What is the lightest element on the periodic table?
What is the periodic table?
How are atomic nuclei determined?
What is the charge of an atom?
How to determine the stability of an isotope?
How are atoms determined?
What is the number of neutrons in an atom?
See 4 more
About this website
Where is strontium on the table?
strontium (Sr), chemical element, one of the alkaline-earth metals of Group 2 (IIa) of the periodic table.
Is strontium a metal or nonmetal?
Strontium is the chemical element with the symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive.
What family is strontium in on the periodic table?
The Alkaline Earth MetalsGroup 2A (or IIA) of the periodic table are the alkaline earth metals: beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).
What are 3 interesting facts about strontium?
Strontium is a soft, silvery metal with a number of uses: It blocks X-rays emitted by TV picture tubes; it causes paint to glow in the dark; and it is responsible for the brilliant reds in fireworks.
What type of element is strontium?
alkaline earth metalStrontium is a chemical element with symbol Sr and atomic number 38. Classified as an alkaline earth metal, Strontium is a solid at room temperature.
Is strontium a rare earth metal?
Strontium is the most reactive alkaline earth metal after barium and radium. It reacts directly with halogens, oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur. It always forms compounds in which it is present as a divalent cation.
Is strontium a metal?
A soft, silvery metal that burns in air and reacts with water. Strontium is best known for the brilliant reds its salts give to fireworks and flares. It is also used in producing ferrite magnets and refining zinc.
What is the charge of Sr?
2+18, 2022, thoughtco.com/element-charges-chart-603986....Table of Common Element Charges.NumberElementCharge36krypton037rubidium1+38strontium2+39yttrium3+88 more rows•Jul 18, 2022
Is Sr a metalloid?
The metalloids are intermediate in their properties. In their physical properties, they are more like the nonmetals, but under certain circumstances, several of them can be made to conduct electricity. These semiconductors are extremely important in computers and other electronic devices....Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals.1ARb2ASrYZr4ASn12 more columns
Is strontium toxic?
There are no harmful effects of stable strontium in humans at the levels typically found in the environment. The only chemical form of stable strontium that is very harmful by inhalation is strontium chromate, but this is because of toxic chromium and not strontium itself.
Is strontium highly radioactive?
Strontium is a soft, silvery metallic element found in rocks, soil, dust, coal and oil. Strontium found in nature is not radioactive and is sometimes called stable strontium.
Why strontium is called a bone seeker?
Strontium-90 behaves like calcium in the human body and tends to deposit in bone and blood- forming tissue (bone marrow). Thus, strontium- 90 is referred to as a "bone seeker," and exposure will increase the risk for several diseases including bone cancer, cancer of the soft tissue near the bone, and leukemia.
Is strontium a metal?
A soft, silvery metal that burns in air and reacts with water. Strontium is best known for the brilliant reds its salts give to fireworks and flares. It is also used in producing ferrite magnets and refining zinc.
Is SR a metalloid?
The metalloids are intermediate in their properties. In their physical properties, they are more like the nonmetals, but under certain circumstances, several of them can be made to conduct electricity. These semiconductors are extremely important in computers and other electronic devices....Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals.1ARb2ASrYZr4ASn12 more columns
Is silicon a non metal?
Silicon is neither metal nor non-metal; it's a metalloid, an element that falls somewhere between the two.
Is sodium metal or non metal?
Sodium is a very soft silvery-white metal. Sodium is the most common alkali metal and the sixth most abundant element on Earth, comprising 2.8 percent of Earth's crust.
How many protons, electrons, and neutrons does Strontium-38 have?
Strontium has 38 protons (necessarily!), and 38 electrons (necessarily), and has generally 48, 49, or 50 neutrons depending on the isotope. For strontium, Z = 38. There are 38 positively charged particles in its nucleus. Because the element is neutral, there must be a corresponding number of electrons, negatively charged particles, orbiting the nucleus. It atomic mass is 87.62 g*mol^-1 ...
What is Strontium - Chemical Properties of Strontium - Symbol Sr
Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structure.The chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H. With a standard atomic weight of circa 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass.
Strontium (Sr) - Properties, Facts & Uses of Strontium |Periodic Table
Strontium with the symbol Sr belongs to the group 2 elements of the periodic table. Get to know about Strontium atomic mass, it's Chemical & Physical properties.
