
Who is credited with arranging the periodic table?
While Dmitri Mendeleev usually gets credit for the invention of the modern periodic table in 1869, Alexandre-Emile Béguyer de Chancourtois organized the elements by atomic weight five years earlier. While Mendeleev and Chancourtois arranged elements by atomic weight, the modern periodic table is ordered according to increasing atomic number (a concept unknown in the 19th century.)
Who was originally put the periodic table together?
The periodic table was originally put together by the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev. He originally set up the periodic table around the existing 63 elements in 1869. He organized them in increasing atomic mass, and in periods (rows) and groups (columns) or specific properties.
Who made the periodic table and why?
The periodic table was invented by chemist Dmitri Mendeleev to organize and compare elements and understand their relations with each other. Mendeleev created the periodic table between 1868 and 1870 while writing his book titled "The Principles of Chemistry." Initially, Mendeleev created the chart for his personal benefit, but others quickly discovered its value, leading to its immediate ...
Who put the periodic table together first?
- The new chart groups elements by atomic radius and electronegativity
- Elements that can form binary compounds, like hydrogen and oxygen, are listed together
- The approach helps scientists predict the properties of yet-to-be-discovered substances
- The precursor to the modern periodic chart was designed by Dimitri Mendeleev in 1869
Who added elements to the periodic table?
Mendeleev himself added these elements to the table as group 0 in 1902, without disturbing the basic concept of the periodic table. In 1905, Swiss chemist Alfred Werner resolved the dead zone of Mendeleev 's table. He determined that the rare-earth elements ( lanthanides ), 13 of which were known, lay within that gap.
Who published the periodic table?
Main table of the periodic table published by Australian chemist David Orme Masson in 1895
What is the difference between Mendeleev and Meyer?
Mendeleev's intent was to aid composition of his textbook, Foundations of Chemistry, whereas Meyer was rather concerned with presentation of theories. Mendeleev's predictions emerged outside of the pedagogical scope in the realm of journal science, while Meyer made no predictions at all and explicitly stated his table and his textbook it was contained in, Modern Theories, should not be used for prediction in order to make the point to his students to not make too many purely theoretically constructed projections.
What did Mendeleev think of the elements?
Mendeleev noticed that there was a significant difference in atomic mass between cerium and tantalum with no element between them; his consideration was that between them, there was a row of yet undiscovered elements, which would display similar properties to those elements which were to be found above and below them: for instance, an eka-molybdenum would behave as a heavier homolog of molybdenum and a lighter homolog of wolfram (the name under which Mendeleev knew tungsten ). This row would begin with a trivalent lanthanum, a tetravalent cerium, and a pentavalent didymium. However, the higher valency for didymium had not been established, and Mendeleev tried to do that himself. Having had no success in that, he abandoned his attempts to incorporate the rare-earth metals in late 1871 and embarked on his grand idea of luminiferous ether. His idea was carried on by Austrian-Hungarian chemist Bohuslav Brauner, who sought to find a place in the periodic table for the rare-earth metals; Mendeleev later referred to him as to "one of the true consolidators of the periodic law".
What elements did Mendeleev predict?
In 1870, he first tried to characterize the yet undiscovered elements, and he gave detailed predictions for three elements, which he termed eka-boron, eka-aluminium, and eka-silicium, as well as more briefly noted a few other expectations. It has been proposed that the prefixes eka, dvi, and tri, Sanskrit for one, two, and three, respectively, are a tribute to Pāṇini and other ancient Sanskrit grammar ians for their invention of a periodic alphabet. In 1871, Mendeleev expanded his predictions further.
What are the four elements that are considered elements?
The four roots, which were later renamed as elements by Plato, were earth, water, air and fire. Similar ideas about these four elements also existed in other ancient traditions, such as Indian philosophy . A few extra elements were known in the age of alchemy ( zinc, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth ).
What are the elements that are found in ancient times?
Early history. Further information: Classical element. A number of physical elements ( carbon, sulfur, iron, copper, silver, tin, gold, mercury, and lead) have been known from antiquity, as they are found in their native form and are relatively simple to mine with primitive tools.
