northeast Pacific and Atlantic contain about 10–30 parts per quadrillion, that makes about 10–30 g/km 3 of gold in form of flakes or nuggets [3].
Where did gold come from?
The word gold has been originated from the word “geolo” used by Anglo-Saxon civilization that inhabited England in the 5 th century. Geolo (Sanskrit origin meaning to shine) means yellow. The symbol of gold comes from a word of Latin origin, aurum, which is originated from Aurora, which is the goddess of morning glow [2].
How many isotopes of gold are there?
There are 35 isotopes of gold, with mass numbers ranging from 171 to 205. These are the artificially produced isotopes of gold. The natural gold consists of one stable isotope, Au-197, which is the only stable isotope. The isotopes with atomic masses above 197 decay by emission of β rays [6].
Why is gold used in astronaut helmets?
Gold plating is used in helmets used by astronauts as gold due to its inert nature can provide protection against dangerous and harmful effects of solar radiations. Radioactive isotope of gold (Au-198) has been used to treat various cancers including prostate and bladder.
What is gold used for?
Uses and Significance. Gold is a precious metal and widely used in making of jewellery, coinage, crowns and decorative items. It is widely used in making components of computerized devices, such as corrosion resistant electrical conductors. Gold is used in the glass industry for making colored-glass. It is used as fillers in tooth restoration.
What can gold react with?
Gold can react with certain halogens, such as fluorine to form gold (III) fluoride. Gold in powdered form can react with chlorine to form gold chloride. Various alloys of gold are formed to alter the strength and hardness of gold and create exotic colors [5].
How much gold is produced in the world?
The annual production of gold in the world is 2500 tons per year. Oceans, including the Northeast Pacific and Atlantic contain about 10–30 parts per quadrillion, that makes about 10–30 g/km 3 of gold in form of flakes or nuggets [3].
What is the oxidation state of gold?
Less common oxidation states of gold include −1, +2, and +5. The −1 oxidation state occurs in aurides, compounds containing the Au − anion. Caesium auride (CsAu), for example, crystallizes in the caesium chloride motif; rubidium, potassium, and tetramethylammonium aurides are also known.
What is the most noble metal?
Although gold is the most noble of the noble metals, it still forms many diverse compounds. The oxidation state of gold in its compounds ranges from −1 to +5, but Au (I) and Au (III) dominate its chemistry. Au (I), referred to as the aurous ion, is the most common oxidation state with soft ligands such as thioethers, thiolates, and tertiary phosphines. Au (I) compounds are typically linear. A good example is Au (CN) 2−, which is the soluble form of gold encountered in mining. The binary gold halides, such as AuCl, form zigzag polymeric chains, again featuring linear coordination at Au. Most drugs based on gold are Au (I) derivatives.
What element is used to make gold?
The possibile production of gold from a more common element, such as lead, has long been a subject of human inquiry, and the ancient and medieval discipline of alchemy often focused on it; however, the transmutation of the chemical elements did not become possible until the understanding of nuclear physics in the 20th century. The first synthesis of gold was conducted by Japanese physicist Hantaro Nagaoka, who synthesized gold from mercury in 1924 by neutron bombardment. An American team, working without knowledge of Nagaoka's prior study, conducted the same experiment in 1941, achieving the same result and showing that the isotopes of gold produced by it were all radioactive.
What color is gold?
Whereas most metals are gray or silvery white, gold is slightly reddish-yellow. This color is determined by the frequency of plasma oscillations among the metal's valence electrons, in the ultraviolet range for most metals but in the visible range for gold due to relativistic effects affecting the orbitals around gold atoms. Similar effects impart a golden hue to metallic caesium .
How many tonnes of gold are there in the world?
A total of 197,576 tonnes of gold exists above ground, as of 2019. [update] .
What is the cation of gold II?
A gold (II) complex, the tetraxenonogold (II) cation, which contains xenon as a ligand, occurs in [AuXe 4 ] (Sb 2 F 11) 2. Gold pentafluoride, along with its derivative anion, AuF−. 6, and its difluorine complex, gold heptafluoride, is the sole example of gold (V), the highest verified oxidation state.
Why did gold sink into the Earth's core?
Because the Earth was molten when it was formed , almost all of the gold present in the early Earth probably sank into the planetary core. Therefore, most of the gold that is in the Earth's crust and mantle has in one model thought to have been delivered to Earth later, by asteroid impacts during the Late Heavy Bombardment, about 4 billion years ago.
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).
What is the CIAAW?
Since 1899 the IUPAC Commission on Isotopic Abundances and Atomic Weights ( CIAAW) has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. For example, Carbon had an atomic weight of 12.00 in 1902 but today it is [12.0096, 12.0116]! Times sure have changed as the source of the sample will determine the value.
What is PubChem working with?
PubChem is working with IUPAC to help make information about the elements and the periodic table machine-readable.
Who is responsible for deciding what needs to be changed?
While much of what is in the periodic table is stable and unlikely to change, the IUPAC organization is responsible for deciding what needs to be changed. They have created criteria for what constitutes the discovery of a new element.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Did Mendeleev's predictions get dismissed?
