What does GE stand for on the periodic table?
Germanium (Ge) – Periodic Table (Element Information & More) This is a SUPER easy guide on Germanium element. In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Germanium element in Periodic table.) So if you want to know anything about Germanium element, then this guide is for you.
What is the most interesting element on the periodic table?
What Is the Coolest Element?
- Carbon. Carbon is cool for several reasons. ...
- Sulfur. You usually think of sulfur as a yellow rock or powder, but one of the cool things about this element is that it changes color under different conditions.
- Lithium. All of the alkali metals react spectacularly in water, so why did lithium make the list while cesium did not?
- Gallium. ...
What are some interesting facts about the periodic table?
Interesting Facts On Periodic Table of Elements
- Founder of Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleyev is the father of the modern periodic table of elements. ...
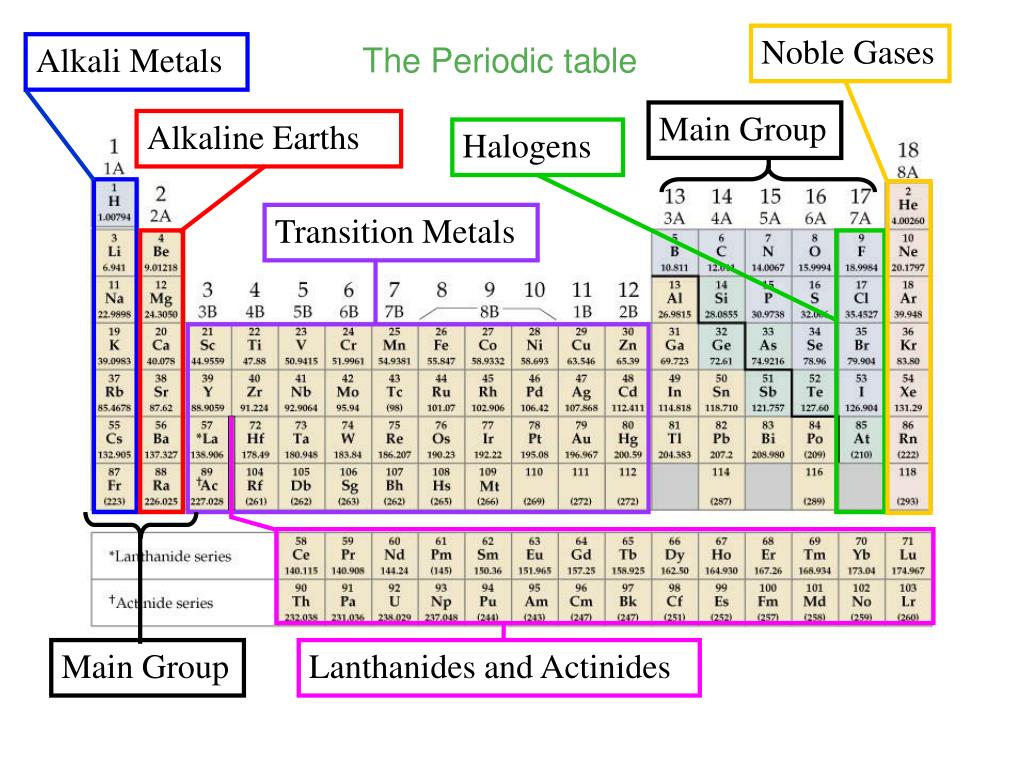
- Columns of the Periodic Table. The periodic table has 18 vertical columns called groups and seven horizontal columns called Periods.
- Size of the Atom. ...
- Unique Elements. ...
- Properties of Elements. ...
- Facts About Hydrogen. ...
What is the number of gases on the periodic table?
There are 11 total, and you may recognize them if you've looked at different sections of the periodic table, which catalogs and organizes chemical elements by their structures and similar properties. The elements that are gases at room temperature are radon (Rn), xenon (Xe), krypton (Kr), argon (Ar), chlorine (Cl), neon (Ne), fluorine (F), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), helium (He) and hydrogen (H).
See more
What is gallium used for?
It has important uses in Blu-ray technology, mobile phones, blue and green LEDs and pressure sensors for touch switches. Gallium readily alloys with most metals. It is particularly used in low-melting alloys. It has a high boiling point, which makes it ideal for recording temperatures that would vaporise a thermometer.
Is gallium metal toxic?
* Gallium is a CORROSIVE CHEMICAL and contact can severely irritate and burn the skin and eyes with possible eye damage. * Breathing Gallium can irritate the nose and throat causing coughing and wheezing. * Gallium may damage the liver and kidneys.
Is gallium a rare element?
Gallium is a rare element on earth, with a content of 19 ppm in the continental crust, its abundance is comparable to that of lithium and lead. It does not occur in elemental form, but only in bound form, mainly in aluminum, zinc or germanium ores.
Does gallium have any value?
The element has no known biological value. In nature, gallium is never found as a free element and cannot be found in a substantial amount in any minerals.
What is gallium worth per pound?
gallium: price conversions and costPrice per units of weight9.781/2 kilogram0.55ounce4.448 ounces8.87pound8 more rows
Can you swallow gallium?
