
Causes
When To Go To The Er For Heavy Menstrual Bleeding? If Menstrual Bleeding Causing an Emergency Get to the nearest emergency room as soon as you notice you’ve developed acute, severe bleeding, in which you soak through about two to four pads or tampons. Upon experiencing any bleeding during pregnancy, be sure to seek medical assistance immediately.
Symptoms
Ways to manage or stop heavy periods
- Lifestyle changes. A person using a menstrual cup may need to change it less than a pad or tampon. ...
- Diet and supplements. ...
- Medications. ...
- Surgeries. ...
- Possible reasons for heavy periods. ...
- When to see a doctor. ...
- Outlook. ...
Complications
What are the treatment options for heavy periods?
- Not treating. ...
- Levonorgestrel intrauterine system (LNG-IUS) The LNG-IUS treatment usually works very well. ...
- Tranexamic acid tablets. ...
- Anti-inflammatory painkillers. ...
- The combined oral contraceptive (COC) pill. ...
- Long-acting progestogen contraceptives. ...
- Norethisterone. ...
- Other medicines. ...
- Surgical treatment. ...
When to go to the ER for heavy menstrual bleeding?
Heavy periods have a wide range of causes, most commonly, they’re due to hormone imbalances, particularly high estrogen levels or not ovulating, but they can be due to a variety of underlying causes from PCOS to an uncommon but not completely rare genetic bleeding disorder that can cause heavy periods (and I mean HEAVY).
How to stop heavy period flow?
What are the treatment options for heavy periods?
What hormone causes heavy periods?
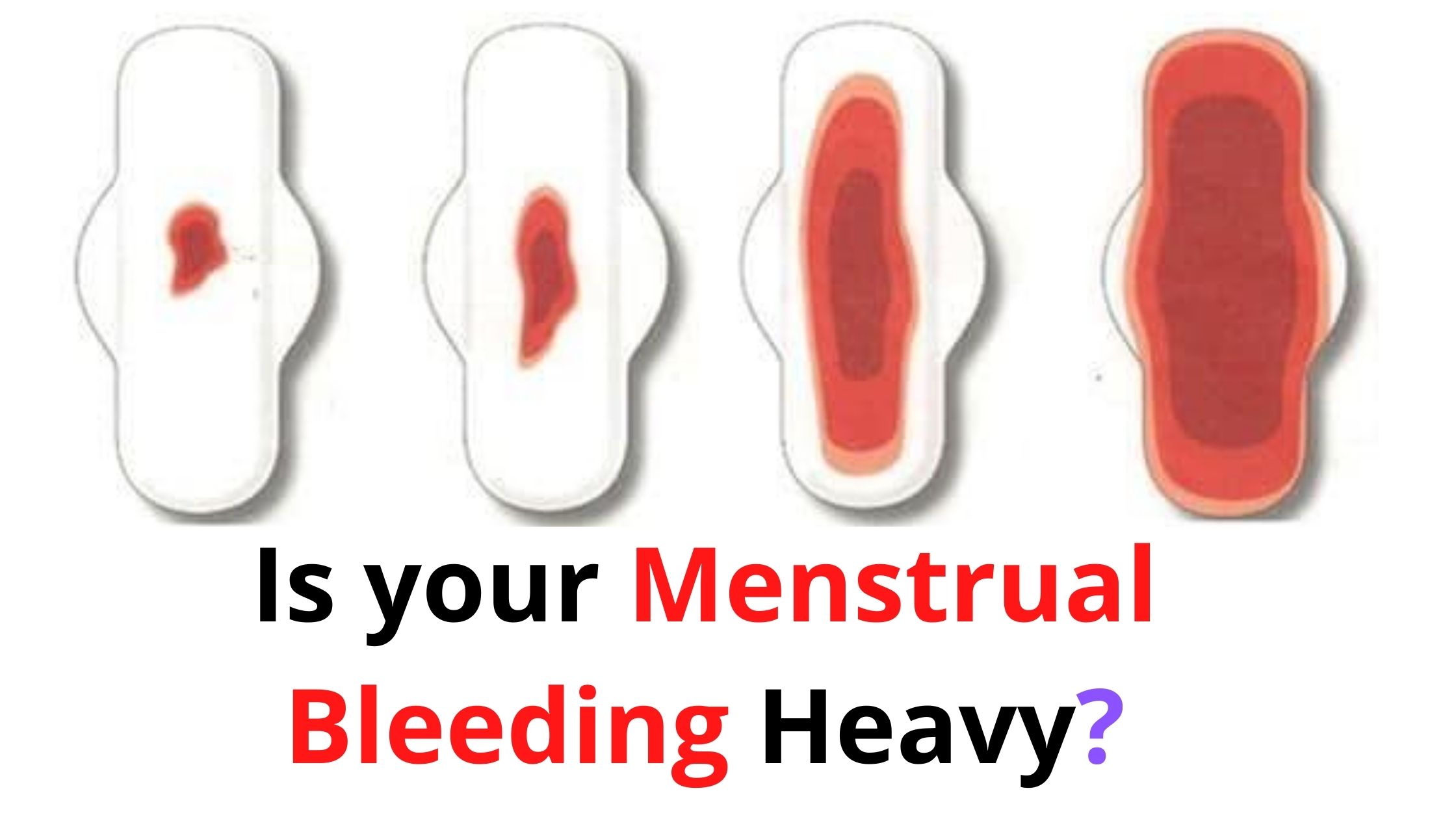
What is considered heavy menstrual bleeding?
