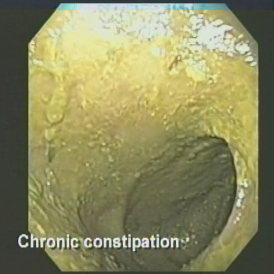
First period comes 1/23. Bleeding still ongoing. Showing retained products of conception (RPOC) measuring around 1.5cm. Did not pass with period.
Full Answer
What is retained product of conception?
When does a placenta get retained?
What happens if you have a placenta after birth?
How to treat RPOC?
Is uterine scarring rare?
Does RPOC prevent uterus from returning to pre-pregnancy state?
See 3 more
About this website

Can retained tissue come out on its own?
The tissue may come away without treatment but this could take a number of days or even weeks.
What are the signs of retained products of conception?
The characteristic clinical manifestations of RPOC include one or more of the following: uterine bleeding, pelvic pain, fever, and/or uterine tenderness. These clinical findings are nonspecific; moreover, it is normal to have some postabortal bleeding and discomfort.
How do I remove RPOC?
The most common treatments for RPOC are medication or surgery. Most women don't experience long-term complications from RPOC. But in rare cases, uterine scarring can affect fertility or future pregnancies. Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 05/12/2021.
What happens if tissue is left after a miscarriage?
Often, some of the pregnancy tissue remains in the uterus after a miscarriage. If it is not removed by scraping the uterus with a curette (a spoon-shaped instrument), you may bleed for a long time or develop an infection.
Can you pass retained placenta on your own?
A natural approach allows the woman's body to naturally expel the placenta on its own. Medical personnel assists the managed approach and usually, occurs when a shot is administered to the thigh while the baby is being born to cause the woman to expel her placenta.
Can retained products cause miscarriage?
In other cases, intrauterine adhesions from retained material can lead to recurring issues with infertility or miscarriage. A small fraction of cases of RPOC lead to increased vascularity, which can, rarely, trigger major hemorrhages in even simple dilation and curettage procedures.
What happens if a piece of placenta is left inside?
If the placenta, or pieces of the placenta, stay inside your uterus, you can develop an infection. A retained placenta or membrane has to be removed and you will need to see your doctor right away. If you have major bleeding, this is a medical emergency and you should go to your nearest hospital immediately.
Can I pass tissue and still be pregnant?
Later in your pregnancy, you might notice signs like cramping pain, bleeding or passing fluid and blood clots from your vagina. Depending on how many weeks pregnant you are, you may pass tissue that looks more like a fetus, or a fully-formed baby.
How does miscarriage tissue look like?
If you are less than 8 weeks pregnant when the miscarriage occurs, the expelled tissue will look no different from heavy menstrual bleeding. If you have reached 8 to 10 weeks, more tissue will be expelled which can resemble large blood clots, possibly some pinkish/grayish material, or even a discernible sac.
Will a pregnancy test be negative after a miscarriage?
It takes time for your hormones to return to their pre-pregnancy levels after a miscarriage. The amount of the pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) may still be high enough to trigger a positive result on a pregnancy test for several weeks after a miscarriage.
What should you not do after a miscarriage?
How can I prevent infection after a miscarriage?Using sanitary pads rather than tampons. Wait until your next period before using tampons again.Do not douche.Do not go into swimming pools or hot tubs.Take showers instead of baths.Do not have sexual intercourse.
How long does it take an incomplete miscarriage to pass?
If you have no signs of infection, you might choose to let the miscarriage progress naturally. Usually this happens within a couple of weeks of determining that the embryo has died. Unfortunately, it might take up to three or four weeks.
What happens if an incomplete miscarriage is not treated?
But sometimes the body has trouble passing the tissue, and the miscarriage remains incomplete until a woman seeks treatment. If the tissue isn't removed, the incomplete miscarriage can cause very heavy bleeding, prolonged bleeding, or an infection.
How long after hCG is zero will I get my period?
Many women can expect their first period four to six weeks after a miscarriage. The exact timing may vary by several weeks, however, depending on when your hCG levels return to zero. Your body will still think it's pregnant until this hormone is gone.
Is a retained placenta The Doctors fault?
Physicians such as the primary care doctor, OB/GYN, nurses, or other healthcare staff could all be responsible for a retained placenta that causes a mother serious personal injuries.
How long can placenta be retained?
Your body typically expels the placenta within 30 minutes of delivery. However, if the placenta or parts of the placenta remain in your womb for more than 30 minutes after childbirth, it's considered a retained placenta.
Does retained placenta affect milk supply?
The drop in estrogen and progesterone trigger a rise in prolactin, the hormone responsible for producing breast milk. If any part of the placenta remains in your body after the delivery of your baby, your prolactin levels will not rise, and your body will not begin to make breast milk.
Can you have RPOC with negative pregnancy test?
Conclusions. Negative urine hCG testing may not be a reliable predictor of an empty uterine cavity or completed abortion in symptomatic patients. Other modalities, such as high-resolution TVS and SIS may be more reliable in detecting RPOC in symptomatic women with a negative urine pregnancy test.
Can misoprostol remove retained placenta?
Conclusion: High dose rectal misoprostol does not give a promising result in cases of retained placenta. It is ineffective to facilitate placental separation in cases of retained placenta and does not seem to decrease the rate of MROP.