Gallium compounds are mildly toxic, they are not considered dangerous but should not be inhaled or ingested. We don't recommend eating elemental gallium, but if small quantities were accidently ingested, it most likely would not be harmful.
How much is gallium metal worth?
Gallium is a chemical element that is soft and silvery. On the periodic table, gallium is represented by the symbol Ga and the atomic number 31....All Metal Prices.MetalPriceDateUpdatedGallium$336.76 kg10/14Oct 14, 2022Gold$1652.97 oz10/17Oct 17, 2022Indium$197.89 kg10/14Oct 14, 202220 more rows
How much does a gallium cost?
How Much Does a Gallium Scan Cost? On MDsave, the cost of a Gallium Scan ranges from $1,191 to $3,441. Those on high deductible health plans or without insurance can save when they buy their procedure upfront through MDsave.
Where is gallium mined?
The two deposits in this dataset occur in Alaska and Texas. Gallium is used to manufacture integrated circuits and optoelectronic devices, which include laser diodes, light-emitting diodes (LEDs), photodetectors and solar cells. Gallium is primarily recovered as a byproduct of processing aluminum or zinc ores.
Is gallium expensive metal?
Not surprisingly then, consumption of gallium rose has grown with global appetite for these devices. Between 2000 and 2008, the average gallium metal price (99.99% min.) ranged between US$ 200 and US$ 400 per kilogram.
Is gallium found in nature?
Gallium usually cannot be found in nature. It exists in the earth's crust, where its abundance is about 16.9 ppm. It is extracted from bauxite and sometimes sphalerite. Gallium can also be found in coal, diaspore and germanite.
Who is the largest producer of gallium?
China produces more than 95% of the world's raw gallium, a soft, bluish metal used in making chipsets for generating high frequency radio waves in 5G base stations. Gallium is also one of 35 elements that the U.S. government calls a national security concern.
Is gallium as toxic as mercury?
Gallium Is a Liquid Metal Element Like Mercury but Nontoxic.
Is gallium a carcinogen?
The International Agency for Research on Cancer has classified gallium arsenide as a human carcinogen.
Does gallium melt in your hand?
Melts In Your Hands, Not On Your Table. The element gallium is an unexpected metal—it's a soft, silvery-white metal that is solid at room temperature (similar to aluminum) but it can literally melt in the palm of your hand.
Does gallium react with water?
Gallium metal does not react with either water or sodium chloride. Gallium metal (like aluminum) reacts with the oxygen in the air to form a passivating layer of gallium oxide, Ga2O3.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers , electron configurations, and chemical properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements.
What is the mass number of gallium?
Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Gallium are 69; 71.
How many protons and electrons are in hydrogen?
Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H.
How to determine the stability of an isotope?
To determine the stability of an isotope you can use the ratio neutron/proton (N/Z). Also to help understand this concept there is a chart of the nuclides, known as a Segre chart. This chart shows a plot of the known nuclides as a function of their atomic and neutron numbers. It can be observed from the chart that there are more neutrons than protons in nuclides with Z greater than about 20 (Calcium). These extra neutrons are necessary for stability of the heavier nuclei. The excess neutrons act somewhat like nuclear glue. Only two stable nuclides have fewer neutrons than protons: hydrogen-1 and helium-3.
How are the chemical properties of a solid, liquid, gas, and plasma determined?
The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
Which gases have high thermal conductivity?
The mean free path also depends on the diameter of the molecule, with larger molecules more likely to experience collisions than small molecules, which is the average distance traveled by an energy carrier (a molecule) before experiencing a collision. Light gases , such as hydrogen and helium typically have high thermal conductivity. Dense gases such as xenon and dichlorodifluoromethane have low thermal conductivity.
Is gallium a free element?
Gallium has similarities to the other metals of the group, aluminium, indium, and thallium. Gallium does not occur as a free element in nature, but as gallium (III) compounds in trace amounts in zinc ores and in bauxite.
What is the vertical column in the periodic table?
A vertical column in the periodic table. Members of a group typically have similar properties and electron configurations in their outer shell. A horizontal row in the periodic table. The atomic number of each element increases by one, reading from left to right.
Where was gallium discovered?
Gallium was discovered in Paris by Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875. He observed a new violet line in the atomic spectrum of some zinc he had extracted from a sample of zinc blende ore (ZnS) from the Pyrenees. He knew it meant that an unknown element was present.
What is gallium nitride used for?
It has important uses in Blu-ray technology, mobile phones, blue and green LEDs and pressure sensors for touch switches.
What is the element of Gallus?
Lecoq de Boisbaudran named the element after France (‘Gaul’ in Latin) and also himself, since Lecoq, which means ‘the rooster’ translates to ‘Gallus’ in Latin. A silvery metallic rooster is shown on a background of an antique map of France.
Is gallium a biological substance?
Gallium has no known biological role. It is non-toxic.
Who discovered the element ekaaluminium?