Who created the periodic table?
This was the first and very important arrangement created by Dmitri Mendeleev in the year 1869. Many chemists considered this as a very important classification. I know you can’t read anything from the above image (hahaha).
When was the periodic table first created?
And if the property of elements didn’t match, then he placed it in the row. In this way, Mendeleev prepared his first Periodic table in 1869.
Why did Mendeleev put nickel and cobalt together?
But Mendeleev placed Cobalt (Co) along with Rhodium (Rh) because Cobalt (Co) and Rhodium (Rh) were having similar properties. Also the properties of Nickel (Ni) is similar to the Palladium element (Pd), so he placed Nickel (Ni) along with Palladium (Pd). Tellurium (Te) and Iodine (I) also show the exceptions.
What did Mendeleev find?
Now during the year 1869, Mendeleev was finding the relation between atomic mass of elements and their physical and chemical properties. Mendeleev found the chemical properties of known elements through their chemical reaction with hydrogen and oxygen. But the question is;
How many elements were in Mendeleev's first periodic table?
The elements in this First Periodic table were arranged in the increasing order of their atomic masses, and there were only 63 elements in his table. The genius work which Mendeleev did was to leave empty gaps for ...
Why did Mendeleev place some elements with higher atomic mass before lower ones?
The simple answer: Mendeleev placed some elements with higher atomic mass before lower ones, so that he can group the elements with similar properties together.
When was Mendeleev's periodic table created?
In this way, Mendeleev prepared his first Periodic table in 1869. The modified version of Mendeleev’s Periodic table is as shown below. The important thing to note down here is that the elements in the above table are arranged in the increasing order of their Atomic Masses. The vertical columns are called the groups and ...
When was the periodic table first published?
Periodic table at the Chemical Auditorium of the Gdańsk University of Technology, 1904. The first version of Mendeleev's periodic table, 1 March 1869 (N.S.): An attempt at a system of elements based on their atomic weights and chemical similarities.
What is the periodic table?
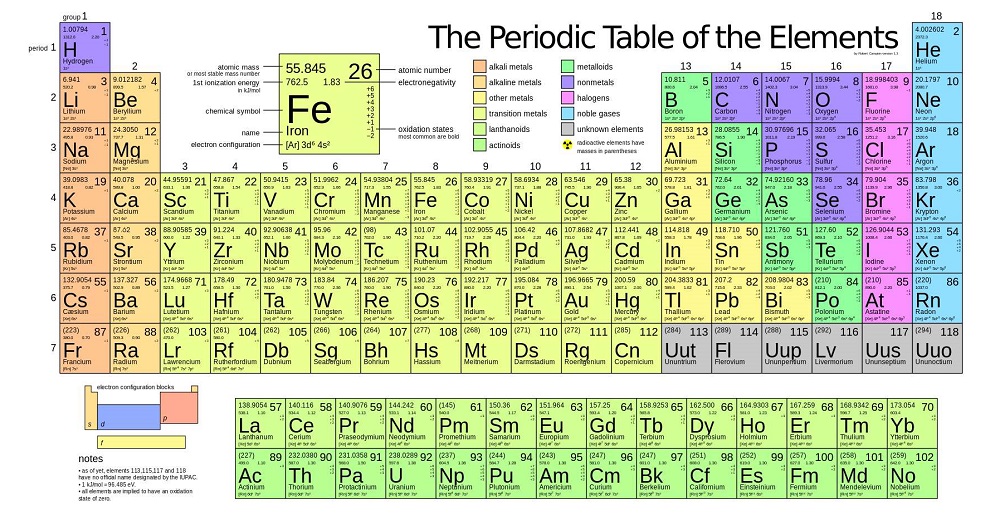
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of elements, is a tabular display of the chemical elements, which are arranged by atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The structure of the table shows periodic trends. The seven rows of the table, called periods, generally have metals on ...
What is the atomic number plotted against?
Atomic number plotted against atomic radius, excluding the noble gases. Atomic radii vary in a predictable and explainable manner across the periodic table. For instance, the radii generally decrease along each period of the table, from the alkali metals to the noble gases; and increase down each group.