There were plenty of skeptics and it took years to gain international acceptance, but once newly-discovered elements matched the ones that Mendeleev predicted, his patterns could not be dismissed. In addition, some of the properties that he "fudged" were later recalculated and found to be much closer to his predictions.
Who knew?
Two-thirds of the world's gold is mined in South Africa, according to Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory.
How much gold is in a ring?
Pure gold is 24 karats. Bars of gold kept in Fort Knox and elsewhere around the world are considered to be 99.95 percent pure, 24-karat gold.
How much does a bar weigh?
Each bar weighs 400 troy ounces according to the U. S. Department of Treasury. One troy ounce equals about 1.1 avoirdupois ounces. The entire stockpile now weighs 147.3 million troy ounces, which is worth about $130 billion at today's prices.
What is the vein of gold?
Veins of gold mined from the earth are the result of hot fluids flowing through gold-bearing rock, picking up gold and concentrating it in fractures, according to the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH).
How tall is the gold vault at Fort Knox?
To quell people’s fears, the director of the United States Mint guided congressmen and journalists through one room of the vault, and its 8-foot-tall stacks of 36,236 bars of gold.
What is the average mass of an atom?
Atomic Weight (average mass of the atom): 196.9665
What is gold used for?
Facts About Gold. It's a pirate's booty and an ingredient in microcircuits. It's been used to make jewelry since at least 4000 B.C. and to treat cancer only in recent decades. It's in the pot at the end of the rainbow and in the coating on astronaut visors.
What is the energy of ionization?
The first ionization energy is the energy it takes to remove one electron from an atom, the second ionization energy is the energy it takes to remove a second electron from the atom, and so on. For a given atom, successive ionization energies increase with the degree of ionization. For magnesium as an example, the first ionization energy is 738 kJ/mol and the second is 1450 kJ/mol. Electrons in the closer orbitals experience greater forces of electrostatic attraction; thus, their removal requires increasingly more energy. Ionization energy becomes greater up and to the right of the periodic table.
What is the atomic number plotted against?
Atomic number plotted against atomic radius, excluding the noble gases. Atomic radii vary in a predictable and explainable manner across the periodic table. For instance, the radii generally decrease along each period of the table, from the alkali metals to the noble gases; and increase down each group.
What is the electron configuration of a neutral atom?
The electron configuration or organisation of electrons orbiting neutral atoms shows a recurring pattern or periodicity. The electrons occupy a series of electron shells (numbered 1, 2, and so on). Each shell consists of one or more subshells (named s, p, d, f and g). As atomic number increases, electrons progressively fill these shells and subshells more or less according to the Madelung rule or energy ordering rule, as shown in the diagram. The electron configuration for neon, for example, is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. With an atomic number of ten, neon has two electrons in the first shell, and eight electrons in the second shell; there are two electrons in the s subshell and six in the p subshell. In periodic table terms, the first time an electron occupies a new shell corresponds to the start of each new period, these positions being occupied by hydrogen and the alkali metals.
What are metals and nonmetals?
In chronological order, this section discusses metals and nonmetals (and metalloids); categories of elements; groups and periods; and periodic table blocks. While the recognition of metals as solid, fusible and generally malleable substances dates from antiquity, Antoine Lavoisier may have the first to formally distinguish between metals and nonmetals ('non-métalliques') in 1789 with the publication of his 'revolutionary' Elementary Treatise on Chemistry. In 1811, Berzelius referred to nonmetallic elements as metalloids, in reference to their ability to form oxyanions. In 1825, in a revised German edition of his Textbook of Chemistry, he subdivided the metalloids into three classes. These were: constantly gaseous 'gazolyta' (hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen); real metalloids (sulfur, phosphorus, carbon, boron, silicon); and salt-forming 'halogenia' (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine). Only recently, since the mid-20th century, has the term metalloid been widely used to refer to elements with intermediate or borderline properties between metals and nonmetals. Mendeleev published his periodic table in 1869, along with references to groups of families of elements, and rows or periods of his periodic table. At the same time, Hinrichs wrote that simple lines could be drawn on a periodic table in order to delimit properties of interest, such as elements having metallic lustre (in contrast to those not having such lustre). Charles Janet, in 1928, appears to have been the first to refer to the periodic table's blocks.
How many electrons are in neon?
The electron configuration for neon, for example, is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. With an atomic number of ten, neon has two electrons in the first shell, and eight electrons in the second shell; there are two electrons in the s subshell and six in the p subshell. In periodic table terms, the first time an electron occupies a new shell corresponds to ...
What are the columns of periodic table called?
The seven rows of the table, called periods, generally have metals on the left and nonmetals on the right. The columns, called groups , contain elements with similar chemical behaviours.
How many categories are there in the periodic table?
The elements of the periodic table shown here are divided into nine categories; six for the metals, and two for nonmetals, and a metalloid category. The nine categories (or sets) correspond to those found in the literature for the applicable part of the periodic table. Different authors may use different categorisation schema depending on the properties of interest.