See more
Who actually invented the periodic table?
Dmitri MendeleevAlbert GhiorsoPeriodic table/Inventors
Who created the periodic table and why?
In 1869, Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev created the framework that became the modern periodic table, leaving gaps for elements that were yet to be discovered. While arranging the elements according to their atomic weight, if he found that they did not fit into the group he would rearrange them.
What was the first periodic table?
Mendeleev's periodic table, published in 1869, was a vertical chart that organized 63 known elements by atomic weight. This arrangement placed elements with similar properties into horizontal rows.
Why is it called the periodic table?
Why is the periodic table called the periodic table? It is called the periodic table because of the way the elements are arranged. You'll notice they're in rows and columns. The horizontal rows (which go from left to right) are called 'periods' and the vertical columns (going from up to down) are called 'groups'.
Why did Mendeleev create the periodic table?
He used them to correct properties of other elements such as the valence and also to predict properties of some three elements which were undiscovered by then; by putting them in order according to their atomic weights, he realized that physical and chemical properties were related to their atomic mass.
Why is the periodic table important?
The periodic table of elements puts all the known elements into groups with similar properties. This makes it an important tool for chemists, nanotechnologists and other scientists. If you get to understand the periodic table, and learn to use it, you'll be able to predict how chemicals will behave.
How and why is the periodic table arranged?
The chemical elements are arranged from left to right and top to bottom in order of increasing atomic number, or the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, which generally coincides with increasing atomic mass.
What did Henry Moseley contribute to the periodic table?
Moseley's contribution to the periodic table was that he arranged the elements in the periodic table according to atomic numbers. He realized his findings indicated that the identity of an element is how many protons it has. The number of protons represents the atomic number of an element.
Who published the periodic table?
Main table of the periodic table published by Australian chemist David Orme Masson in 1895
Who added elements to the periodic table?
Mendeleev himself added these elements to the table as group 0 in 1902, without disturbing the basic concept of the periodic table. In 1905, Swiss chemist Alfred Werner resolved the dead zone of Mendeleev 's table. He determined that the rare-earth elements ( lanthanides ), 13 of which were known, lay within that gap.
What is the difference between Mendeleev and Meyer?
Mendeleev's intent was to aid composition of his textbook, Foundations of Chemistry, whereas Meyer was rather concerned with presentation of theories. Mendeleev's predictions emerged outside of the pedagogical scope in the realm of journal science, while Meyer made no predictions at all and explicitly stated his table and his textbook it was contained in, Modern Theories, should not be used for prediction in order to make the point to his students to not make too many purely theoretically constructed projections.
What did Mendeleev think of the elements?
Mendeleev noticed that there was a significant difference in atomic mass between cerium and tantalum with no element between them; his consideration was that between them, there was a row of yet undiscovered elements, which would display similar properties to those elements which were to be found above and below them: for instance, an eka-molybdenum would behave as a heavier homolog of molybdenum and a lighter homolog of wolfram (the name under which Mendeleev knew tungsten ). This row would begin with a trivalent lanthanum, a tetravalent cerium, and a pentavalent didymium. However, the higher valency for didymium had not been established, and Mendeleev tried to do that himself. Having had no success in that, he abandoned his attempts to incorporate the rare-earth metals in late 1871 and embarked on his grand idea of luminiferous ether. His idea was carried on by Austrian-Hungarian chemist Bohuslav Brauner, who sought to find a place in the periodic table for the rare-earth metals; Mendeleev later referred to him as to "one of the true consolidators of the periodic law".
What elements did Mendeleev predict?
In 1870, he first tried to characterize the yet undiscovered elements, and he gave detailed predictions for three elements, which he termed eka-boron, eka-aluminium, and eka-silicium, as well as more briefly noted a few other expectations. It has been proposed that the prefixes eka, dvi, and tri, Sanskrit for one, two, and three, respectively, are a tribute to Pāṇini and other ancient Sanskrit grammar ians for their invention of a periodic alphabet. In 1871, Mendeleev expanded his predictions further.