HMB, which used to be called “menorrhagia,” is prolonged or excessive heavy bleeding during periods that can be so bad it can interfere with your daily life. It can be nerve-wracking when you’re just not sure why your periods are so heavy, and HMB can make you dread getting your period each month.
What is HMB treatment?
HMB treatment is determined by your health care provider based on a variety of factors, including: Your medical history and general health. Your capacity to tolerate specific therapies, medicines, or procedures. The cause and severity of HMB.
What does it mean when you have a heavy bleeding period?
Heavy menstrual bleeding is the presence of abnormally prolonged or heavy bleeding. With HMB, you may have to change a pad or tampon almost every hour for several hours in a row. You may also have severe painful cramps that can interfere with your usual activities.
What is heavy bleeding?
What is heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) HMB is characterized by having periods with abnormally prolonged or heavy bleeding that interferes with physical, emotional, and social daily life. Heavy menstrual bleeding used to be called menorrhagia, but that word’s not used in medicine anymore. If you have HMB, it can be difficult to maintain your normal ...
What is the procedure to remove the topmost layer of the endometrium?
Procedures. There are several medical procedures that can be prescribed to manage HMB in some cases. Dilation and Curettage (D &C): This is a surgical method in which the health care provider removes the topmost layer of the endometrium to reduce heavy menstrual bleeding.
How to tell if you have a heavy period?
These symptoms and signs may indicate a heavy menstrual flow: 1 You soak through one or more tampons or pads an hour for several hours in a row. 2 You have to use two kinds of period products at the same time to control heavy flowing periods. 3 You have to get up at night to change your sanitary pads or products. 4 Your periods last longer than eight days. 5 You pass blood clots that are 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) or larger during your periods. 6 Your periods soak through your bedding or clothes. 7 You have to restrict your everyday activities because of heavy menstrual bleeding. 8 You experience symptoms and signs of iron-deficiency anemia, including shortness of breath, fatigue, or tiredness.
How to measure blood flow during menstruation?
Several methods exist to measure your flow during menses: The alkaline hematin technique: In this technique, the blood present in a used sanitary pad is measured chemically. This is the gold standard to diagnose heavy menstrual bleeding, and blood loss that’s greater than 80 milliliters per cycle is considered heavy.
What is the term for a condition in which the endometrial uterine cells grow into the muscular wall?
Uterine adenomyosis is a condition in which the endometrial uterine cells grow into the muscular wall of the uterus, causing uterine enlargement and painful, heavy bleeding. Hormonal birth control methods can help control the condition, and the definitive treatment for adenomyosis is a hysterectomy. 7
What is the procedure for removing fibroids?
4 Surgical options include myomectomy (removal of the fibroid) and uterine artery embolization (the blood supply is cut off to the fibroid). 5 .
How long does it take to get a tampon out of your system?
Go to the nearest emergency room if you experience severe, acute bleeding in which you soak through four or more pads or tampons in a two-hour period. 1 If you are pregnant, seek immediate medical care if you have any menstrual bleeding.
How to tell if you have heavy bleeding?
Other signs of heavy menstrual bleeding include: Wearing more than one pad at a time in order to control the bleeding. Having to change your tampon or pad in the middle of the night. If your menstrual blood contains clots that are the size of a quarter or bigger.