Strontium - Atomic Mass - Atomic Weight - Sr - Periodic Table
Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structure.The chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H. With a standard atomic weight of circa 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass.
Where is strontium found?
Strontium is found mainly in the minerals celestite and strontianite. China is now the leading producer of strontium. Strontium metal can be prepared by electrolysis of the molten strontium chloride and potassium chloride, or by reducing strontium oxide with aluminium in a vacuum.
When was strontium first discovered?
Strontium metal itself was isolated in 1808 at the Royal Institution in London by Humphry Davy by means of electrolysis, using the method with which he had already isolated sodium and potassium.
How long does a strontium 90 stay in the body?
Strontium-90, a radioactive isotope, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and present in nuclear fallout. It has a half-life of 28 years. It is absorbed by bone tissue instead of calcium and can destroy bone marrow and cause cancer.
What is the oxidation state of an atom?
The oxidation state of an atom is a measure of the degree of oxidation of an atom. It is defined as being the charge that an atom would have if all bonds were ionic. Uncombined elements have an oxidation state of 0. The sum of the oxidation states within a compound or ion must equal the overall charge.
How are elements organized into blocks?
Elements are organised into blocks by the orbital type in which the outer electrons are found. These blocks are named for the characteristic spectra they produce: sharp (s), principal (p), diffuse (d), and fundamental (f). The number of protons in an atom.
What is a vertical column in the periodic table?
A vertical column in the periodic table. Members of a group typically have similar properties and electron configurations in their outer shell. A horizontal row in the periodic table.
Where was the rock found?
In 1787, an unusual rock which had been found in a lead mine at Strontian, Scotland, was investigated by Adair Crawford, an Edinburgh doctor. He realised it was a new mineral containing an unknown ‘earth’ which he named strontia. In 1791, another Edinburgh man, Thomas Charles Hope, made a fuller investigation of it and proved it was a new element. He also noted that it caused the flame of a candle to burn red.
Where is strontium found?
Strontium commonly occurs in nature, being the 15th most abundant element on Earth (its heavier congener barium being the 14th), estimated to average approximately 360 parts per million in the Earth's crust and is found chiefly as the sulfate mineral celestine ( SrSO 4) and the carbonate strontianite (SrCO 3 ). Of the two, celestine occurs much more frequently in deposits of sufficient size for mining. Because strontium is used most often in the carbonate form, strontianite would be the more useful of the two common minerals, but few deposits have been discovered that are suitable for development. Because of the way it reacts with air and water, strontium only exists in nature when combined to form minerals. Naturally occurring strontium is stable, but its synthetic isotope Sr-90 is only produced by nuclear fallout.
What is the atomic number of strontium?
face-centered cubic (fcc) Strontium is the chemical element with the symbol Sr and atomic number 38 . An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is exposed to air.
What is the dominant species of strontium?
At intermediate to acidic pH Sr 2+ is the dominant strontium species. In the presence of calcium ions, strontium commonly forms coprecipitates with calcium minerals such as calcite and anhydrite at an increased pH. At intermediate to acidic pH, dissolved strontium is bound to soil particles by cation exchange.
How is strontium metal made?
The strontium is distilled from the mixture. Strontium metal can also be prepared on a small scale by electrolysis of a solution of strontium chloride in molten potassium chloride: Sr 2+ + 2. e−. → Sr. 2 Cl − → Cl 2 + 2.
What is the composition of strontium?
Natural strontium is a mixture of four stable isotopes: 84 Sr, 86 Sr, 87 Sr, and 88 Sr. Their abundance increases with increasing mass number and the heaviest, 88 Sr, makes up about 82.6% of all natural strontium, though the abundance varies due to the production of radiogenic 87 Sr as the daughter of long-lived beta-decaying 87 Rb. This is the basis of rubidium–strontium dating. Of the unstable isotopes, the primary decay mode of the isotopes lighter than 85 Sr is electron capture or positron emission to isotopes of rubidium, and that of the isotopes heavier than 88 Sr is electron emission to isotopes of yttrium. Of special note are 89 Sr and 90 Sr. The former has a half-life of 50.6 days and is used to treat bone cancer due to strontium's chemical similarity and hence ability to replace calcium. While 90 Sr (half-life 28.90 years) has been used similarly, it is also an isotope of concern in fallout from nuclear weapons and nuclear accidents due to its production as a fission product. Its presence in bones can cause bone cancer, cancer of nearby tissues, and leukemia. The 1986 Chernobyl nuclear accident contaminated about 30,000 km 2 with greater than 10 kBq/m 2 with 90 Sr, which accounts for about 5% of the 90 Sr which was in the reactor core.
