Why do I have a refractory period?
The refractory period occurs right after you reach your sexual climax. It refers to the time between an orgasm and when you feel ready to be sexually aroused again. It’s also called the “resolution” stage. Does everyone have one? Yes! It’s not just limited to people with penises.
What are the advantages of the refractory period?
The refractory period causes 3 things to occur:
- The brain will be able to perceive nerve impulses as separated events since there is a time lag between them.
- The number of generated impulses or repetitive firing rate of a neuron will be limited in a given period of time.
- The nerve impulses will only travel in one direction. ...
What is the difference between absolute and relative refractory period?
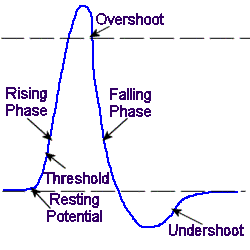
What is the difference between absolute and relative refractory period? Absolute: Is the period of time during which a second action potential ABSOLUTELY cannot be initiated, no matter how large the applied stimulus is. Relative: Is the interval immediately following the Absolute Refractory Period during which initiation of a second action ...
What age comes after the Cretaceous period?
The Cretaceous was a geologic period of time that lasted from approximately 145 to 65 million years ago. It was preceded by the Jurassic period and followed by the Paleogene period, the latter boundary also forming the demarcation between the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras.

What happens during refractory period quizlet?
a brief time period after an action potential has been initiated during which an axon is either incapable of generating another action potential. The excitable plasma membrane recovers at this time and becomes ready to respond to another stimulus.
What happens during the refractory period of a neuron?
These transitory changes make it harder for the axon to produce subsequent action potentials during this interval, which is called the refractory period. Thus, the refractory period limits the number of action potentials that a given nerve cell can produce per unit time.
What is refractory period and why does it happen?
After an action potential initiates, the cardiac cell is unable to initiate another action potential for some duration of time (which is slightly shorter than the "true" action potential duration). This period of time is referred to as the refractory period, which is 250ms in duration and helps to protect the heart.
Which of the following is true about the refractory period?
Answer and Explanation: The correct answer is c - the relative refractory period is defined as the phase of the action potential during which a new action potential can be evoked, but a greater than normal stimulus would be required.
What channels are open during refractory period?
The Refractory Period Once the K+ voltage-dependent channels have opened they remain open until the membrane potential reaches the equilibrium potential of K+.
What is the refractory period of a man?
Genitalia. As a general rule, the male refractory period is longer than the female refractory period. The average range for men is between a few minutes and two hours before they can ejaculate again; for women, it's between a few seconds and a few minutes before they can achieve another climax.
What is the refractory period in muscle contraction?
The absolute refractory period of a human muscle fibre is typically between 2.2 and 4.6 ms. The refractory period causes 3 things to occur: The brain will be able to perceive nerve impulses as separated events since there is a time lag between them.
Which process underlies the refractory period?
The refractory period arises in part due to the increase in sodium conductance across the membrane. The refractory period arises in part due to the decrease in potassium conductance across the membrane.
How does the refractory period set the direction of action potential propagation?
Propagation of Action Potentials The areas of the membrane that have recently depolarised will not depolarise again due to the refractory period - meaning that the action potential will only travel in one direction. These local currents would eventually decrease in charge until a threshold is no longer reached.
How does refractory period influence direction of impulse?
The refractory period ensures that an action potential will only travel forward down the axon, not backwards through the portion of the axon that just underwent an action potential.
How do the refractory periods affect the frequency of action potential production?
With very strong stimuli, subsequent action potentials occur following the completion of the absolute refractory period of the preceding action potential. Thus, the maximum frequency of action potentials is ultimately limited by the duration of the absolute refractory period.
What is an example of a refractory period?
An example of the refractory period is when talking on the phone while driving causes you to react slower to seeing a stopped car in front of you. So the next time you see a friend texting and driving, remind them that by doing so they are slowing their reaction time, which could be dangerous.
What is a refractory period?
Summary. The refractory period is the span of time after having an orgasm during which a person is not sexually responsive. The refractory period can have both mental and physiological effects. During the refractory period, a person might lose interest in sex, or they might not be able to have sex. It may not be possible for a person ...
What is a physiological refractory period?
This type of response is a physiological refractory period, meaning a person is physically unable to have sex again. Unlike males, many females can have multiple orgasms, suggesting they do not usually experience a physiological refractory period.
How long does a refractory period last?
The length of the refractory period varies greatly from person to person, from a few minutes to 24 hours, or longer.
What factors can influence the length of a refractory period?
Many factors can influence the length of the refractory period, including: a person’s overall health. relationship quality. quality of sex. frequency of sex. Dopamine plays a key role during sex. A review. Trusted Source. of the research suggests that dopamine levels may influence whether a male can get an erection.
What is the cycle of sexual desire?
Brain imaging studies suggest that the cycle of a sexual response follows a similar pattern to other pleasurable activities. It begins with intensifying desire, culminates in satisfying that desire, and concludes with decreased desire.
Is a refractory period male or female?
Scientists have thoroughly documented the refractory period in males. In females, the refractory period is more controversial.
Does a teenager's refractory period change as they age?
The refractory period a person has when they are young will also determine how it changes as they age. Someone with a long refractory period as a teenager may find it continues to get longer over time.
How long is the refractory period?
Although we have reported the refractory period to be 3-4 ms long, it should be noted that the hyperpolarization phase can last up to 15 ms in some neurons. In these neurons, therefore, the relative refractory period is much longer.
What happens during the absolute refractory period?
During the absolute refractory period, a second stimulus (no matter how strong) will not excite the neuron. During the relative refractory period, a stronger than normal stimulus is needed to elicit neuronal excitation.
What is the absolute refractory period?
The absolute refractory period is responsible for setting the upper limit on the maximum number of action potentials that can be generated during any given time period. In other words, the absolute refractory period determines the maximum frequency of action potentials that can be generated at any point along the axon plasma membrane. This action potential frequency, in turn, has important physiological implications for how the nervous system can respond to high-frequency stimuli, and also for the ability of the nervous system to send high-frequency signals to effector organs when needed (see Frequency Coding in the Nervous System ).
Which channel is responsible for the absolute refractory period?
In summary, inactivation of Na + channels is solely responsible for the absolute refractory period. Both Na + channel inactivation and greater than resting pK value are responsible for the relative refractory period.