What is the treatment for PID?
In PID, one or more reproductive organs can be infected—including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and/or cervix. The recommended treatment for PID is antibiotic therapy. 8 . An Overview of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.
What is a PID?
PID is most often caused by an untreated sexually transmitted infection (STI), however, it can sometimes occur following childbirth, abortion, or other gynecological procedures. In PID, one or more reproductive organs can be infected—including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and/or cervix. The recommended treatment for PID is antibiotic therapy. 8
Can menorrhagia cause heavy periods?
Anita Sadaty, MD. Updated on January 15, 2021. Menorrhagia —excessive menstrual bleeding—can be a cause of medical issues, and it can cause serious complications. You should make an appointment to see your gynecologist if you have heavy periods. Sometimes heavy bleeding is an emergency that warrants prompt medical attention.
How long does menorrhagia last?
Menorrhagia is the medical term for menstrual bleeding lasting for longer than 7 days. About 1 in every 20 women has menorrhagia. Some of the bleeding can be very heavy, meaning you would change your tampon or pad after less than 2 hours. It can also mean you pass clots the size of a quarter or even larger.
How do you know if you have menorrhagia?
Signs of menorrhagia include: Soaking 1 or more tampons or pads every hour for many consecutive hours. Doubling up on pads. Changing pads or tampons during the night. Long-lasting menstrual periods (longer than 7 days) Blood clots the size of a quarter or larger.
What is the best treatment for uterine bleeding?
Antifibrinolytic medicines to reduce bleeding. Dilation and curettage to reduce bleeding by removing the top layer of uterus lining. Operative hysteroscopy to remove fibroids and polyps and remove lining of uterus. Endometrial ablation or resection to remove all or part of the lining of the uterus.
How to stop bleeding during period?
Common treatments include: Iron supplements to put more iron into your blood. Ibuprofen to reduce pain and amount of bleeding. Birth control to make periods more regular and reduce bleeding (pills, vaginal ring, patch) Intrauterine contraception (IUD) to make periods more regular and reduce bleeding.
What tests are done to diagnose menorrhagia?
Physical tests or exams done to diagnose menorrhagia may include: Pelvic exam. Blood test to check thyroid, check for anemia and how the blood clots. Pap test to check cells from cervix for changes. Endometrial biopsy to check uterine tissue for cancer or abnormalities.
What causes menorrhagia?
Menorrhagia can be caused by uterine problems, hormone problems or other illnesses. Other causes include:
What is the purpose of ultrasound?
Ultrasound to check function of blood vessels, tissues and organs. Sometimes additional tests are still required to understand the cause of bleeding, including: Sonohysterogram to check for problems in the lining of the uterus. Hysteroscopy to check for polyps, fibroids or other problems.
What is very heavy period flow or menses?
Normal blood loss during period in women is usually less than 80mls. If your period is more than 80mls then it is heavy. However, it may be difficult to calculate how much of blood you’ve lost during menstruation.
What causes heavy period flow in women?
If your period is heavy with very frequent change of pads in few hours or your periods are now lasting longer than usual, then these are the possible causes.
What is Normal period length and menstrual flow?
In women, period occurs due to regular cyclic shredding of the endometrium covering the uterus. This is due to hormonal changes that occur during the menstrual cycle.
Why does my period flow so fast?
Endometrial hyperplasia, which is the overgrowth and thickening of the endometrium, can cause heavy period flow. It is due to unopposed effects of estrogen especially in women taking hormone replacement or diseases like polycystic ovarian syndrome. Symptoms are: Bleeding or spotting between period.
What is a fibroid?
Fibroid are benign mass or growth that affects the uterus. It can cause infertility in women and very heavy bleeding. Uterine fibroid can be found on the surface of the uterus or within the uterine muscle.
Why is my period so heavy?
If you have a heavy menstruation for the first time, then it may likely not be a problem. However, heavy persistent period is abnormal. One of these may be the reason your period is heavier this month. Vaginal infections. Stress.
What to do if you have a heavy bleeding during your period?
If the cause of your heavy bleeding during periods is due to PID, it will be treated will antibiotics.
What causes uterine bleeding?
