How to find atomic number?
What is Atomic Number?
- The total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom gives us the atomic number of that atom.
- It is represented with the letter ‘Z.’
- All the atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons, and hence the same atomic number.
- Atoms of different elements have different atomic numbers.
What are the atomic numbers?
The atomic number or proton number is defined as the total number of protons in the nucleus and is given the symbol Z. The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the atomic number.
What is the meaning of atomic number?
The atomic number is simply the number of protons in an atom. For this reason, it's sometimes called the proton number. In calculations, it is denoted by the capital letter Z. The symbol Z comes from the German word zahl, which means number of numeral, or atomzahl, a more modern word which means atomic number.
What is the atomic number of an atom?
The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom or the number of electrons in an electrically neutral atom. For example, in a sodium atom, there are 11 electrons and 11 protons. Thus the atomic number of Na atom = number of electrons = number of protons = 11.

What does the atomic mass come from on the periodic table?
The atomic mass is a weighted average of all of the isotopes of that element, in which the mass of each isotope is multiplied by the abundance of that particular isotope.
What does the atomic of an element represent?
Explanation: Atomic number of an element shows the number of protons in the nucleus of that atom.
What does the atomic number of an element represent quizlet?
The atomic number of an atom represents the number of protons located in its nucleus. (Since elements are neutrally charged, the number of protons are equivalent to the number of electrons. Thus, the atomic number also tells the number of electrons.)
What three things does the atomic number of an element tell us?
The three main atomic particles are protons, neutrons and electrons. The atomic number of an atom identifies the number of protons in the atom. This is the defining characteristic of an element. An atom can gain or lose neutrons or electrons while retaining its elemental identity.
What two things does the atomic number represent?
The term atomic number, conventionally denoted by the symbol Z, indicates number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom, which is also equal to the number of electrons in an uncharged atom.
Does the atomic number represent electrons?
The atomic number equals the charge on the nucleus. It therefore also equals the number of protons in the nucleus and also equals numerically the number of electrons in the neutral atom. The atomic number has the symbol Z.
What does the atomic mass unit represent?
The atomic mass unit (AMU or amu) of an element is a measure of its atomic mass. Also known as the dalton (Da) or unified atomic mass unit (u), the AMU expresses both atomic masses and molecular masses. AMU is defined as one-twelfth the mass of an atom of carbon-12 (12C).
What two things does the atomic mass represent?
The atomic mass tells us the weight of protons and neutrons.
What is the atomic number of an element?
Element Atomic Number. One number you will find on all periodic tables is the atomic number for each element. This is the number of protons in the element, which defines its identity. How to Identify It: There isn't a standard layout for an element cell, so you need to identify the location of each important number for the specific table.
What is the value of an atom in the periodic table?
However, the value given in the periodic table is an average of the mass of all isotopes of a given element. While the number of electrons does not contribute significant mass to an atom, isotopes have differing numbers of neutrons, which do affect mass.
Why do periodic tables not have periods?
Most periodic tables do not number them because they are fairly obvious, but some tables do. The period indicates the highest energy level att ained by electrons of an atom of the element in the ground state. How to Identify It: Period numbers are located on the left-hand side of the table. These are simple integer numbers.
Why do periodic tables omit electron configuration?
Most tables omit this value because it takes up a lot of room.
What is the lowest atomic number?
The atomic number is easy because it is an integer that increases as you move from left to right across the table. The lowest atomic number is 1 ( hydrogen ), while the highest atomic number is 118. Examples: The atomic number of the first element, hydrogen, is 1. The atomic number of copper is 29.
How to identify atomic mass?
How to Identify It: The atomic mass is a decimal number. The number of significant figures varies from one table to another. It's common to list values to two or four decimal places. Also, the atomic mass is recalculated from time to time, so this value may change slightly for elements on a recent table compared with an older version.
What is the atomic mass of hydrogen?
Examples: The atomic mass of hydrogen is 1.01 or 1.0079. The atomic mass of nickel is 58.69 or 58.6934.
What is the significance of the atomic number?
The Significance of the Atomic Number in Chemistry. Each element has its own unique atomic number, which is the number of protons in its atom. Steven Hunt, Getty Images. Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, ...
What is the atomic number of an element?
In fact, this number is how you can distinguish one element from another. The atomic number is simply the number of protons in an atom. For this reason, it's sometimes called the proton number. In calculations, it is denoted by the capital letter Z.
How many protons are in an atom of carbon?
No matter how many neutrons or electrons it has, an atom with one proton is always atomic number 1 and always hydrogen. An atom the contains 6 protons is by definition an atom of carbon. An atom with 55 protons is always cesium.
What happens to the number of protons and neutrons in an element?
Theoretically, there is no maximum number, but elements become unstable with more and more protons and neutrons, making them susceptible to radioactive decay. Decay may result in products with a smaller atomic number, while the process of nuclear fusion may produce atoms with a larger number.
Why are atomic numbers always whole numbers?
