What are the trends in the periodic table called?
Major periodic trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, valency and metallic character. These trends exist because of the similar electronic configuration of the elements within their respective groups or periods and because of the periodic nature of the elements.
How do you find the periodic trend?
Moving left to right on the periodic table causes an increase in atomic number (number of protons) as well as electron affinity and electronegativity. Atomic radius, however, will decrease when moving left to right. As more protons are added to the nucleus, they have a stronger attraction to the electrons.
What are the 3 factors that influence periodic trends?
There are three factors that help in the prediction of the trends in the periodic table: number of protons in the nucleus, number of energy levels, and the shielding effect. The atomic radii increase from top to the bottom in any group. The atomic radii decrease from left to right across a period.
What are the 5 periodic trends?
Major trends are electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius, and metallic character. The existence of these trends is due to the similarity in atomic structure of the elements in their group families or periods and because of the periodic nature of elements.
What are the 4 periodic trends?
There are four main periodic trends: electronegativity, atomic size, ionization energy, and electron affinity.
What are the 7 periodic properties?
7. S: Periodic Properties of the Elements (Summary)7.1: Development of the Periodic Table.7.2: Effective Nuclear Charge.7.3: Sizes of Atoms and Ions.7.4: Ionization Energy.7.5: Electron Affinities.7.6: Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids.7.7: Group Trends for the Active Metals.7.8: Group Trends for Selected Nonmetals.
What properties follow a periodic trend?
Major periodic trends include: electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius, melting point, and metallic character. Periodic trends, arising from the arrangement of the periodic table, provide chemists with an invaluable tool to quickly predict an element's properties.
Which of the following is not a periodic trend?
The correct option is (D) Radioactivity.
What are periodic trends?
Periodic trends are specific patterns in the properties of chemical elements that are revealed in the periodic table of elements. Major periodic trends include electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radii, ionic radius, metallic character, and chemical reactivity . Periodic trends arise from the changes in ...
How do periodic trends arise?
Periodic trends arise from the changes in the atomic structure of the chemical elements within their respective periods (horizontal rows) and groups in the periodic table. These laws enable the chemical elements to be organized in the periodic table based on their atomic structures and properties. Due to the periodic trends, ...
How does ionization energy change as you go down the periodic table?
As one progresses down a group on the periodic table, the ionization energy will likely decrease since the valence electrons are farther away from the nucleus and experience a weaker attraction to the nucleus's positive charge . There will be an increase of ionization energy from left to right of a given period and a decrease from top to bottom. As a rule, it requires far less energy to remove an outer-shell electron than an inner-shell electron. As a result, the ionization energies for a given element will increase steadily within a given shell, and when starting on the next shell down will show a drastic jump in ionization energy. Simply put, the lower the principal quantum number, the higher the ionization energy for the electrons within that shell. The exceptions are the elements in the boron and oxygen family, which require slightly less energy than the general trend.
Why do atomic radii increase?
However, atomic radii tend to increase diagonally, since the number of electrons has a larger effect than the sizeable nucleus.
Why is ionization energy lower for elements lower down in a group?
The greater the number of core electrons, the greater the shielding of electrons from the core charge of the nucleus. For this reason ionization energy is lower for elements lower down in a group, and polarizability of species is higher for elements lower down in a group.
What is the significance of the discovery of periodic law?
The Discovery of Periodic Law constitutes one of the most important events in the history of chemical science. Almost every chemist makes extensive and continued use of Periodic Law. Periodic Law also led to the development of the periodic table, which is widely used nowadays.
How many types of atomic radius are there?
There are 4 types of atomic radius:
What are Periodic trends?
You feel hot in summer and cold in winter. That means the climate or weather changes throughout the year starting from January to December.
What is the change in properties of elements down the groups (from top to bottom) and across the periods (from left?
Periodic Trends: The change in properties of elements down the groups (from top to bottom) and across the periods (from left to right) in the Periodic table is known as Periodic trends.
What happens to the atomic size as the number of shells increases?
So as the number of shells increases, the atomic size increases . Now as the atomic size increases, the attractive force between the electron and nucleus decreases. Thus the electron will be lost very easily, which is a property of metals. Thus down the group (from top to bottom), the Metallic character increases.
What happens to the value of an element as you move down the period?
As we move across the period (from left to right), the Valency of the elements first increases and then decreases . While moving down the group (from top to bottom), the Valency of elements remains the same.
What is the tendency to attract the shared pair of electrons?
Short answer: Electronegativity is a tendency to attract the shared pair of electrons.
Can you find every detail of an interactive periodic table?
You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table.
Can we remember the trends in the periodic table?
So based on the very first image, we can easily remember the Periodic trends in Periodic table.
What is ionization potential?
Ionization potential Trends: Ionization potential is defined as the amount of energy required to remove an electron from the outermost shell of a gaseous atom and convert it into a positively charged gaseous ion. The periodic properties in terms of ionization potential increase because the atomic size decreases across a period due ...
What are the properties of the periodic table?
