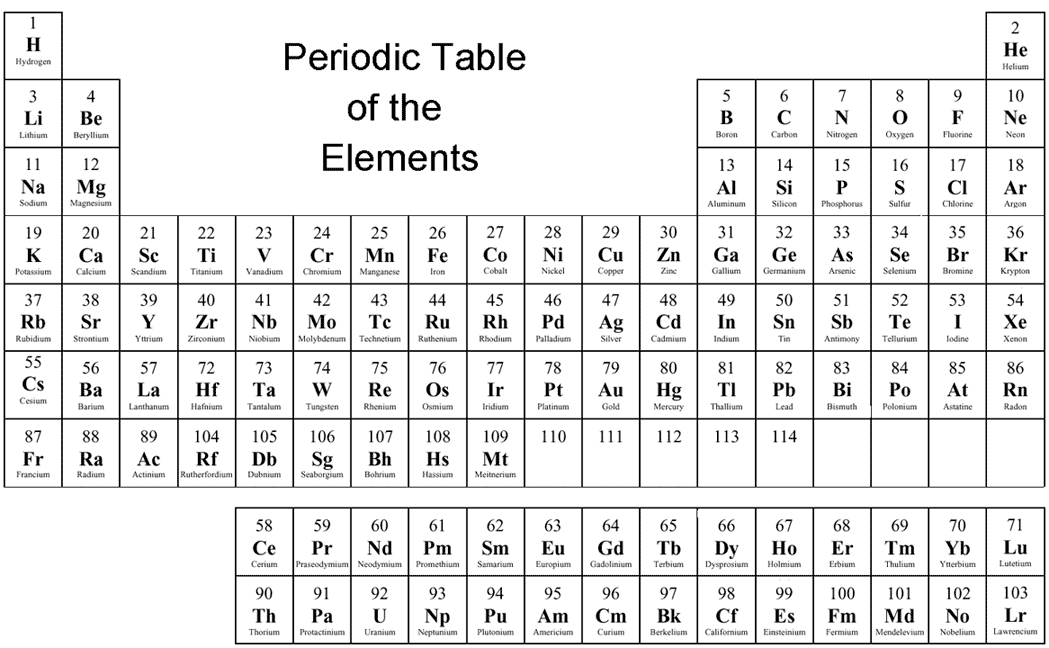
What does 'BA' stand for in the periodic table?
The s-block elements include hydrogen (H), helium (He), lithium (Li), beryllium (Be), sodium (Na), magnesium (Mg), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), rubidium (Rb), strontium (Sr), cesium (Cs), barium (Ba), francium (Fr) and radium (Ra). The periodic table shows exactly where these elements are within the s-block.
What are some interesting facts about the periodic table?
Interesting Facts On Periodic Table of Elements
- Founder of Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleyev is the father of the modern periodic table of elements. ...
- Columns of the Periodic Table. The periodic table has 18 vertical columns called groups and seven horizontal columns called Periods.
- Size of the Atom. ...
- Unique Elements. ...
- Properties of Elements. ...
- Facts About Hydrogen. ...
What are the energy levels on the periodic table?
When you look at the Periodic Table of the Elements, the energy levels of the atoms correspond to the rows of the table. The two elements in the top row, hydrogen and helium, are filling their first energy level with their final electrons. The eight elements of the second row are filling their second energy level.
What are the basic elements of the periodic table?
- Element 13 - Aluminum
- Element 31 - Gallium
- Element 49 - Indium
- Element 50 - Tin
- Element 81 - Thallium
- Element 82 - Lead
- Element 83 - Bismuth
- Element 113 - Ununtrium - will probably be a basic metal.
- Element 114 - Flerovium - will probably be a basic metal.
- Element 115 - Ununpentium - will probably be a basic metal.
See more
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).
Where is boron found?
It is a naturally occurring element that is found in sedimentary rocks, coal, shale, and some soils. The most common use of boron is in boric acid, which is used as a natural pesticide and can be used to...
What is the most common source of boron?
The most common sources of boron are tourmaline, borax, and kernite. Boron is used to produce the color green in pyrotechnics and flares. It is also used as an ignition source in rockets, and also in nuclear reactors as radiation shields and neutron detectors. Boron filaments are often used in the aerospace industry because of their light weight and great strength.
What is the name of the element that is found in sedimentary rocks?
Boron , which is number 5 on the chart, is identified by the letter B. It is a naturally occurring element that is found in sedimentary rocks, coal, shale, and some soils. The most common use of boron is in boric acid, which is used as a natural pesticide and can be used to treat fungal infections. The commercial name for boric acid is "borax," which can be used in detergents. (I have used borax to kill fleas in carpets; some people prefer it because it is not as harmful to children or pets as other pesticides are.)