Adenomyosis : Endometrial tissue, which normally lines the inside of the uterus, grows into the muscle wall of the uterus. Bleeding disorders : Certain inherited bleeding disorders, such as von Willebrand’s disease, which prevents blood from clotting properly, can cause abnormal bleeding. Cancer : Cervical cancer and uterine cancer can cause heavy ...
How to treat heavy bleeding?
If there is a reason estrogen should not be prescribed, an oral progestin might be recommended. Over-the-counter treatments such as ibuprofen can help decrease the amount of bleeding and pain, as well.
Where do fibroids grow?
Uterine fibroids : Noncancerous tumors made up of muscle tissue can grow in the walls of the uterus, the lining inside the uterus (endometrial cavity), or on the outside of the uterus. Uterine polyps : Overgrowth of endometrial tissue can form growths called polyps inside the uterus.
What is the test used to look for abnormalities?
Used to look for any abnormalities. Pap smear: Sample of cells from the cervix that are examined under a microscope for infection or changes that can lead to cancer or already are cancerous. Endometrial biopsy: A test that samples a small amount of endometrial tissue for examination under a microscope.
How long does it take for a tampon to bleed?
Bleeding for more than seven days. Bleeding that soaks through one or more tampons or pads every hour for several hours in a row. Need to use multiple pads to control menstrual flow. Need to change pads or tampons during the night. Menstrual flow with blood clots larger than a quarter.
What is the name of the disorder that causes small cysts in the ovaries?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) : PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can cause small cysts, or fluid-filled sacs, to develop in the ovaries, causing irregular periods
How often do women have periods?
For most women, menstrual cycles occur about every 28 days, and periods last four to seven days. Abnormal menstruation includes problems such as heavy bleeding, known as menorrhagia, irregular menstrual bleeding, and pain during periods, known as dysmenorrhea. UT Southwestern gynecologic surgeons, specialists, and their teams are nationally ...
Why does dysmenorrhea make cramps worse?
But menorrhagia makes dysmenorrhea look like an amateur when it comes to causing painful cramps because then it becomes so severe due to heavy menstrual bleeding with clots larger than a quarter that you might need to be evaluated medically . Nobody wants to live through this much pain, you definitely don’t want either.
What is the term for the increase in menstrual blood loss?
Menorrhagia is the increased menstrual blood loss (defined as >80mL/cycle). In reality, menstrual blood loss is rarely measured. And very often only these women who have developed heavy menstrual bleeding interfering with life visit their healthcare providers.
How to diagnose menorrhagia?
Some test which might help to diagnose menorrhagia include: 1 Ultrasound or laparoscopy. These tests due to its imaging abilities help to show the image of your uterus, pelvis and ovaries using sound waves/ direct visualization and so can help detect abnormalities if spotted. 2 Pap smear/test. This test works with the collection of cells from your cervix. These cells are tested to look out for inflammation or an infection around the cervix which may be cancerous and so lead to heavy bleeding when you menstruate or irregularly. 3 Blood tests. Your doctor takes your blood sample and checks if there is a case of iron deficiency in your blood due to Anemia and some other problems like blood-clotting anomalies and thyroid disorder (TFT- thyroid function test). 4 Endometrial biopsy. A tissue sample of your uterine wall might be taken to a pathologist by your doctor in order to know why it keeps shedding blood. 5 Further tests such as hysteroscopy, sonohysterography, etc. depending on what the previous set of tests would show.
What is a DUB?
It is an abnormal thing if you have to use 2 or more pads within two 2 hours. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB). This is a heavy and/or irregular bleeding in the absence of recognizable pelvic pathology. It is associated with anovulatory menstrual cycles .
How effective is progesterone in utero?
They reduce bleeding by up to 86% at 3 months, 97% at 1 year. They are effective in dysfunctional uterine bleeding and reduce fibroid volume after 6-18 months use.
How long does it take for a tampon to soak?
You should call the attention of your doctor when you notice one or some of the following symptoms: Extremely heavy menstrual bleeding from the vagina which soaks one tampon at least within the space of two hours. Irregular vaginal bleeding. Always take note of when you begin to notice bleeding in between periods.
What causes perimenopausal women to have a bleed?
In perimenopausal women, consider endometrial carcinoma. General bleeding problems such as von Willebrand's disease (vWF) may be the cause as well.
What is the thyroid gland?