We observe a common trend in properties as we move across a period from left to right or down the group. This trend in properties is known as periodic properties. The important periodic properties are atomic size, metallic character, non-metallic character, ionization potential, electron affinity, and electronegativity.
Why does ionization potential increase?
The periodic properties in terms of ionization potential increase because the atomic size decreases across a period due to increase in the nuclear charge. When we move down the group, ionization potential decreases due to the increase in atomic size.
Why does the atomic size increase in a group?
In a group the atomic size increases due to the addition of shells as we move from one period to another. Across a period the atomic size decreases as the number of shells remain the same while the nuclear charge increases. This leads to the pulling of electrons from the outermost shell towards the nucleus thereby decreasing the size.
What is the tendency to gain electrons?
The tendency to gain electrons increases on moving across a period due to an increase in the nuclear charge and decrease in the atomic size. Hence, non-metallic character increases across a period.
What is the melting point of an element?
The melting point of an element is basically the energy required to change the state of an element from its solid state to its liquid state. Which essentially implies breaking a few bonds. Thus, higher the stronger the bond between the atoms, higher will be the melting point.
Which element loses electrons to form cations?
The elements which lose electrons to form cations are known as metals . Metallic character increases as we move down the group because the atomic size increases which lead to easy loss of electrons. On the other hand, it decreases across a period as we move from left to right.
Why is the periodic table useful?
One of the reasons the periodic table is so useful is because its structure allows us to qualitatively determine how some properties of the elements vary versus their position on the periodic table. The variation of properties versus position on the periodic table is called periodic trends. There is no other tool in science that allows us to judge relative properties of a class of objects like this, which makes the periodic table a very useful tool. Many periodic trends are general. There may be a few points where an opposite trend is seen, but there is an overall trend when considered across a whole row or down a whole column of the periodic table.
What happens when you go from left to right on the periodic table?
These protons serve to pull the electrons closer to the nucleus. Thus, we expect that as you go from left to right along each period, ATOMIC SIZE DECREASES.
What happens to the valence electron configuration as you go down a group?
As you go down a group, the valence electron configuration stays the same, but the number of shells is increasing. Each shell represents distance from the nucleus (as well as energy), thus we expect that ATOMIC SIZE INCREASES as you go down a row on the periodic table.
What properties can be qualitatively understood by the positions of the elements on the periodic table?
Certain properties—notably effective atomic radius, IE, and EA —can be qualitatively understood by the positions of the elements on the periodic table.
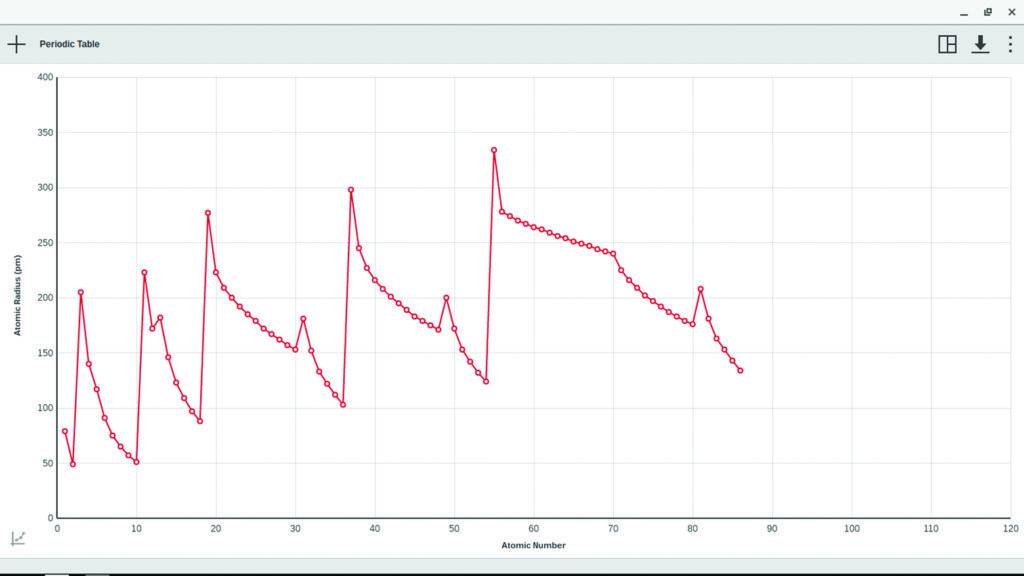
What is the atomic radius?
The atomic radius is an indication of the size of an atom. Although the concept of a definite radius of an atom is a bit fuzzy, atoms behave as if they have a certain radius. Such radii can be estimated from various experimental techniques, such as the x-ray crystallography of crystals.
Why do elements show periodicity?
In modern periodic table elements have been arranged according to their atomic numbers and as stated above atomic numbers are directly related to their physical and chemical properties. That’s why elements show periodicity in their physical and chemical properties in the periodic table. For example, as we move from left to right in a period, ...
What is modern periodic law?
Modern periodic law is the base of periodic trends of properties of elements in the modern periodic table. Following properties of elements show a very clear periodic trends in periodic table –
How does reactivity of metals depend on its electropositive character?