What are the columns of periodic table called?
The seven rows of the table, called periods, generally have metals on the left and nonmetals on the right. The columns, called groups , contain elements with similar chemical behaviours.
How many categories are there in the periodic table?
The elements of the periodic table shown here are divided into nine categories; six for the metals, and two for nonmetals, and a metalloid category. The nine categories (or sets) correspond to those found in the literature for the applicable part of the periodic table. Different authors may use different categorisation schema depending on the properties of interest.
When is the 150th anniversary of the periodic table?
In celebration of the periodic table's 150th anniversary, the United Nations declared the year 2019 as the International Year of the Periodic Table, celebrating "one of the most significant achievements in science".
When was Deming's table published?
Merck and Company prepared a handout form of Deming's 18-column medium table, in 1928, which was widely circulated in American schools. By the 1930s Deming's table was appearing in handbooks and encyclopedias of chemistry. It was also distributed for many years by the Sargent-Welch Scientific Company.
Who was the first to arrange the elements into a periodic table with increasing order of atomic masses?
Dmitri Mendeleev. Lothar Meyer. British chemist John Newlands was the first to arrange the elements into a periodic table with increasing order of atomic masses. He found that every eight elements had similar properties and called this the law of octaves.
Who created the table of elements?
Among the scientists who worked to created a table of the elements were, from left, Antoine Lavoisier, Johann Wolfang Döbereiner, John Newlands and Henry Moseley. In 1789, French chemist Antoine Lavoisier tried grouping the elements as metals and nonmetals.
What elements did Mendeleev predict?
The later discovery of elements predicted by Mendeleev, including gallium (1875), scandium (1879) and germanium (1886), verified his predictions and his periodic table won universal recognition. In 1955 the 101st element was named mendelevium in his honor. The 1869 periodic table by Mendeleev in Russian, with a title that translates "An experiment ...
Why is the periodic table important?
The periodic table provides information about the atomic structure of the elements and the chemical similarities or dissimilarities between them. Scientists use the table to study chemicals and design experiments. It is used to develop chemicals used in the pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries and batteries used in technological devices.
What are the horizontal rows in the periodic table called?
In the periodic table, the horizontal rows are called periods, with metals in the extreme left and nonmetals on the right. The vertical columns, called groups, consist of elements with similar chemical properties. The periodic table provides information about the atomic structure of the elements and the chemical similarities or dissimilarities ...
What is the periodic table of chemical elements?
On its website marking the celebration, UNESCO wrote, “The Periodic Table of Chemical Elements is more than just a guide or catalogue of the entire known atoms in the universe; it is essentially a window on the universe, helping to expand our understanding of the world around us.”.
Why is the periodic table celebrated in 2019?
UNESCO named 2019 the International Year of the Periodic Table to mark the 150 th anniversary of Mendeleev’s publication. Researchers and teachers worldwide took this opportunity to reflect on the importance of the periodic table and spread awareness about it in classrooms and beyond.
How are the elements in the periodic table arranged?
The Periodic table elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic number. The arrangement of elements in the Periodic table starts from the very first top left corner. The first element with atomic number 1 (i.e hydrogen) is placed in the first cell, then gradually the elements with atomic number 2, 3, 4 upto 118, ...
Why is the periodic table arranged by atomic number?
Periodic table is arranged by Atomic number because of electrons present in the outermost orbit (which are responsible for the chemical properties of the elements.)
What is the relationship between the number of protons and the number of electrons?
What is a relationship between number of protons and number of electrons? Simple answer: In a neutral atom, the number of protons and number of electrons are equal. For example, this is a neutral helium atom. Here you can see that the helium atom has 2 protons and the number of electrons are also 2.
What does atomic number mean?
Atomic number = Number of electrons. The electrons present in the outermost orbit represent the chemical properties of the elements. Hence to classify the elements on the basis of similarities in their chemical properties, they are arranged in the Periodic table on the basis of atomic number. In other words, Atomic number indicates the number ...
What did Rutherford discover about atoms?
