What is atomic mass and how is it determined?
The atomic mass of the atom is the mass of the protons plus the mass of the neutrons, 6 + 7, or 13. 3) Weighted Average for All Atoms of an Element The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average of all the element's isotopes based on their natural abundance. It is simple to calculate the atomic mass of an element with these steps.
Where is the atomic number located on the periodic chart?
The atomic number or proton number (symbol Z) of a chemical element is the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of that element. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element. It is identical to the charge number of the nucleus.
How do atomic masses vary throughout periodic table?
The atomic mass is the total number of nucleons (neutrons and protons) in an atom. The mass varies within an element based on the number of neutrons. Each variety of an atom within an element based on a different number of neutrons is called an isotope of that element.
What is 46 on the periodic table?
Palladium is a chemical element with atomic number 46 which means there are 46 protons and 46 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Palladium is Pd. Palladium, platinum, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium form a group of elements referred to as the platinum group metals (PGMs).

How do you find the atomic mass on a periodic table?
0:552:23Understanding Atomic Number and Atomic Mass - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe number that appears below the element symbol is called the atomic mass the mass of an atomMoreThe number that appears below the element symbol is called the atomic mass the mass of an atom depends on the number of protons neutrons.
Is atomic mass included in the periodic table?
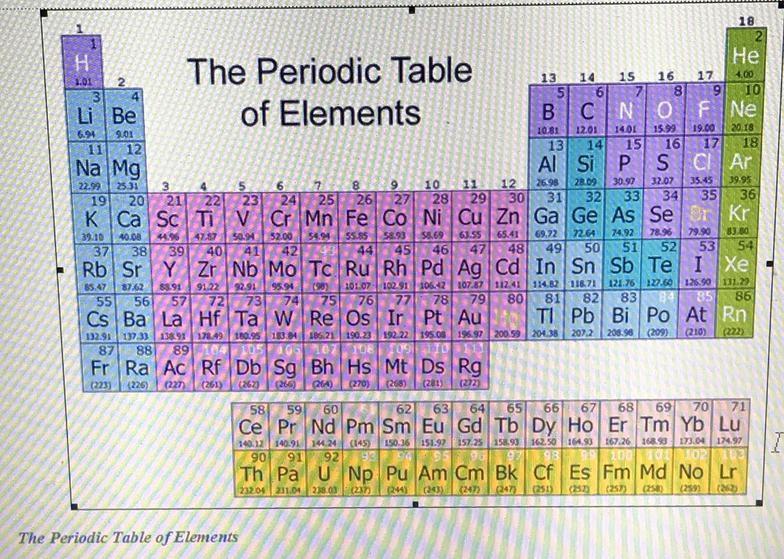
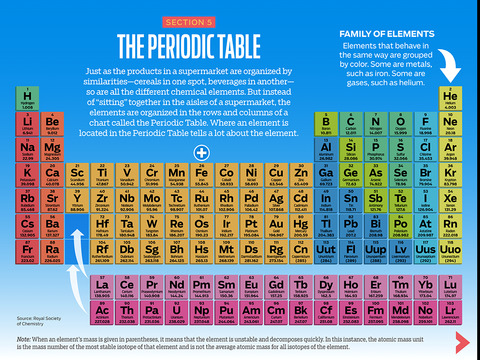
This is a periodic table with atomic mass, element name, element symbol, and atomic number. The atomic mass is the average number of protons and neutrons in atoms of a chemical elements, allowing for the natural abundances of the element's isotopes.
Why is the atomic mass on the periodic table a decimal?
Answer and Explanation: Many of the atomic masses listed on the periodic table are decimal values because it's the weighted average mass of all of the isotopes of that element. The mass of each isotope of an element is multiplied by its percent abundance in nature.
Why are elements on the periodic table not arranged by mass?
Elements are not ordered by mass, but by atomic number, or the number of protons. This is because ordering them by atomic number causes the properties of elements to repeat due to the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus.
Is mass number and atomic mass same?
Mass number is a whole number because it is the sum of number of proton and number of neutrons whereas atomic mass is fractional because it is the average relative mass of its atoms as compared with mass an atom of C-12 isotope taken as 12.
What is atomic number of periodic table?
In the modern periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons define the identity of an element (i.e., an element with 6 protons is a carbon atom, no matter how many neutrons may be present).
What are the first 20 elements of the periodic table?
The first 20 Elements of the Periodic Table: Hydrogen, Helium, Lithium, Beryllium, Boron, Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine, Neon, Sodium, Magnesium, Aluminium, Silicon, Phosphorus, Sulphur, Chlorine, Argon, Potassium, Calcium. The symbol for sodium is "Na".
What is atomic mass and atomic number?
Atomic mass is associated with the number of neutrons and protons that are present in a particular nucleus of an element. Atomic number is usually the number of protons present in an element's nucleus. It is the average weight of an element.
What is the atomic mass of a periodic table?
The atomic mass (atomic weight) values cited on a periodic table are weighted averages of naturally occurring isotopes. From one year to the next, the values may change slightly (usually only in the last significant digit) as more information about the source of each element becomes available.
What is the black and white periodic table?
This black and white periodic table contains the accepted atomic weights of each element as accepted by the IUPAC.
Where do the accepted values apply to chemistry?
For most chemistry calculations, the most recent table of accepted values should be used. These values do not apply to elements collected anywhere except the Earth's crust. The weighted atomic mass for an element from the Earth's core, the Moon, the Sun, etc., would not be the same as the accepted value.
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).
What is the atomic mass unit?
The Atomic masses are represented in the Atomic mass unit (u). The elements whose atomic masses are written in bracket ( ) are the synthetic elements and their atomic masses values represent the Atomic Mass of the most stable isotope.
When is the atomic mass of all elements 2021?
Atomic Mass of all Elements (Chart + Rounded values) June 10, 2021 March 7, 2021 by Admin. Atomic mass of all elements (along with the rounded off values) is mentioned in the chart below. Atomic Number.
What Is Atomic Mass?
Atomic mass is the sum of the masses of the protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom, or the average mass, in a group of atoms. However, electrons have so much less mass than protons and neutrons that they don't factor into the calculation. So, the atomic mass is the sum of the masses of protons and neutrons. There are three ways to find atomic mass, depending on your situation. Which one to use depends on whether you have a single atom, a natural sample of the element, or simply need to know the standard value.
How to find the mass of an element?
To calculate the atomic mass of a single atom of an element, add up the mass of protons and neutrons.
Why do the atomic mass values on the periodic table change?
This happens when scientists revise the estimated isotope ratio in the crust. In modern periodic tables, sometimes a range of values is cited rather than a single atomic mass.
How to find the mass of an isotope?
Multiply each isotope's mass by its abundance. If your abundance is a percent, divide your answer by 100. Add these values together. The answer is the total atomic mass or atomic weight of the element.
Is electron mass factored in chemistry?
Electrons are much smaller than protons and neutrons, so their mass isn't factored into the calculation. Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. You may be asked to calculate atomic mass in chemistry ...
Is the atomic mass of carbon higher than the periodic table?
Advanced Note: This atomic mass is slightly higher than the value given in the periodic table for the element carbon. What does this tell you? The sample you were given to analyze contained more carbon-13 than average. You know this because your relative atomic mass is higher than the periodic table value, even though the periodic table number includes heavier isotopes, such as carbon-14. Also, note the numbers given on the periodic table apply to the Earth's crust/atmosphere and may have little bearing on the expected isotope ratio in the mantle or core or on other worlds.