What happens to electron affinity across the period?
When moving left to right across a period, the electron affinity increases. This is because the number of protons increases moving to the right of the row. The increase in positive charge increases the attraction between the nucleus and the electrons of the atom. What happens to electron affinity across the period and down the group?
What is the trend for electron affinity?
What is the trend for electron affinity? Electron affinity increases upward across periods of a periodic table for the groups and from left to right, because the electrons added to the energy levels get closer to the nucleus, making the nucleus and its electrons more attractive.
Why does electron affinity increase with increasing atomic number?
When you go across a period of the periodic table , atomic number increases, but electrons are being added to the same energy level…..A more negative energy per mole means that more is given off when the atom adds an electron , so electron affinity increases.
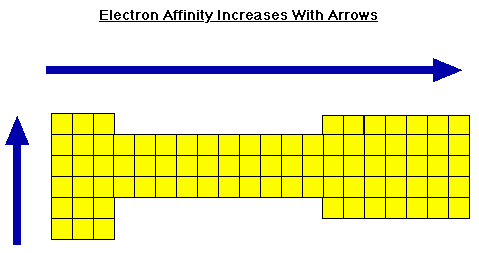
What is the trend for electron affinity?
Electron Affinity increases across a period from left to right because of increasing effective nuclear charge and decreasing size of atoms. Electro...
Is electron affinity positive or negative?
When an electron is added to a neutral atom, energy is released and Electron Affinity is generally exothermic. Due to electronic repulsions, the se...
Who discovered the concept of electron affinity?
Electron Affinity was a concept that was discovered in 1901 in view of the discovery of electron negativity by Linus Carl Pauling. Electron Affinit...
Why is the electron affinity of noble gases positive?
The enthalpy of electron gain for halogens is highly negative because by accepting an extra electron they can acquire the nearest stable noble gas...
Why do halogens have high electron affinity?
The halogens’ high electron affinities are due to their small size, high effective nuclear charge and an almost full outer shell of electrons. When...
Why is the electron affinity of nonmetals negative?
This is because nonmetals have enough energy to form negatively charged ions, anions. This means that the electron affinity value of nonmetals is typically negative. Nonmetals have more electron affinity than metals do because ...
What are ions in chemistry?
Ions of atoms may have a net positive charge or a net negative charge. Positively charged atoms are called cations while negatively charged ions are called anions. The energy of an atom has can be gained or lost through chemical reactions, so these chemical reactions form either anions or cations. Ionization energies deal with the formation of positive ions while electron affinities deal with the formation of negative ions. It’s important to remember that, so you’ll know that electron affinities deal exclusively with negative ions of atoms and that their use is almost always relegated to the elements found within groups 16 and 17 of the element table.
What is the electron affinity trend?
The electron affinity trend describes the trend across the periodic table and describes how much energy in an atom is released or spent when an electron is added to a neutral atom or the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral atom. The electron affinity trend describes how as one follows the periodic table left ...
Why do electrons have lower affinity?
The opposite trend holds true as well, electron affinity decreases from right to left and down the groups because the electrons are located farther away from the nucleus and therefore have less attraction . The reason that elements lower in groups don’t have higher electron affinities despite their higher number of valence electrons is the shielding effect. The shielding effect increases as one moves down a group, making electrons repel each other more.
Why does electron affinity decrease from right to left?
The opposite trend holds true as well, electron affinity decreases from right to left and down the groups because the electrons are located farther away from the nucleus and therefore have less attraction .
How are reactivity and electron affinity related?
Reactivity and electron affinity are tightly correlated, with the reactivity of an element increasing as the electron affinity increases. In other words, the greater an element’s tendency to gain electrons, the more reactive the element is.
Why does the electron affinity of an atom depend upon the initial addition of an electron to a neutral atom?
The initial addition of an electron to a neutral atom, the first electron affinity, will always have negative energy. This is because energy is released when an electron is added to a neutral atom. The ion is now negative, and more energy is necessary when an electron is ...
What is Electron Affinity?
The amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom to form an anion.
Why is the enthalpy of electron gain for halogens highly negative?
The enthalpy of electron gain for halogens is highly negative because by accepting an extra electron they can acquire the nearest stable noble gas configuration. Noble gases have significant positive enthalpy in the gain of electrons.
What happens when you add another electron to an atom?
Now if we add another electron to this anion, a force of repulsion is experienced by the electron and energy is absorbed. Therefore, the second electron affinity ...
Why does electron affinity decrease when moving down the group?
Going down the group the electron affinity should decrease since the electron is being added increasingly further away from the atom. Less tightly bound and therefore closer in energy to a free electron. In a period, as we move from left to right the atomic size decreases due to the increase in the nuclear force hence the electron gain enthalpy ...
What are the factors that affect electron affinity?
The general factors that affect the electron affinity are listed below. 1. Atomic size: If the atomic size is small, then there will be greater electron gain enthalpy because the effective nuclear forces will be greater in the smaller atoms and the electrons will be held firmly. 2.
Why do halogens have high electron affinities?
Why do halogens have high electron affinity? The halogens’ high electron affinities are due to their small size, high effective nuclear charge and an almost full outer shell of electrons. When an electron is added to halogens with very high electron affinity, high energy is released.
What is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom?
Ionization potential is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom. Energy is supplied for removing an atom implies that energy will be released if an extra electron is added to the atom. The amount of energy released when a neutral atom in its gaseous state accepts an electron and gets converted into a negatively charged ion is known as electron affinity.
What is the electron affinity of a beryllium atom?