What percentage of strontium is used in televisions?
At the peak of production of television cathode ray tubes, as much as 75 percent of strontium consumption in the United States was used for the faceplate glass. With the replacement of cathode ray tubes with other display methods, consumption of strontium has dramatically declined.
How many dihalides are in strontium?
All four dihalides of strontium are known. Due to the large size of the heavy s-block elements, including strontium, a vast range of coordination numbers is known, from 2, 3, or 4 all the way to 22 or 24 in SrCd 11 and SrZn 13. The Sr 2+ ion is quite large, so that high coordination numbers are the rule.
What is the physical characteristic of strontium?
Strontium is a silvery white metal with a yellowish tint. It is characterized as an alkaline earth metal. It is soft metal and has a density of around 2.64 g/cm 3. Strontium burns with a distinctive red color flame. There are three allotropi c forms of strontium.
How many isotopes of strontium are there?
Naturally occurring strontium has four stable isotopes: strontium-84, strontium-86, strontium-87 and strontium -88. The most abundant stable isotope is strontium-88 (82.58 %). Strontium-87 is thought to be produced during the Big Bang and is also obtained during the radioactive decay of rubidium.
What is the radioactive isotope of strontium used for?
Radioactive isotope of strontium (strontium-90) is used in nuclear power plants, spacecrafts and satellites as power generators (radioisotope thermoelectric generator RTGs). Strontium-89 (radioactive isotope) is used in prostate cancer therapy to treat bone pain as the primary ingredient in medicine called Metastron.
What is strontium used for?
Strontium is used to make fireworks (pyrotechnics) for industrial and military purposes, including oxygen candles, safety matches and explosive bolts. Chloride of strontium are used in manufacturing of medicinal toothpastes for sensitive teeth. Strontium is used to make high quality pottery glaze.
What is the reaction of strontium?
It reacts with air to forms yellowish strontium oxide. Stron tium readily reacts with water to form strontium hydroxide. Strontium reacts with nitrogen at high temperature, above 380°C. In powdered form, strontium undergoes spontaneous ignition (is pyrophoric) when exposed to air.
Why was strontium used in the 19th century?
Strontium was used to produce sugar in the 19 th century [2]. Large scale production of strontium was started due to its high demand and use in making television tube (cathode ray tubes) and its demand dramatically decreased with advancements in methods to make display screens and tubes.
When was strontium discovered?
Strontium is an alkaline earth metal discovered in 1808 by Humphry Davy. It is a reactive element and has various useful radioactive isotopes.
How is strontium obtained?
Strontium may be obtained in the form of sticks by the contact cathode method of electrolysis, in which a cooled iron rod, acting as a cathode, just touches the surface of a fused mixture of potassium and strontium chlorides and is raised as the strontium solidifies on it.
What percentage of strontium is consumed in pyrotechnics?
About 5–10 percent of all strontium production is consumed in pyrotechnics. Strontium hydroxide, Sr (OH) 2, is sometimes used to extract sugar from molasses because it forms a soluble saccharide from which the sugar can be easily regenerated by the action of carbon dioxide.
What is the formula for strontium ferrites?
Strontium ferrites comprise a family of compounds of general formula SrFe x O y, formed from the high- temperature (1,000–1,300 °C, or 1,800–2,400 °F) reaction between SrCO 3 and Fe 2 O 3. Permanent ceramic magnets are made from strontium ferrites and find use in applications as diverse as loudspeakers, motors for automobile windshield wipers, and children’s toys.
What is the chemical name for sr?
Strontium (Sr), chemical element, one of the alkaline-earth metals of Group 2 (IIa) of the periodic table. It is used as an ingredient in red signal flares and phosphors and is the principal health hazard in radioactive fallout. The periodic table is made up of 118 elements.
What is the chemical element of the periodic table?
chemical element. Professor, Department of Chemistry, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee. Strontium (Sr), chemical element, one of the alkaline-earth metals of Group 2 (IIa) of the periodic table. It is used as an ingredient in red signal flares and phosphors and is the principal health hazard in radioactive fallout.
How many atoms are in silicon?
Its cosmic abundance is estimated as 18.9 atoms (on a scale where the abundance of silicon = 10 6 atoms). It composes about 0.04 percent of Earth ’s crust.