What was Mendeleev's success?
However, success of Mendeleev's predictions helped spread the word about his periodic table. Later chemists used the successes of these Mendeleev's predictions to justify his table. By 1890, his periodic table had been universally recognized as a piece of basic chemical knowledge.
What are the four elements that are considered elements?
The four roots, which were later renamed as elements by Plato, were earth, water, air and fire. Similar ideas about these four elements also existed in other ancient traditions, such as Indian philosophy . A few extra elements were known in the age of alchemy ( zinc, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth ).
Who found the periodic table?
It has been the go-to reference on chemical elements for almost 150 years. Yet while the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev is often credited with finding the rules behind the block-like patterns of elements, he was hardly alone: others had found them some years before, but failed to win recognition.
What did Mendeleev discover?
His confidence was vindicated with the discovery of gallium, germanium and scandium, ensuring his place among the great names of 19th-Century science.
Who discovered that elements with similar properties lie close together?
One of these scientists was John Newlands , an English chemist who in the mid-1860s pointed out that elements with similar properties lie close together if arranged according to their atomic mass.
Who invented the periodic table?
But it was the combined efforts of many chemists for the invention of Periodic table. The chemists who invented Periodic table are listed below. Antoine Lavoisier (1789) Johann Dobereiner (1829) Alexandre Beguyer de Chancourtois (1862) ...
When did the periodic table start?
I’ll tell you the complete History of Periodic table starting from 1789 to 1913.
Why Periodic table was invented?
The Periodic table was invented in order to classify all the known elements according to the similarities in their properties.
How did Johann Dobereiner classify the elements?
He classified the known elements by knowing their properties. After few years of this classification, several attempts were also made by other chemists. But some important work was given by Johann Dobereiner after few years. Let us see how Johann Dobereiner contributed to the development of Periodic table.
What did the king prepare for each known element?
He prepared the cards of each known element with their properties and details written on them.
How many elements are there in the universe?
Till today there are total 118 known elements like hydrogen, helium, lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, and so on…
Who was the first person to publish the periodic table?
Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) Henry Moseley (1913) And many more…. Many of you might think that Mendeleev was the person who discovered the Periodic table. But this is not completely true. Yes, he was the first to publish the Periodic table with 63 elements which were discovered during his time.
What is periodic table?
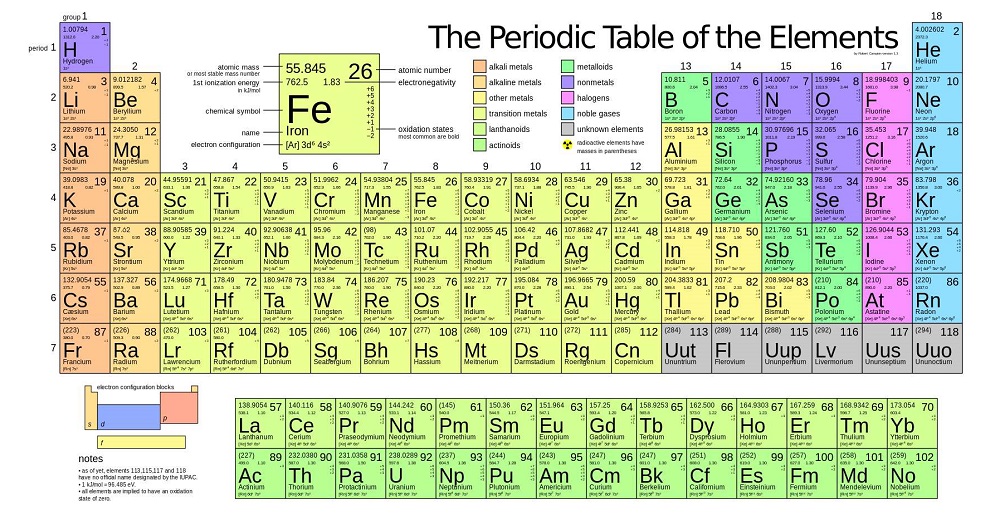
The Periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements according to the increasing order of their atomic number. These chemical elements when arranged in such order, exhibit similar properties with elements that belong to the same group, where such a recurring pattern is called Periodic Law.