Electron affinity of Beryllium, and calcium is practically zero. If the atom has fully or half-filled orbits, its electron affinity will be less. Example: Electron affinity of Be and N is almost 0 because they are having filled electrons in their valence shells. Full filled orbits are all stable due to symmetry.
What is the meaning of electron affinity?
Electron affinity is defined as the quantitative measurement of the energy change that results from adding a new electron to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state. The more negative the electron affinity value, the higher an atom’s affinity for electrons. The energy of an atom is stated when an atom loses or gains energy ...
Why do metals lose valence electrons?
The reason behind losing their valence electrons is that metals’ nuclei do not have a strong pull on their valence electrons. Therefore, metals are said to have lower electron affinities.
Why do non-metals have greater electron affinity?
Non-metals have greater electron affinity because of their atomic structures. There are two reasons associated with why non-metals have greater electron affinity. Non-metals have more valence electrons than metals have, this makes non-metals easy to gain electrons to fulfill a stable octet.
Why do halogens have high electron affinity?
The halogens show high electron affinity due to their small size. It has a high nuclear charge and an almost full outer shell of electrons. The smaller the electron size, the greater the affinity. Halogens prove this factor to be true. High energy is released when an electron is added to halogen.
Why is it harder to remove an electron from an element?
The valence electron shell is closer to the nucleus, this makes it harder to remove an electron. It is rather easy to attract an electron from another element.
Why is second electron affinity positive?
Second Electron Affinity: Positive energy because the energy needed is more than gained.
Answer
Electron affinity increases upward for the groups and from left to right across periods of a periodic table because the electrons added to energy levels become closer to the nucleus, thus a stronger attraction between the nucleus and its electrons
New questions in Chemistry
s shape orbitalF shape Three Dimensional ComplicatedP shape doumbled shapeD shape double bumbledGood morning my ♥️ !
What are the general trends of electron affinity?
In general, electron affinity increases (or becomes more negative) from left to right across a period. This is due to increasing effective nuclear charge, which more readily pulls these new electrons in.
Why do electrons not have to be as close to one another?
Along with this, however, because the valence shells are larger as atomic radii increases, the electrons in those valence shells do not have to be as close to one another and so they do not experience electron-electron repulsions as much.
Why does electron affinity decrease?
This is due to a balance between increasing atomic radii and decreasing electron-electron repulsions.
What is the difference between ionization energy and electron affinity?
While ionization energy is the energy change incurred from losing an electron, electron affinity is the energy change incurred from gaining an electron. For most atoms, this is a negative quantity - or energy is released. For some elements, however, this is not the case. Most notably, noble gases have a positive electron affinity, ...
Why is the group 15 element more positive than the group 14 element?
This is because the addition of an electron to nitrogen's neutral configuration, for example, creates the first paired electrons in the p orbital. Because of electron-electron repulsions, this is energetically unfavorable, making the electron affinity more positive.
Which period has the greatest electron affinity?
Because of electron-electron repulsions, this is energetically unfavorable, making the electron affinity more positive. Notice that the Period 3 elements actually have the greatest electron affinities, instead of the Period 2 elements as the trend suggests.
Why does electron affinity decrease as you go down the periodic table?
Electron affinity decreases down the groups and from right to left across the periods on the periodic table because the electrons are placed in a higher energy level far from the nucleus, thus a decrease from its pull. However, one might think that since the number of valence electrons increase going down the group, the element should be more stable and have higher electron affinity. One fails to account for the shielding affect. As one goes down the period, the shielding effect increases, thus repulsion occurs between the electrons. This is why the attraction between the electron and the nucleus decreases as one goes down the group in the periodic table.
Why do electrons have a higher affinity?
Electron affinity increases upward for the groups and from left to right across periods of a periodic table because the electrons added to energy levels become closer to the nucleus, thus a stronger attraction between the nucleus and its electrons. Remember that greater the distance, the less of an attraction; thus, less energy is released when an electron is added to the outside orbital. In addition, the more valence electrons an element has, the more likely it is to gain electrons to form a stable octet. The less valence electrons an atom has, the least likely it will gain electrons.
What happens to electron affinity as you move from left to right?
In other words, electron affinity in a period, as we move from left to right the atomic size decreases due to the increase in the nuclear force hence the electron gain enthalpy increases. Whereas while moving down a group in periodic table, the A
How do electrons affect the charge of an atom?
There are also increasing numbers of electrons between the nucleus and those outer electrons. These inner electrons screen the charge of the nucleus, effectively reducing the nuclear electric charge seen by the outer electrons. Thus, those outer electrons feel a smaller electrostatic attraction to the nucleus. Because of this reduced attraction to the nucleus, it is much easier for those electrons to be removed from the atom. Hence, the electron affinity, a measure of the ability of an atom to hold onto (excess) electrons, decreases as you move down the group.
What happens when you go across a period of the periodic table?
When you go across a period of the periodic table , atomic number increases, but electrons are being added to the same energy level…..A more negative energy per mole means that more is given off when the atom adds an electron , so electron affinity increases.
Why does electron affinity decrease as we move from left to right?
In other words, electron affinity in a period, as we move from left to right the atomic size decreases due to the increase in the nuclear force hence the electron gain en thalpy increases. Whereas while moving down a group in periodic table, the Atomic size increases thereby Causing a Decrease in the value of electron gain enthalpy.
Why do electrons feel smaller in the nucleus?
There are also increasing numbers of electrons between the nucleus and those outer electrons. These inner electrons screen the charge of the nucleus, effectively reducing the nuclear electric charge seen by the outer electrons. Thus, those outer electrons feel a smaller electrostatic attraction to the nucleus. Because of this reduced attraction to the nucleus, it is much easier for those electrons to be removed from the atom. Hence, the electr
.PNG)