Later on in 1911, Rutherford came up with a discovery of atomic structure, and he found that there are protons and neutrons in the central part of atoms (In other words, Rutherford found that there is a nucleus in the central part of atom which consists of protons and neutrons.)
What are electrons responsible for?
These electrons are responsible for the chemical properties of an element. Hence for grouping the elements according to the similar chemical properties, the elements of the Periodic table are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic number. Later on, we saw that there are groups as well as periods on the Periodic table.
Why are elements 58 to 71 and 90 to 103 in separate rows?
These elements are placed in separate rows at the bottom of the Periodic table because they differ in the chemical properties, plus by placing them at the bottom, ...
How does the periodic table work?
Here's how it works: Elements are listed in numerical order by atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom of that element. So element number 1 (hydrogen) is the first element.
How many periods are there in the periodic table?
There are seven periods on the periodic table. Elements in the same period all have the same electron ground state energy level. As you move from left to right across a period, elements transition from displaying metal characteristics toward nonmetallic properties.
What are the trends in the periodic table?
As you progress in chemistry, there are other trends in the periodic table you'll need to know: 1 Atomic radius and ionic radius increase as you move down a group, but decrease as you move across a period. 2 Electron affinity decreases as you move down a group, but increases as you move across a period until you get to the last column. The elements in this group, the noble gases, have practically no electron affinity. 3 The related property, electronegativity, decreases going down a group and increases across a period. Noble gases have practically zero electronegativity and electron affinity because they have complete outer electron shells. 4 Ionization energy decreases as you move down a group, but increases moving across a period. 5 Elements with the highest metallic character are located on the lower left side of the periodic table. Elements with the least metallic character (most nonmetallic) are on the upper right side of the table.
What are the two main types of elements?
The two main types of elements are metals and nonmetals . There are also elements with properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals. These elements are called metalloids or semimetals. Examples of groups of elements that are metals include alkali metals, alkaline earths, basic metals, and transition metals.
Why is the periodic table important?
The periodic table is one of the most valuable tools for chemists and other scientists because it orders the chemical elements in a useful way. Once you understand how the modern periodic table is organized, you'll be able to do much more than just look up element facts like their atomic numbers and symbols.
What is the element symbol?
The element symbol is a shorthand notation that is either one capital letter or a capital letter and a lowercase letter. The exception is the elements at the very end of the periodic table, which have placeholder names (until they are officially discovered and named) and three-letter symbols.
What is the atomic number of an element?
Every atom of hydrogen has 1 proton. Until a new element is discovered, the last element on the table is element number 118 . Every atom of element 118 has 118 protons.
Why is the periodic table called the periodic table?
The table was named the periodic table because similar properties occur at regular intervals. Elements with similar properties are in columns called groups. Elements to the left of this line are metals. Elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of electrons in their outer shell.
What was the first attempt to classify elements?
Early attempts to classify the elements involved placing them in order of their atomic weights. This resulted in incomplete tables and the placing of some elements in inappropriate groups based on their chemical properties.
What was Dmitri Mendeleev's solution to the problem of atomic weights?
The Russian Chemist Dmitri Mendeleev’s solution was to leave some gaps for elements that he correctly predicted were yet to be discovered. He also reordered some elements based on atomic weights. Increased understanding of isotopes made it possible to explain why the order based on atomic weights was not always correct.
Which element reacts to form positive ions?
Metals are elements that react to form positive ions.
Overview
Atomic theory and isotopes
In 1907 it was discovered that thorium and radiothorium, products of radioactive decay, were physically different but chemically identical; this led Frederick Soddy to propose in 1910 that they were the same element but with different atomic weights. Soddy later proposed to call these elements with complete chemical identity “isotopes“.