When was the first neutron discovered?
When James Chadwick discovered neutrons for the first time in 1932, isotopes were also identified, which made the complete basis for the periodic table. An experiment was done to split an atom by bombarding lithium in a particle accelerator by an Englishman named Cockroft and an Irishman called Walton, which resulted in two helium nuclei. Lanthanides and actinides were identified by Glenn Seaborg in 1945, whose atomic number is greater than 92, are placed below the periodic table.
Who created the periodic table?
The periodic table was invented by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. However, prior to Mendeleev, chemists had been pondering for decades how to classify the elements. Beginning in 1789, Antoine Lavoisier began classifying elements by their properties. Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner showed in 1817 that elements could be arranged by their atomic ...
Who used atomic weights to classify the elements?
Atomic weights were used by English chemist John Newlands in 1864 in classifying the elements. After arranging the elements in order by atomic weight, Newlands noted that every eighth element seemed to have similar chemical properties. By analogy with the seven-note musical scale, he called this the law of octaves.
How is an element's position on the periodic table determined?
It was not until the early 20th century that it was discovered that an element’s position in the periodic table is determined by its atomic number (the amount of protons in its atomic nucleus).
How many columns did Mendeleev have in his 1869 table?
His 1869 table contained 17 columns (or groups, as they are now known). He revised this into an eight-group table in 1871. In his 1871 table, Mendeleev correctly predicted that the then known atomic weights of 17 elements were wrong.
Who discovered the periodic table?
Ask most chemists who discovered the periodic table and you will almost certainly get the answer Dmitri Mendeleev. Certainly Mendeleev was the first to publish a version of the table that we would recognise today, but does he deserve all the credit?#N#A number of other chemists before Mendeleev were investigating patterns in the properties of the elements that were known at the time. The earliest attempt to classify the elements was in 1789, when Antoine Lavoisier grouped the elements based on their properties into gases, non-metals, metals and earths. Several other attempts were made to group elements together over the coming decades. In 1829, Johann Döbereiner recognised triads of elements with chemically similar properties, such as lithium, sodium and potassium, and showed that the properties of the middle element could be predicted from the properties of the other two.#N#It was not until a more accurate list of the atomic mass of the elements became available at a conference in Karlsruhe, Germany in 1860 that real progress was made towards the discovery of the modern periodic table.#N#This area of the website celebrates the work of many famous scientists whose quest to learn more about the world we live in and the atoms that make up the things around us led to the periodic table as we know it today.
When was the periodic table first discovered?
It was not until a more accurate list of the atomic mass of the elements became available at a conference in Karlsruhe, Germany in 1860 that real progress was made towards the discovery of the modern periodic table.
What did Newlands discover about the periodic table?
Just four years before Mendeleev announced his periodic table, Newlands noticed that there were similarities between elements with atomic weights that differed by seven. He called this The Law of Octaves, drawing a comparison with the octaves of music.
What is the name of the three-dimensional arrangement of the elements that is used to determine the atomic weights of?
His principal contribution to chemistry was the 'vis tellurique' (telluric screw), a three-dimensional arrangement of the elements constituting an early form of the periodic classification, published in 1862. The telluric screw plotted the atomic weights of the elements on the outside of a cylinder, so that one complete turn corresponded ...
How is the periodic table arranged?
It wasn’t until 1913, six years after Mendeleev’s death that the final piece of the puzzle fell into place. The periodic table was arranged by atomic mass, and this nearly always gives the same order as the atomic number. However, there were some exceptions (like iodine and tellurium, see above), which didn’t work. Mendeleev had seen that they needed to be swapped around, but it was Moseley that finally determined why.
Which scientist used a periodic arrangement of all known elements?