Reactivity of metals depends on its electropositive character. So, more is the metallic character , more is the electropositive nature of the element and more is its reactivity. As metallic character decreases across a period left to right, so reactivity also decreases. Although reactivity of nonmetals increases on moving left to right across a period. Thus, we can conclude, as we move left to right in a period, the reactivity of elements gradually decreases up to the group thirteen and then starts increasing.
What happens when you move left to right across a period in the periodic table?
Across a Period – on moving left to right across a period in the periodic table, first valency increases then decreases.
Why do atomic radii increase in intergases?
The reason for this type of exceptional behavior is that atomic radius refers to van der Waal’s radius in case of noble gases while in case of other elements it refers to covalent radius.
Which elements are present in the 1st group?
For example, hydrogen, lithium, and sodium elements are present in the 1st group and have the same number of valence electrons which is one.
What is the atomic radius?
Atomic Radius. Atomic radius is the distance between the center of the nucleus of an atom to its outermost shell. Periodic trend of atomic radius across a period – As we move from left to right in a period, atomic radius gradually decreases.
What are periodic trends?
Periodic trends are observable patterns in the properties of an element that are dependent on its position in the Periodic Table. These trends have allowed scientists in the past to predict certain characteristics of unknown elements. This is due to the structural similarities’ elements have within a period or family that allows for these trends to take place. We discuss trends for properties such as electronegativity, atomic radius, first ionization energy, reactivity and electron affinity.
How does reactivity affect the periodic table?
The reactivity of metals increases further left along a period, and further down a group. On the other hand, reactivity in non-metals increase further right down a period, and further up a group.
What is the reactivity of an element?
Reactivity describes the ability of a molecule or atom to undergo a chemical reaction, followed by a release in energy. This property is dependent on characteristics such as electronegativity and ionization energy. These are factors that affect the interactions of electrons that chemical reactions undergo. Reactivity is dependent on the classification of an element (metals and non-metals), as they both have differing periodic trends. The reactivity of metals increases further left along a period, and further down a group. On the other hand, reactivity in non-metals increase further right down a period, and further up a group. The most highly reactive element to be observed is cesium, as it spontaneously reacts with air and water!
What is the measure of the tendency of an atom to attract electrons to form a bond?
Electronegativity is a property that measures the tendency of an atom to attract electrons to form a bond. The scale that was formed in order to measure this property is the Pauling scale. It was created by measuring the bond energy of the different elements joined by covalent bonding.
What is the atomic radius?
Atomic Radius: Atomic Radius is a term describing the distance between an atom’s nucleus, and its outermost electron shell. Several factors affect this distance; including the number of an element, and the number of electron shells. Through Periodic trends, the atomic radius increases in size further left of a period, and lower down a group.

Overview
Periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of a certain element. They were discovered by the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in the year 1863. Major periodic trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, valency and metallic character. These trends exist because of the similar electronic con…
Atomic radius
The atomic radius is the distance from the atomic nucleus to the outermost electron orbital in an atom. In general, the atomic radius decreases as we move from left to right in a period, and it increases when we go down a group. This is because in periods, the valence electrons are in the same outermost shell. The atomic number increases within the same period while moving from left to right, which in turn increases the effective nuclear charge. The increase in attractive force…
Ionization energy
The ionization energy is the minimum amount of energy that an electron in a gaseous atom or ion has to absorb to come out of the influence of attracting force of the nucleus. It is also referred to as ionization potential. The first ionization energy is the amount of energy that is required to remove the first electron from a neutral atom. The energy needed to remove the second electron from the neutral atom is called the second ionization energy and so on.
Electron affinity
The energy released when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom to form an anion is known as electron affinity. Trend-wise, as one progresses from left to right across a period, the electron affinity will increase as the nuclear charge increases and the atomic size decreases resulting in a more potent force of attraction of the nucleus and the added electron. However, suppose one moves down in a group. In that case, the electron affinity will decrease as atomic s…
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself is known as electronegativity. It is a dimensionless property because it is only a tendency. The most commonly used scale to measure electronegativity was designed by Linus Pauling. The scale has been named the Pauling scale in his honour. According to this scale, fluorine is the most electronegative element, while cesium is the least electronegative element.
Valency
The valency of an element is the number of electrons that must be lost or gained by an atom to obtain a stable electron configuration. In simple terms, it is the measure of the combining capacity of an element to form chemical compounds. Electrons found in the outermost shell are generally known as valence electrons; the number of valence electrons determines the valency of an atom.
Trend-wise, while moving from left to right across a period, the number of valence electrons of e…
Metallic and non-metallic properties
Metallic properties generally increase down the groups, as decreasing attraction between the nuclei and outermost electrons causes these electrons to be more loosely bound and thus able to conduct heat and electricity. Across each period, from left to right, the increasing attraction between the nuclei and the outermost electrons causes the metallic character to decrease. In contrast, the nonmetallic character decreases down the groups and increases across the periods.
See also
1. Periodic table
2. History of the periodic table
3. List of elements by atomic properties