Yet for all its strangeness the discovery of this odd element was no accident. Dmitri Mendeleev, the bearded Russian chemist who constructed the periodic table as we know it today, spotted a number of gaps and discrepancies in his arrangement. One of these was the absence of an element which he expected to fit below Aluminum. So confident was he in the correctness of his framework that he named the as yet undiscovered element ekaaluminium. Six years later in 1875, an ambitious French element hunter François Lecoq de Boisbaudran one of the earliest proponents of the new-fangled technique of spectroscopy spotted a line in the violet part of the visible spectrum at 417nm in a sample of zinc sulphide, he realized that this must come from a new element. Working in his home laboratory in spite of starting from some 52 kilos of an ore from the Pyrenees, it took three weeks for him to accumulate a couple of milligrams of the mysterious material. He then scaled up his extraction and took the product of his labours to Paris where he studied it further in Adolphe Wurtz's lab. Just before Christmas in 1875, Lecoq presented his results to the French academy proudly displaying a sample of almost 600mg, less than a gram of material harvested from 450 kilos of ore. And the name Lecoq patriotically chose to base it on the Latin name for France, Gallia; Gaul in English. But it was immediately pointed out that there might be something more to the name than met the eye. The Latin word for a rooster is Gallus, Lecoq, rooster, Gallium, get it. It seems he may have been a rather cunning linguist as well as a chemist. Either way, Lecoq could look back with some satisfaction at having helped to cement Mendeleev's table, was the foundation stone of chemistry. He then moved on to the intriguing mystery of the 'rare earths', ultimately isolating two more elements and conforming the existence of several more.
Is gallium a metal?
Gallium is a soft, silvery-white metal, similar to aluminium. Uses. Gallium arsenide has a similar structure to silicon and is a useful silicon substitute for the electronics industry. It is an important component of many semiconductors.
How are the chemical properties of a solid, liquid, gas, and plasma determined?
The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
Which element has the same electron configuration in the outer electron shell?
Magnesium is a shiny gray solid which bears a close physical resemblance to the other five elements in the second column (group 2, or alkaline earth metals) of the periodic table: all group 2 elements have the same electron configuration in the outer electron shell and a similar crystal structure.
How many protons and electrons are in hydrogen?
Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H.
How many protons does helium have?
Helium is a chemical element with atomic number 2 which means there are 2 protons and 2 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Helium is He.
Is lithium a solid or a metal?
It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and is stored in mineral oil.
Is oxygen a nonmetal?
It is a member of the chalcogen group on the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. By mass, oxygen is the third-most abundant element in the universe, after hydrogen and helium.
Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).

What Is Gallium
Atomic Number of Gallium
- Gallium is a chemical element with atomic number 31 which means there are 31 protons and 31 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Gallium is Ga. The atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic …
Neutron Number and Mass Number of Gallium
- Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Gallium are 69; 71. The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z …
Atomic Mass of Gallium
- Atomic mass of Gallium is 69.723 u. The atomic mass is the mass of an atom. The atomic mass or relative isotopic mass refers to the mass of a single particle, and therefore is tied to a certain specific isotope of an element. The atomic mass is carried by the atomic nucleus, which occupies only about 10-12 of the total volume of the atom or less, but it contains all the positive charge an…
Atomic Radius of Gallium
- The atomic radius of Gallium atom is122pm(covalent radius). It must be noted, atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron cloud extends from the nucleus. However, this assumes the atom to exhibit a spherical shape, which is only obeyed for atoms in vacuum or free space. Therefore, there are …
Density of Gallium
- Density of Gallium is 5.904g/cm3. Typical densities of various substances are at atmospheric pressure. Density is defined as the mass per unit volume. It is an intensive property, which is mathematically defined as mass divided by volume: ρ = m/V In words, the density (ρ) of a substance is the total mass (m) of that substance divided by the total volume (V) occupied by th…
First Ionization Energy of Gallium
- First Ionization Energy of Gallium is 5.9993 eV. Ionization energy, also calledionization potential, is the energy necessary toremove an electronfrom the neutral atom. X + energy → X+ + e− where X is any atom or molecule capable of being ionized, X+ is that atom or molecule with an electron removed (positive ion), and e−is the removed electron. A Gallium atom, for example, requires th…
Gallium – Melting Point and Boiling Point
- Melting point of Gallium is 29.76°C. Boiling point of Gallium is 2204°C. Note that, these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure.
Gallium – Thermal Conductivity
- Thermal conductivity of Gallium is 40.6 W/(m·K). The heat transfer characteristics of a solid material are measured by a property called the thermal conductivity, k (or λ), measured in W/m.K. It is a measure of a substance’s ability to transfer heat through a material by conduction. Note that Fourier’s lawapplies for all matter, regardless of its state (solid, liquid, or gas), therefore, it i…
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of Gallium
- Linear thermal expansion coefficient of Gallium is 18 µm/(m·K) Thermal expansion is generally the tendency of matter to change its dimensions in response to a change in temperature. It is usually expressed as a fractional change in length or volume per unit temperature change. Thermal expansion is common for solids, liquids and for gases. Unlike gases or liquids, solid ma…