Early history
A number of chemical elements, such as carbon, sulfur, iron, copper, silver, tin, gold, mercury, and lead, have been known since before antiquity, as they are found in their native form and are relatively simple to mine with primitive tools. Around 330 BCE, the Greek philosopher Aristotle proposed that everything is made up of a mixture of one or more roots, an idea originally suggested by the Sicilian philosopher Empedocles. The four roots, which the Athenian philosopher Plato called ele…
First categorizations
The history of the periodic table is also a history of the discovery of the chemical elements. The first person in recorded history to discover a new element was Hennig Brand, a bankrupt German merchant. Brand tried to discover the philosopher's stone—a mythical object that was supposed to turn inexpensive base metals into gold. In 1669, or later, his experiments with distilled human urine resulted …
Comprehensive formalizations
Properties of the elements, and thus properties of light and heavy bodies formed by them, are in a periodic dependence on their atomic weight.— Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev, formulating the periodic law for the first time in his 1871 article "Periodic regularity of the chemical elements"
French geologist Alexandre-Émile Béguyer de Chancourtois noticed that the ele…
Priority dispute and recognition
That person is rightly regarded as the creator of a particular scientific idea who perceives not merely its philosophical, but its real aspect, and who understands so to illustrate the matter so that everyone can become convinced of its truth. Then alone the idea, like matter, becomes indestructible.— Mendeleev in his 1881 article in British journal Chemical News in a correspondence debate with Meyer over priority of the periodic table invention
Inert gases and ether
The great value of Newland's, Mendeleef's, and Lothar Meyer's generalisation, known as the periodic arrangement of the elements, is universally acknowledged. But a study of this arrangement, it must be allowed, is a somewhat tantalising pleasure; for, although the properties of elements do undoubtedly vary qualitatively, and, indeed, show approximate quantitative rela…
Later expansions and the end of the periodic table
We already feel that we have neared the moment when this [periodic] law begins to change, and change fast.— Russian physicist Yuri Oganessian, co-discoverer of several superheavy elements, in 2019
As early as 1913, Bohr's research on electronic structure led physicists such as Johannes Rydberg to extrapolate the properties of undiscovered elements heavier than uranium. Many agreed that …
Summary
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a tabular display of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of chemistry. It is a graphic formulation of the periodic law, which states that the properties of the chemical elements exhibit a periodic dependence on their atomic numbers. Th…
Overview
The periodic table is a 2-dimensional structured table. The elements are placed in table cells, in reading order of ascending atomic number. The table columns are called groups, the rows are called periods. The breaks at the end of each period occur according to a repetition (or periodicity) of physical and chemical properties of the elements.
Periodic trends
As chemical reactions involve the valence electrons, elements with similar outer electron configurations may be expected to react similarly and form compounds with similar proportions of elements in them. Such elements are placed in the same group, and thus there tend to be clear similarities and trends in chemical behaviour as one proceeds down a group. As analogous configurations return …
Classification of elements
Many terms have been used in the literature to describe sets of elements that behave similarly. The group names alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, pnictogen, chalcogen, halogen, and noble gas are acknowledged by IUPAC; the other groups can be referred to by their number, or by their first element (e.g., group 6 is the chromium group). Some divide the p-block elements from groups 13 to …
History
In 1817, German physicist Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner began to formulate one of the earliest attempts to classify the elements. In 1829, he found that he could form some of the elements into groups of three, with the members of each group having related properties. He termed these groups triads. Chlorine, bromine, and iodine formed a triad; as did calcium, strontium, and barium; lithi…
Current questions
Although the modern periodic table is standard today, some variation can be found in period 1 and group 3. Discussion is ongoing about the placements of the relevant elements. The controversy has to do with conflicting understandings of whether chemical or electronic properties should primarily decide periodic table placement, and conflicting views of how the evidence should be used. A similar potential problem has been raised by theoretical investigations of the superheav…
Future extension beyond the seventh period
The most recently named elements – nihonium (113), moscovium (115), tennessine (117), and oganesson (118) – completed the seventh row of the periodic table. Future elements would have to begin an eighth row. These elements may be referred to either by their atomic numbers (e.g. "element 119"), or by the IUPAC systematic element names which directly relate to the atomic …
Alternative periodic tables
The periodic law may be represented in multiple ways, of which the standard periodic table is only one. Within 100 years of the appearance of Mendeleev's table in 1869, Edward G. Mazurs had collected an estimated 700 different published versions of the periodic table. Many forms retain the rectangular structure, including Janet's left-step periodic table (pictured below), and the m…