Is boron a metal?
Boron is a Group 13 element whose properties place it on the border between metals and nonmetals. It is a semiconductor, and chemically it is closer to silicon than to aluminum, gallium, indium, and thallium.
What does the B symbol mean in the periodic table?
The symbol "B" on the periodic table (Chemistry) stands for Boron.
How does the periodic table order elements?
The periodic table describes the elements in their very atomic origin ordered by the number of protons in their nuclei (atomic number). The different neutron configurations that describe the isotopes per element are left out. Besides atomic number it orders elements according to electronic configuration to classify elements with similar chemical behavior. That can be in the form of columns or in the form of rows.
What is the A group of elements?
Before the IUPAC got hold of the periodic table and numbered all the columns from 1 through 18, there was the A-group of elements, also known as the representative elements, or the main-group elements, and the B-group of eleme
What is the most common source of boron?
The most common sources of boron are tourmaline, borax, and kernite. Boron is used to producing the color green in pyrotechnics and flares. It is also used as an ignition source in rockets, and also in nuclear reactors as radiation shields and neutron detectors. Boron filaments are often used in the aerospace industry because of their light weight and great strength.
What is the chemical formula for acetyl?
In organic chemistry, acetyl is a moiety, the acyl with chemical formula CH3CO. It is sometimes represented by the symbol Ac (not to be confused with the element actinium).
What is the Latin word for copper?
Cuprum Shortened to Cu, is Latin for the elements we now call Copper. many element retain there original Latin based symbol.
What does group 1 represent?
The columns are most straightforward to understand. For example, group 1 represent the alkali metals with all cations of 1+ in inorganic compounds and group 17 (IUPAC) represent the halogens with all 1- anions.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of elements, is a tabular display of the chemical elements, which are arranged by atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The structure of the table shows periodic trends. The seven rows of the table, called periods, generally have metals on ...
What are the columns of periodic table called?
The seven rows of the table, called periods, generally have metals on the left and nonmetals on the right. The columns, called groups , contain elements with similar chemical behaviours.
What is the atomic number plotted against?
Atomic number plotted against atomic radius, excluding the noble gases. Atomic radii vary in a predictable and explainable manner across the periodic table. For instance, the radii generally decrease along each period of the table, from the alkali metals to the noble gases; and increase down each group.
What is the electron configuration of a neutral atom?
The electron configuration or organisation of electrons orbiting neutral atoms shows a recurring pattern or periodicity. The electrons occupy a series of electron shells (numbered 1, 2, and so on). Each shell consists of one or more subshells (named s, p, d, f and g). As atomic number increases, electrons progressively fill these shells and subshells more or less according to the Madelung rule or energy ordering rule, as shown in the diagram. The electron configuration for neon, for example, is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. With an atomic number of ten, neon has two electrons in the first shell, and eight electrons in the second shell; there are two electrons in the s subshell and six in the p subshell. In periodic table terms, the first time an electron occupies a new shell corresponds to the start of each new period, these positions being occupied by hydrogen and the alkali metals.
What are metals and nonmetals?
In chronological order, this section discusses metals and nonmetals (and metalloids); categories of elements; groups and periods; and periodic table blocks. While the recognition of metals as solid, fusible and generally malleable substances dates from antiquity, Antoine Lavoisier may have the first to formally distinguish between metals and nonmetals ('non-métalliques') in 1789 with the publication of his 'revolutionary' Elementary Treatise on Chemistry. In 1811, Berzelius referred to nonmetallic elements as metalloids, in reference to their ability to form oxyanions. In 1825, in a revised German edition of his Textbook of Chemistry, he subdivided the metalloids into three classes. These were: constantly gaseous 'gazolyta' (hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen); real metalloids (sulfur, phosphorus, carbon, boron, silicon); and salt-forming 'halogenia' (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine). Only recently, since the mid-20th century, has the term metalloid been widely used to refer to elements with intermediate or borderline properties between metals and nonmetals. Mendeleev published his periodic table in 1869, along with references to groups of families of elements, and rows or periods of his periodic table. At the same time, Hinrichs wrote that simple lines could be drawn on a periodic table in order to delimit properties of interest, such as elements having metallic lustre (in contrast to those not having such lustre). Charles Janet, in 1928, appears to have been the first to refer to the periodic table's blocks.
How many electrons are in neon?
The electron configuration for neon, for example, is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. With an atomic number of ten, neon has two electrons in the first shell, and eight electrons in the second shell; there are two electrons in the s subshell and six in the p subshell. In periodic table terms, the first time an electron occupies a new shell corresponds to ...
How many categories are there in the periodic table?
