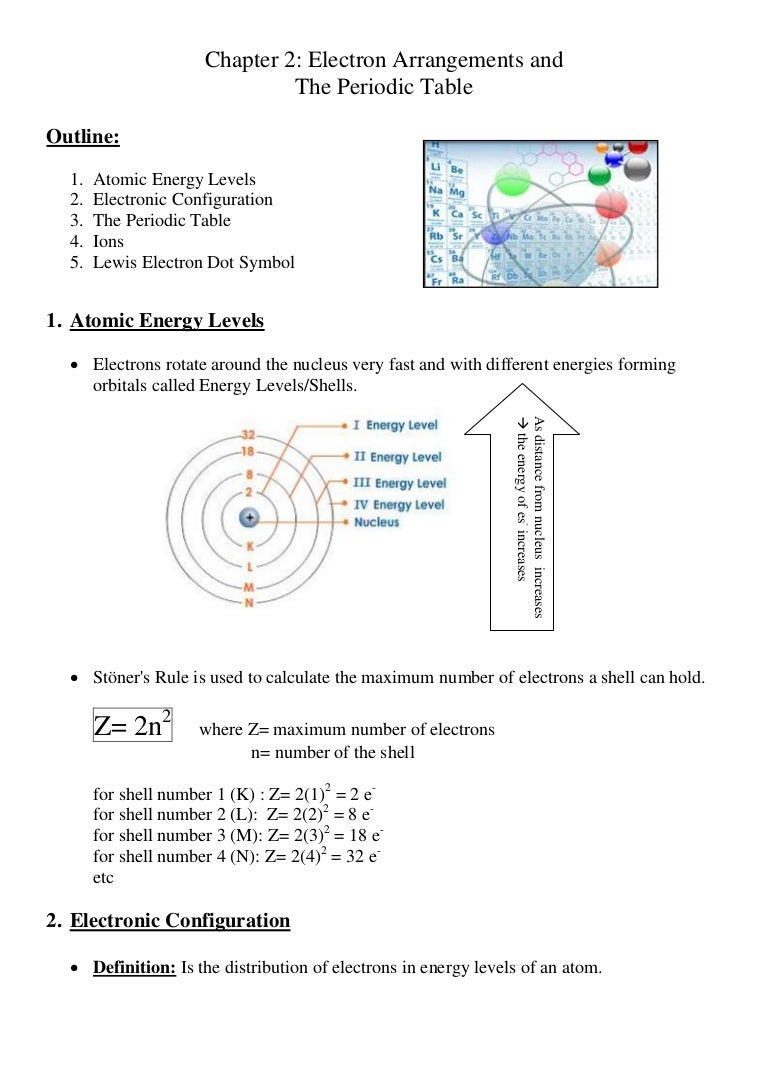
How does atomic size change down the periodic table?
For main group elements, atomic size gets larger as you go down a group (column) and atomic size gets smaller as you go across a period (row). Let’s use the following condensed periodic table to show the relative sizes of the main group elements. Why do atoms get larger as you go down a group?
Why does atomic radius decrease down a group?
In general, atomic radius decreases across a period and increases down a group. A higher effective nuclear charge causes greater attractions to the electrons, pulling the electron cloud closer to the nucleus which results in a smaller atomic radius. Why does atomic size increase down a group?
Why do atoms get smaller as you go across the period?
As you go across a period from left to right and atom to atom, each step adds another electron to the same energy level (shell) and a proton to the nucleus.
What happens to the size of atoms as they move down?
As you move down an element group (column), the size of atoms increases. This is because each atom further down the column has more protons and neutrons and also gains an additional electron energy shell. As you move across an element period (row), the overall size of atoms decreases slightly.
How does atomic size change as you go down a group?
Why do atoms size increase as you move down a group?
How does each step of the atom affect the energy level of the atom?
How to find the effective nuclear charge of Li?
What is the name of the shell that puts valence electrons in the highest and largest shell?
Why does the effective nuclear charge decrease?
How to measure atomic radius?
See 2 more

Why does the atomic radius increase as you move down an element group?
As you move down an element group (column), the size of atoms increases. This is because each atom further down the column has more protons and neutrons and also gains an additional electron energy shell.
What happens to the atoms as you move across an element period?