Although the telluric screw did not correctly display all the trends that were known at the time, de Chancourtois was the first to use a periodic arrangement of all of the known elements, showing that similar elements appear at periodic atom weights.
Why do chemists look for ways to arrange the elements?
Chemists have always looked for ways of arranging the elements to reflect the similarities between their properties. The modern periodic table lists the elements in order of increasing atomic number (the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom). Historically, however, relative atomic masses were used by scientists trying to organise ...
Who created the table of elements?
Among the scientists who worked to created a table of the elements were, from left, Antoine Lavoisier, Johann Wolfang Döbereiner, John Newlands and Henry Moseley. In 1789, French chemist Antoine Lavoisier tried grouping the elements as metals and nonmetals.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table of elements is a common sight in classrooms, campus hallways and libraries, but it is more than a tabular organization of pure substances . Scientists can use the table to analyze reactivity among elements, predict chemical reactions, understand trends in periodic properties among different elements and speculate on ...
What elements did Mendeleev predict?
The later discovery of elements predicted by Mendeleev, including gallium (1875), scandium (1879) and germanium (1886), verified his predictions and his periodic table won universal recognition. In 1955 the 101st element was named mendelevium in his honor. The 1869 periodic table by Mendeleev in Russian, with a title that translates "An experiment ...
Why is the periodic table important?
The periodic table provides information about the atomic structure of the elements and the chemical similarities or dissimilarities between them. Scientists use the table to study chemicals and design experiments. It is used to develop chemicals used in the pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries and batteries used in technological devices.
What are the horizontal rows in the periodic table called?
In the periodic table, the horizontal rows are called periods, with metals in the extreme left and nonmetals on the right. The vertical columns, called groups, consist of elements with similar chemical properties. The periodic table provides information about the atomic structure of the elements and the chemical similarities or dissimilarities ...
What is the periodic table of chemical elements?
On its website marking the celebration, UNESCO wrote, “The Periodic Table of Chemical Elements is more than just a guide or catalogue of the entire known atoms in the universe; it is essentially a window on the universe, helping to expand our understanding of the world around us.”.
Why is the periodic table celebrated in 2019?
UNESCO named 2019 the International Year of the Periodic Table to mark the 150 th anniversary of Mendeleev’s publication. Researchers and teachers worldwide took this opportunity to reflect on the importance of the periodic table and spread awareness about it in classrooms and beyond.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is an arrangement of chemical elements in the form of a table, to get a first-hand glimpse of ‘periodically’ recurring properties of elements. Since the ancient period, scientists have suggested various forms of the periodic table, but the credit for the modern form of periodic table goes to the Russian chemist, ...
How are the elements in the periodic table arranged?
In the modern form of periodic table, the elements are arranged in accordance with their increasing atomic number. The elements are grouped in four blocks: s, p, d and f. The transuranium elements or the radioactive elements are placed below the main table as lanthanides and actinides. The vertical column of the periodic table, called a ‘group’, ...
Why is the periodic table important?
The periodic table helps us to classify and compare various elements on the basis of their chemical behavior. Read on to know how the periodic table evolved over a period of time... Like it? Share it! The periodic table helps us to classify and compare various elements on the basis of their chemical behavior.
How many elements are there in the periodic table?
There are a total number of 118 chemical elements in the periodic table. Out of them, 94 elements are found naturally on the surface of the earth and the rest are all synthetic elements. Usually, each element in the periodic table is represented with its symbol, atomic number and atomic mass.
What does a row of the periodic table mean?
A row of the table signifies the number of shells that are filled by electrons in an atom. In some sections of the periodic table, the horizontal trends of the key characteristics of chemical elements are more significant than the vertical trends.
What is the vertical column of the periodic table called?
The vertical column of the periodic table, called a ‘group’, includes those elements which have the same electronic configuration in the outermost shell of their atoms. For this reason, elements in the same group show similar properties. The horizontal row of the periodic table is called a ‘period’. A row of the table signifies the number of shells ...
What period are synthetic elements in the periodic table?