The elements of the periodic table shown here are divided into nine categories; six for the metals, and two for nonmetals, and a metalloid category. The nine categories (or sets) correspond to those found in the literature for the applicable part of the periodic table. Different authors may use different categorisation schema depending on the properties of interest.
What is the periodic table?
periodic table, in full periodic table of the elements, in chemistry, the organized array of all the chemical elements in order of increasing atomic number —i.e., the total number of protons in the atomic nucleus. When the chemical elements are thus arranged, there is a recurring pattern called the “periodic law” in their properties, ...
Why do the elements in the periodic table have different orbits?
The arrangement of the elements in the periodic table comes from the electronic configuration of the elements. Because of the Pauli exclusion principle, no more than two electrons can fill the same orbital. The first row of the periodic table consists of just two elements, hydrogen and helium. As atoms have more electrons, they have more orbits available to fill, and thus the rows contain more elements farther down in the table.
What are the rows of lanthanoid and actinoid?
These rows contain elements in the lanthanoid and actinoid series, usually from 57 to 71 ( lanthanum to lutetium) and 89 to 103 ( actinium to lawrencium ), respectively. There is no scientific reason for this. It is merely done to make the table more compact.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element . Hydrogen has 1 proton, and oganesson has ...
What elements are triads?
Döbereiner in 1817 showed that the combining weight, meaning atomic weight, of strontium lies midway between those of calcium and barium, and some years later he showed that other such “ triads ” exist (chlorine, bromine, and iodine [halogens] and lithium, sodium, and potassium [alkali metals]). J.-B.-A. Dumas, L. Gmelin, E. Lenssen, Max von Pettenkofer, and J.P. Cooke expanded Döbereiner’s suggestions between 1827 and 1858 by showing that similar relationships extended further than the triads of elements, fluorine being added to the halogens and magnesium to the alkaline-earth metals, while oxygen, sulfur, selenium, and tellurium were classed as one family and nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth as another family of elements.
What are the elements that are related to the first seven?
Newlands proposed classifying the elements in the order of increasing atomic weights, the elements being assigned ordinal numbers from unity upward and divided into seven groups having properties closely related to the first seven of the elements then known: hydrogen, lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen . This relationship was termed the law of octaves, by analogy with the seven intervals of the musical scale.
Who proposed the periodic law?
Then in 1869, as a result of an extensive correlation of the properties and the atomic weights of the elements, with special attention to valency (that is, the number of single bonds the element can form), Mendeleyev proposed the periodic law, by which “the elements arranged according to the magnitude of atomic weights show a periodic change of properties.” Lothar Meyer had independently reached a similar conclusion, published after the appearance of Mendeleyev ’s paper.
What is the first group of elements in the periodic table?
Group 1: Alkali metals group. Alkali metals group is the very first group (group 1) on the periodic table. The elements included in the Alkali metals group are; Lithium (Li)
What is the oxygen group on the periodic table?
Oxygen group is the group 16 on the periodic table.
Why are the elements in the bottom two rows of the periodic table included in group 3?
The elements in the two bottom rows of the periodic table are also included in these groups. They are placed in the two separate rows at the bottom because they show few different properties. Actually, the elements in the bottom rows are the extension of group 3 only. So they are included in group 3. But as these elements have few different ...
How many groups are there in the periodic table?
Groups are the vertical columns on the periodic table. There are total 18 vertical columns on periodic table. Hence there are 18 groups. The elements lying in the same groups show similar chemical properties and they also have same number of valence electrons.
What is an example of group 18?
Example of group 18. All the elements of group 18 are chemically inert (that means they do not easily react with other elements). And all the elements of group 18 have a complete octet (that means they have 8 electrons in their outer shell).
Which group is alkaline earth metals?
Alkaline earth metals are the group 2 elements on the periodic table.
Can you find every detail of an interactive periodic table?
You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table.
What are the horizontal rows on the periodic table called?
The horizontal rows on the periodic table are known as Periods.
Why are period 4 and period 5 called long periods?
Period 4 and period 5 are given the name long periods of the periodic table because there are 18 elements in these periods. The elements of the long periods are shown in tables below.
Why is period 1 the shortest period?
Period 1 of the periodic table is given the name shortest period because there are only two elements in period 1.
Why is period 2 called a short period?
Period 2 and period 3 of the periodic table are named as the short period because there are 8 elements in these periods.
Which period has the longest period?
Period 6 and 7: Longest period. Period 5 and period 6 are named as longest periods of the periodic table because there are 32 elements in these periods. The elements of the longest periods are shown in tables below.
How many energy shells does period 2 have?
All the elements of period 2 have two energy shells (or orbits).
Is the Interactive Periodic Table free?
Checkout Interactive Periodic table and download it’s high resolution image now ( It’s FREE)