How many isotopes are produced by nuclear reactions?
About 16 synthetic radioactive isotopes have been produced by nuclear reactions, of which the longest-lived is strontium-90 (28.9-year half-life ). This isotope, formed by nuclear explosions, is considered the most dangerous constituent of fallout.
What is the lightest element on the periodic table?
With a standard atomic weight of circa 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass.
How many protons does helium have?
Helium is a chemical element with atomic number 2 which means there are 2 protons and 2 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Helium is He.
How many electrons does neon have?
Neon is a chemical element with atomic number 10 which means there are 10 protons and 10 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Neon is Ne.
How many protons does nitrogen have?
Nitrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 7 which means there are 7 protons and 7 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Nitrogen is N.
How is atomic weight determined?
Therefore it is determined by the mass number (number of protons and neutrons).
What is the number of neutrons in an atom?
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
What is the difference between the mass of the nucleus and the rest mass of the nucleus?
Note that, it was found the rest mass of an atomic nucleus is measurably smaller than the sum of the rest masses of its constituent protons, neutrons and electrons. Mass was no longer considered unchangeable in the closed system. The difference is a measure of the nuclear binding energy which holds the nucleus together. According to the Einstein relationship ( E=mc 2 ), this binding energy is proportional to this mass difference and it is known as the mass defect.
What is the lightest element on the periodic table?
With a standard atomic weight of circa 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass.
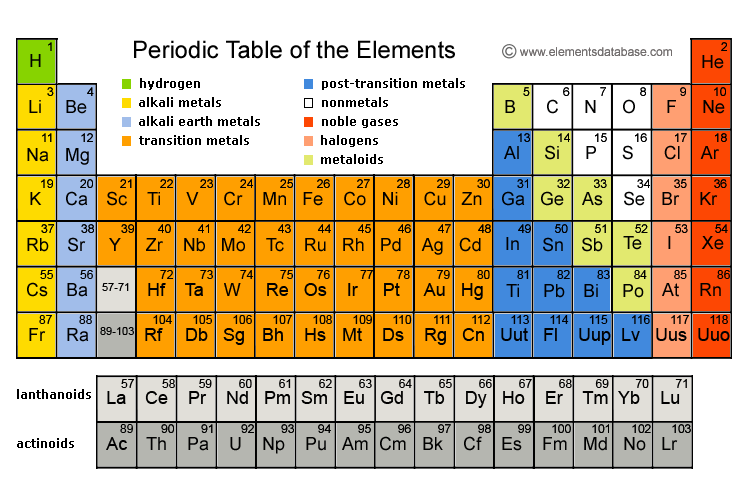
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements.
How are atomic nuclei determined?
Properties of atomic nuclei (atomic mass, nuclear cross-sections) are determined by the number of protons and number of neutrons (neutron number). It must be noted, especially nuclear cross-sections may vary by many orders from nuclide with the neutron number N to nuclide with the neutron number N+1. For example, actinides with odd neutron number are usually fissile (fissionable with slow neutrons) while actinides with even neutron number are usually not fissile (but are fissionable with fast neutrons). Heavy nuclei with an even number of protons and an even number of neutrons are (due to Pauli exclusion principle) very stable thanks to the occurrence of ‘paired spin’. On the other hand, nuclei with an odd number of protons and neutrons are mostly unstable.
What is the charge of an atom?
Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs. In a neutral atom there are as many electrons as protons moving about nucleus. It is the electrons that are responsible for the chemical bavavior of atoms, and which identify the various chemical elements.
How to determine the stability of an isotope?
To determine the stability of an isotope you can use the ratio neutron/proton (N/Z). Also to help understand this concept there is a chart of the nuclides, known as a Segre chart. This chart shows a plot of the known nuclides as a function of their atomic and neutron numbers. It can be observed from the chart that there are more neutrons than protons in nuclides with Z greater than about 20 (Calcium). These extra neutrons are necessary for stability of the heavier nuclei. The excess neutrons act somewhat like nuclear glue. Only two stable nuclides have fewer neutrons than protons: hydrogen-1 and helium-3.
How are atoms determined?
The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
What is the number of neutrons in an atom?