As you move across an element period (row), the overall size of atoms decreases slightly. Even though atoms further to the right have more protons, neutrons, and electrons, the outer electron shell is the same. The increased number of protons exerts a stronger positive charge, pulling the electrons in toward the nucleus.
What is periodic table?
Periodic table showing the relative sizes of the elements based on atomic radius data. Todd Helmenstine
When does the atomic size decrease in the periodic table?
In the modern periodic table, the atomic size decreases when moving from left to right along a period. Why?
Why does the size of an atom decrease?
This is because, within a period or family of elements, all electrons are added to the same shell. However, at the same time, protons are being added to the nucleus, making it more positively c
How does atomic size change?
Atomic size gradually decreases from left to right across a period of elements. This is because, within a period or family of elements, all electrons are added to the same shell. However, at the same time, protons are being added to the nucleus, making it more positively charged. The effect of increasing proton number is greater than that of the increasing electron number; therefore, there is a greater nuclear attraction. This means that the nucleus attracts the electrons more strongly, pulling the atom's shell closer to the nucleus. The valence electrons are held closer towards the nucleus of the atom. As a result, the atomic radius decreases.
Why do electrons get bigger as you move left to right?
What might be counterintuitive, is that more protons and electrons attracting each other pulls them closer together and reduces the atomic radius. Think of magnets attracting each other. The stronger (More charge) the more they will attract.
How does the number of protons change as you move from left to right?
As you move from left to right across the periodic table, the number of protons increases, and the number of electrons increases , but the number of energy levels stays the same. So for example, all the atoms of the elements in the 2nd row of the periodic table have 2 energy levels; the elements in the 3rd row have 3 energy levels, and so on.
What happens to the atomic radii when you go from left to right?
With each additional proton as you go from left to right across a period the positive charge of the nucleus is increasing. Also as you go from left to right across a period the number of electrons are also increasing. However these electrons are increasing within the same orbital This result in more attraction between the positive charged nucleus and the electrons reducing the space between the nucleus and the valence electrons, this causes the atomic radii to contract as one goes from left to right across a period
Why do atoms get smaller?
Because protons and electrons are attracted to each other, the overall attraction between the nucleus and the atom’s electrons increases as you move from left to right across a row — consequently, the atoms get smaller.
How does atomic size change as you go down a group?
For main group elements, atomic size gets larger as you go down a group (column) and atomic size gets smaller as you go across a period (row). Let’s use the following condensed periodic table to show the relative sizes of the main group elements.
Why do atoms size increase as you move down a group?
The size increase because the effective nuclear charge (positive charge of nucleus) experienced by the outer electrons decreases down a group.
How does each step of the atom affect the energy level of the atom?
As you go across a period from left to right and atom to atom, each step adds another electron to the same energy level (shell) and a proton to the nucleus. The added electron is slightly repelled by the other electrons in the shell, while the added proton increases the positive charge of the nucleus. This increase in nuclear charge cause the nucleus to attract the electrons and their orbitals more strongly, shrinking the size of the atom.
How to find the effective nuclear charge of Li?
Because of this, we can predict the effective nuclear charge (Z*) experienced by the electron in the 2s orbital by subtracting the two inner electrons from the number of protons. That is: 3 – 2= +1, where 3 is the number of protons (nuclear charge) and 2, the inner electrons. As you can see, the +1 effective nuclear charge experienced by the 1s electron is far less than the nuclear charge.
What is the name of the shell that puts valence electrons in the highest and largest shell?
As you go down a group one atom at a time each step puts valence electron (s) in the highest and largest shell called energy leve l. In addition to that the electrons buried deep inside the atom (inner electrons) usually repel the outer electrons. This repulsion, called screening by the inner electrons usually cause the nucleus to attract ...
Why does the effective nuclear charge decrease?
Effective nuclear charge decreases because the inner electrons repel the outer electrons, weakening the nucleus pull for the outer electrons. We can write a relationship that describes the effective nuclear charge as: Where Z* is the effective nuclear charge, Z, the nuclear charge, and δ, the screening effect by the inner electrons. ...
How to measure atomic radius?
And atomic radius can be measured by x-ray diffraction. A technique in which atoms inside a crystal scatter x-rays. For a particular substance, the pattern of scattering is usually unique, and it can be used to deduce the size of an atom.