Because protons are units of matter, atomic numbers are always whole numbers. At present, they range from 1 (the atomic number of hydrogen) to 118 (the number of the heaviest known element). As more elements are discovered, the maximum number will go higher. Theoretically, there is no maximum number, but elements become unstable with more and more protons and neutrons, making them susceptible to radioactive decay. Decay may result in products with a smaller atomic number, while the process of nuclear fusion may produce atoms with a larger number.
Why is the atomic number important?
Why the Atomic Number Is Important. The main reason the atomic number is important is because it's how you identify the element of an atom. Another big reason it matters is because the modern periodic table is organized according to increasing atomic number.
Where are protons and neutrons found?
Protons are found together with neutrons in the atomic nucleus. The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom is its atomic mass number (denoted by the letter A). The average sum of the number of protons and neutrons in a sample of an element is its atomic mass or atomic weight .
What does the atomic number tell us about an element?
Every element on the periodic table has an atomic number that tells us how many protons are in the nucleus of an atom of that element . To understand this a little better, let's recall the structure of an atom.
How to find the atomic number of an element?
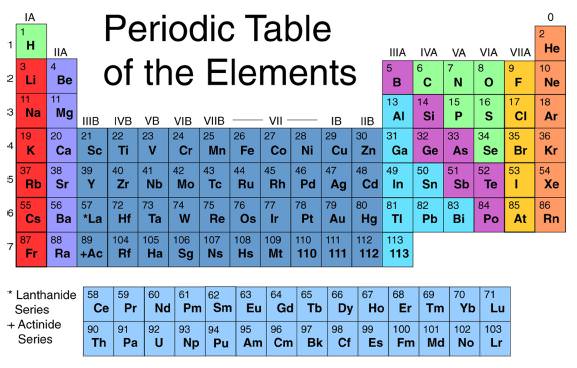
When we look at the periodic table, we will find an element's atomic number at the top left-hand corner of the box containing its symbol. The elements are arranged by their atomic numbers with the numbers increasing one by one as we move from left to right across each period (or horizontal row). We can see, then, that hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, for it has one proton in its nucleus. It also has one electron. Iron, on the other hand, has an atomic number of 26, so it has twenty-six protons.
How many particles are in an atom?
An atom is made up of three particles, protons, neutrons, and electrons. The protons and neutrons are found in the atom's nucleus, its center, while the electrons are found on the electron shells arranged around the nucleus. Atoms have equal numbers of protons and electrons so that the atom's charge remains balanced. Protons are positively charged, and electrons are negatively charged. Looking at an element's atomic number, therefore, also tells us the number of electrons that element has in each of its atoms.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is equal to the total number of protons in the nucleus of the atoms of that element. The atomic number can provide insight into the electronic configuration of the element. For example, carbon has an electron configuration of [He] 2s 2 2p 2, since its atomic number is 6.
Why is the atomic number important?
This number is very important, because it is unique to a given element’s atoms. An element’s atoms all have the same number of protons and each element has a different number of protons in its atoms. Test your knowledge on periodic table elements.
What is the number of protons in the nucleus called?
The number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number. The atomic number of each element is unique.
Why is the atomic number of each element unique?
While the atomic number always stays the same some elements have atoms with different atomic mass numbers. This is because some elements have a different number of neutrons in the nucleus.
How to find the mass of an element?
The number of protons and the number of neutrons shall determine the mass number of an element. Since the isotopes of an element have slightly different mass numbers, it calculates the atomic mass by obtaining the mean of the mass numbers for its isotopes.
How can periodic trends be observed?
Periodic trends in the properties of the elements can be observed down the groups and across the periods of the modern periodic table. Every chemical element has a specific atomic number, which provides insight into the number of protons present within its nucleus.
What is the name of the tabular arrangement of all the elements on the basis of their respective atomic numbers?
The periodic table is the tabular arrangement of all the chemical elements on the basis of their respective atomic numbers. In the periodic table , the vertical columns are called ‘groups’ and the horizontal rows are called ‘periods’.
What happens when atomic number increases?
As the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost shell, causing the atomic radius to decrease due to the increasing nuclear charge.
What does the increasing atomic number mean?
In the modern periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons define the identity of an element (i.e., an element with 6 protons is a carbon atom, no matter how many neutrons may be present).
What do you think happens to the size of an atom as the atomic number increases justify your answer?
This is because atomic number increases down a group, and thus there is an increased distance between the valence electrons and nucleus, or a greater atomic radius.
Does atomic number increase or decrease across the period?
As you move across a period, the atomic mass increases because the atomic number also increases. When the atomic number increases, this means that there are more protons and neutrons that add to the atomic mass of an atom.
Why does atomic number increase down a group?
Down a group, the number of energy levels (n) increases, so there is a greater distance between the nucleus and the outermost orbital. This results in a larger atomic radius.
Why does atomic mass increase?
Explanation: As you go from left to right in the Periodic Table, you are adding more protons and neutrons to the nuclei. The atoms in the rows further down have even more protons and nucleons. Therefore, atomic mass increases from left to right and from top to bottom of the Periodic Table.
What does the atomic number of an element represent?
The number of protons in a nucleus is called the atomic number and always equals the number of electrons in orbit about that nucleus (in a nonionized atom). Thus, all atoms that have the same number of protons–the atomic number–are atoms of the same element.