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
Overview
Strontium is the chemical element with the symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is exposed to air. Strontium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of its two vertical neighbors in the periodic table, calcium and barium. It occurs …
Characteristics
Strontium is a divalent silvery metal with a pale yellow tint whose properties are mostly intermediate between and similar to those of its group neighbors calcium and barium. It is softer than calcium and harder than barium. Its melting (777 °C) and boiling (1377 °C) points are lower than those of calcium (842 °C and 1484 °C respectively); barium continues this downward trend in the melting point (7…
History
Strontium is named after the Scottish village of Strontian (Gaelic Sròn an t-Sìthein), where it was discovered in the ores of the lead mines.
In 1790, Adair Crawford, a physician engaged in the preparation of barium, and his colleague William Cruickshank, recognised that the Strontian ores exhibited properties that differed from those in other "heavy spars" sources. This allowe…
Occurrence
Strontium commonly occurs in nature, being the 15th most abundant element on Earth (its heavier congener barium being the 14th), estimated to average approximately 360 parts per million in the Earth's crust and is found chiefly as the sulfate mineral celestine (SrSO4) and the carbonate strontianite (SrCO3). Of the two, celestine occurs much more frequently in deposits of sufficient size for m…
Production
The three major producers of strontium as celestine as of 2015 are China (150,000 t), Spain (90,000 t), and Mexico (70,000 t); Argentina (10,000 t) and Morocco (2,500 t) are smaller producers. Although strontium deposits occur widely in the United States, they have not been mined since 1959.
A large proportion of mined celestine (SrSO4) is converted to the carbonate b…
Applications
Consuming 75% of production, the primary use for strontium was in glass for colour television cathode-ray tubes, where it prevented X-ray emission. This application for strontium has been declining because CRTs are being replaced by other display methods. This decline has a significant influence on the mining and refining of strontium. All parts of the CRT must absorb X-rays. In the neck …
Biological role
Acantharea, a relatively large group of marine radiolarian protozoa, produce intricate mineral skeletons composed of strontium sulfate. In biological systems, calcium is substituted to a small extent by strontium. In the human body, most of the absorbed strontium is deposited in the bones. The ratio of strontium to calcium in human bones is between 1:1000 and 1:2000, roughly in the same range as in the blood serum.
Nuclear waste
Strontium-90 is a radioactive fission product produced by nuclear reactors used in nuclear power. It is a major component of high level radioactivity of nuclear waste and spent nuclear fuel. Its 29-year half life is short enough that its decay heat has been used to power arctic lighthouses, but long enough that it can take hundreds of years to decay to safe levels. Exposure from contaminated water and food may increase the risk of leukemia, bone cancer and primary hyperparathyroidism.
Occurrence
Physical Characteristics
- Strontium is a silvery white metal with a yellowish tint. It is characterized as an alkaline earth metal. It is soft metal and has a density of around 2.64 g/cm3. Strontium burns with a distinctive red color flame. There are three allotropic forms of strontium. Strontium has a considerably high refractive index. Strontium readily dissolves in liquid ammonia and forms a dark blue solution .
Chemical Characteristics
- Strontium is highly reactive. It reacts with air to forms yellowish strontium oxide. Strontium readily reacts with water to form strontium hydroxide. Strontium reacts with nitrogen at high temperature, above 380°C. In powdered form, strontium undergoes spontaneous ignition (is pyrophoric) when exposed to air. Strontium is stored in kerosene or mineral oil to increase its shelf life and avoid r…
Significance and Uses
- Strontium is widely used in the manufacturing of aerosol paints.
- Strontium is used to make fireworks (pyrotechnics) for industrial and military purposes, including oxygen candles, safety matches and explosive bolts.
- Chloride of strontium are used in manufacturing of medicinal toothpastes for sensitive teeth.
- Strontium is used to make high quality pottery glaze.
Health Hazards
- Strontium is highly similar to calcium, and that is why it is absorbed in bone in place of calcium. This retention in body is mostly harmless as stable forms of strontium do not cause any health hazard. However, radioactive isotope, strontium-90 can lead to bone cancer. The Chernobyl nuclear incident (1986) is the most tragic example of radiation contamination as it polluted arou…
Isotopes of Strontium
- There are sixteen naturally occurring isotopes of strontium. Naturally occurring strontium has four stable isotopes: strontium-84, strontium-86, strontium-87 and strontium -88. The most abundant stable isotope is strontium-88 (82.58 %). Strontium-87 is thought to be produced during the Big Bang and is also obtained during the radioactive decay of rubidium. The radioactive isotope, str…