However, there are a few synthetic elements placed in the seventh period of the table which are unnamed and are represented with their temporary names. These elements were discovered in the recent times and will receive their permanent names and symbols from International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (or IUPAC).
Overview
The periodic table is an arrangement of the chemical elements, structured by their atomic number, electron configuration and recurring chemical properties. In the basic form, elements are presented in order of increasing atomic number, in the reading sequence. Then, rows and columns are created by starting new rows and inserting blank cells, so that rows (periods) and columns (groups) s…
Early history
A number of chemical elements, such as carbon, sulfur, iron, copper, silver, tin, gold, mercury, and lead, have been known since before antiquity, as they are found in their native form and are relatively simple to mine with primitive tools. Around 330 BCE, the Greek philosopher Aristotle proposed that everything is made up of a mixture of one or more roots, an idea originally suggested by the Sicilian philosopher Empedocles. The four roots, which the Athenian philosopher Plato called ele…
First categorizations
The history of the periodic table is also a history of the discovery of the chemical elements. The first person in recorded history to discover a new element was Hennig Brand, a bankrupt German merchant. Brand tried to discover the philosopher's stone—a mythical object that was supposed to turn inexpensive base metals into gold. In 1669, or later, his experiments with distilled human urine resulted …
Comprehensive formalizations
Properties of the elements, and thus properties of light and heavy bodies formed by them, are in a periodic dependence on their atomic weight.— Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev, formulating the periodic law for the first time in his 1871 article "Periodic regularity of the chemical elements"
French geologist Alexandre-Émile Béguyer de Chancourtois noticed that the ele…
Priority dispute and recognition
That person is rightly regarded as the creator of a particular scientific idea who perceives not merely its philosophical, but its real aspect, and who understands so to illustrate the matter so that everyone can become convinced of its truth. Then alone the idea, like matter, becomes indestructible.— Mendeleev in his 1881 article in British journal Chemical News in a correspondence debate with Meyer over priority of the periodic table invention
Inert gases and ether
The great value of Newland's, Mendeleef's, and Lothar Meyer's generalisation, known as the periodic arrangement of the elements, is universally acknowledged. But a study of this arrangement, it must be allowed, is a somewhat tantalising pleasure; for, although the properties of elements do undoubtedly vary qualitatively, and, indeed, show approximate quantitative rela…
Atomic theory and isotopes
In 1907 it was discovered that thorium and radiothorium, products of radioactive decay, were physically different but chemically identical; this led Frederick Soddy to propose in 1910 that they were the same element but with different atomic weights. Soddy later proposed to call these elements with complete chemical identity “isotopes“.
Later expansions and the end of the periodic table
We already feel that we have neared the moment when this [periodic] law begins to change, and change fast.— Russian physicist Yuri Oganessian, co-discoverer of several superheavy elements, in 2019
As early as 1913, Bohr's research on electronic structure led physicists such as Johannes Rydberg to extrapolate the properties of undiscovered elements heavier than uranium. Many agreed that …
Why Periodic Table Was invented?
Who Invented Periodic table?
- It was not the efforts of a single person (i.e Dimitri Mendeleev) behind the invention of Periodic table. It was the combined efforts of many scientists who contributed to the discovery of the Periodic table. Following chemists gave their valuable efforts in creating the Periodic table. 1. Antoine Lavoisier (1789) 2. Johann Dobereiner (1829) 3. Ale...
Final Arrangement
- After the valuable contribution of all the above mentioned scholars, many researchers worked on the atomic structure and finally the structure of atoms came into existence. Scientists realized that there is a heavy nucleus in the centre of atoms. This nucleus contains protons and neutrons in it. They also realized that the protons are the unique identity of every single element. The num…
Free Gift For You: Interactive Periodic Table
- Let me tell you how this Interactive Periodic Tablewill help you in your studies. 1).You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table. 2).You will get the detailed information about the periodic table which will convert a newbie into pro. 3).You will also get the HD images of the Periodic table (for FREE). Checkout Interactive Per…