Your thyroid is the gland in your neck responsible for hormone production and distribution. If it’s not functioning properly, it can wreak havoc on your cycle. Conditions like hypothyroid (producing too little thyroid hormone) or hyperthyroid (producing too much thyroid hormone) can impact the flow and severity of your menstrual cycle. In order to properly diagnose a thyroid condition, your doctor should run a thyroid panel, often called a TSH panel, to assess your thyroid’s health. Doctors can also test to see your levels of T3 and T4 hormone and run anti-thyroid antibody panels to see if you have an underlying autoimmune thyroid disease like Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis or Grave’s disease.
What does it mean when you have a heavy period?
Menorrhagia is defined as menstrual bleeding that can be heavier than usual. If you’re changing your tampon every two hours or sooner, or are passing blood clots the size of a quarter or larger, you may be suffering from heavy periods.
What causes a lot of bleeding during your cycle?
It can be very painful and hard to diagnose, but several treatments can make this chronic illness more manageable. 7. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Another condition that can cause heavy clots and bleeding during your cycle, PCOS, is a common hormone imbalance.
What medications cause abnormal menstrual flow?
Anti-inflammatory medications, hormonal medications (like estrogen and progestins) and anticoagulants can contribute to abnormal menstrual flow and bleeding. If you’re passing giant blood clots during periods, try to take inventory of the medications you’re taking and ask your doctor about their potential side effects. 5.
What is a miscarriage in pregnancy?
In the initial stages of pregnancy, if there is a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy (which is when a fetus begins to form outside of the uterus), it can oftentimes be confused for a heavier-than-usual period clot. An early loss of a pregnancy can lead to larger-than-usual blood clots as well.
Why does my period feel heavier?
There are plenty of less-common chronic conditions that can affect your period and make it heavier than it should be: various thyroid diseases, adenomyosis, blood disorders like Von Willebrand disease, certain types of cancers and Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (or PID).
Can fibroids cause clotting?
There are many types of benign fibroids, but submucosal fibroids (fibroids that grow inside the uterine cavity) are the most likely to cause heavy bleeding and large clotting. Uterine polyps that grow on the cervix or in the lining of the uterus can also be a factor in heavy clotting. If you’re experiencing heavy bleeding, ...
Could I have a polyp?
Polyps are soft outgrowths which can arise from the uterus and can cause heavy periods. They are usually benign with prevalence between 6% and 32%. 3 Different research shows different prevalences and as polyps don’t cause any symptoms apart from bleeding they are often under-diagnosed.
Do I have fibroids?
Fibroids are benign growths that arise from the muscle of the uterus. The majority of people with uterine fibroids are asymptomatic and so are often undiagnosed. Their incidence increases with age, and they are more common in Afro-Caribbean people. 7 Prevalence ranges between 5% and 21% and can rise to 70-80% by the age of 50. 8 Their growth is stimulated by oestrogen and progesterone.
Could it be hypothyroidism?
Menstrual abnormalities, particularly menorrhagia, can be one of the first noticeable symptoms of thyroid abnormalities, particularly hypothyroidism. 10 The incidence increases with age and thyroid dysfunction can be masked by menopausal symptoms.
Could it be a coagulation problem?
Although most people with a coagulation (blood clotting) problem are likely to have had menorrhagia at a young age and therefore be diagnosed, it is possible for clotting problems to occur later in life. Bleeding disorders can occur during perimenopause and those that do have sudden heavy bleeding should be investigated. 12 Medication such as warfarin, heparin, or steroids can also effect your clotting, as can disorders of the liver, thyroid, bone marrow.
Why do fibroids enlarge during perimenopause?
Firstly, the increase in oestrogen during the perimenopause can cause fibroids to enlarge, increasing the surface area of the endometrium which in turn exposes more endometrium to oestrogen. Secondly the growth of fibroids can impede blood flow into and from the womb which can cause congestion.
What hormones are produced during the beginning of a normal menstrual cycle?
During the beginning of a normal menstrual cycle, a hormone called follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) rises which stimulates follicles (eggs) to mature in the ovaries. Many follicles are stimulated during a cycle and these follicles produce oestrogen which is required to thicken the lining of the womb (endometrium).
How does the body recruit eggs during perimenopause?
It does this by increasing FSH levels . This part of the cycle can take longer than usual as it becomes harder to recruit eggs. There is an increase in oestrogen from the many follicles stimulated. These higher levels of oestrogen act on the endometrium during the long stimulation period, making it thicker and resulting in heavy periods. 2