What can I use to clean my womb to get pregnant?
10 Detox Tips for Women Trying to Get PregnantDrink Lemon Water Daily. ... Clean Up Your Diet. ... Move Your Body. ... Try Dry Brushing. ... Fertility Cleansing. ... Boost Regular, Daily Detoxification with Specific Herbs. ... Utilize Castor Oil Therapy. ... Fertility Massage.More items...•
What are Asherman's symptoms?
Asherman's syndrome is typically diagnosed when you either experience symptoms of the condition like pelvic pain, amenorrhea (lack of menstruation), abnormal uterine bleeding or an inability to get and stay pregnant. Your medical history can also lead to a diagnosis of Asherman's syndrome.
How does miscarriage tissue look like?
If you are less than 8 weeks pregnant when the miscarriage occurs, the expelled tissue will look no different from heavy menstrual bleeding. If you have reached 8 to 10 weeks, more tissue will be expelled which can resemble large blood clots, possibly some pinkish/grayish material, or even a discernible sac.
What are considered products of conception?
Products of conception is a medical term used to identify any tissues that develop from a pregnancy. It is commonly used by doctors to include not only the fetus but also the placenta and any other tissues that may result from a fertilized egg.
What if I bleed less after taking misoprostol?
If you don't experience vaginal bleeding, abdominal cramps and contractions of the uterus within 4 hours of taking misoprostol (the second medicine), this may indicate that the medical termination has failed. If this happens to you, visit a doctor urgently.
National Center for Biotechnology Information
National Center for Biotechnology Information
retained products of conception (RPOC) - General Practice notebook
Last reviewed 09/2022 'Retained products' is where all or part of the placenta or membranes are left behind in the uterus during the third stage of labour.
Retained products of conception: risk factors and complications ...
Retained products of conception (RPOC) are the placental and/or fetal tissue that remain in the womb following childbirth, a medical termination of pregnancy or a miscarriage. After childbirth it is vital for the attending midwife to examine the placenta carefully to check that it is complete.
Retained Products of Conception (RPOC) - Contemporary OB/GYN
After delivery, there may be partial or complete retention of parts of the placenta or other decidual tissues within the uterus. This condition is termed “retained products of conception” (RPOC).
What is retained product of conception?
What are retained products of conception? Retained products of conception (RPOC) refers to tissue that remains in your uterus (womb) after a pregnancy ends. The tissue is usually from the placenta, which is an organ that develops in your uterus during pregnancy.
When does a placenta get retained?
A retained placenta most commonly happens after a vaginal delivery. But RPOC is more common when a pregnancy ends early. It may not cause problems until days, weeks or even months after the pregnancy ends.
What happens if you have a placenta after birth?
Sometimes the entire placenta (also called “afterbirth”) remains in the womb after childbirth. A retained placenta can lead to hemorrhaging (bleeding), severe infection or even death.
How to treat RPOC?
There are several treatments for RPOC, including: Misoprostol: You may receive this drug by mouth or through your vagina. In pregnant women, it helps to induce labor. After an early pregnancy failure or an incomplete abortion, it triggers your body to expel (force out) retained tissue.
Is uterine scarring rare?
Uterine scarring, or Asherman’s syndrome, is rare, but can increase your risk of:
Does RPOC prevent uterus from returning to pre-pregnancy state?
But in some cases, some of the tissue remains in your womb. RPOC prevent your uterus from returning to its pre-pregnancy state.
What causes menstrual retention?
Some of the causes of vaginal problems that lead to retained menstrual blood have been discussed below. Most of these conditions are congenital in nature, meaning that it has been present from the time of birth. 1. Imperforate Hymen.
Why is my period not flowing?
There are many reasons why a young girl may not menstruate despite obvious signs of puberty and even other menstrual symptoms. From pre gnancy and hormonal disturbances to drugs and even psychological stress, the menstrual cycle can be impacted to varying degrees.
What causes menstrual bleeding in the vagina?
1. Imperforate Hymen. Hematocolpos or accumulation of menstrual blood in the vagina occurs most frequently due to an imperforate hymen. The hymen is a membrane situated at the entrance to the vagina, which partially occludes the vaginal opening.
Where does menstrual blood accumulate?
The menstrual blood can accumulate usually within the vagina and this is known as hematocolpos (“hemato” referring to blood and “colpos” meaning vagina). Accumulation of menstrual blood within the uterus is known as hematometra. Sometimes the menstrual blood may enter the fallopian tubes which is referred to as hematosalpinx.
What is acquired in fetal life?
This can arise with abnormal development during fetal life. Acquired is where the problem develops during the course of life. The lower two thirds of the vagina develop from the urogenital sinus, while the upper vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries develop from the Mullerian duct system.
What is the process of menstruation?
It is important to understand the process of menstruation. The ovary releases an egg cell (ovum) during the ovulation phase. The inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) becomes thicker in preparation for pregnancy. When pregnancy fails to occur then the egg cell along with the thickened endometrium that sloughs off is expelled. This expulsion is known as menstruation.
Can genital tract outflow be detected in early life?
In genital tract outflow obstruction, secretions cannot exit the body of a female. The obstruction may not always be detected in early life. Young girls with genital tract outflow obstruction who have reached puberty will experience many of the symptoms of menstruation without the period. The hormonal changes that occur during the menstrual cycle may still occur as normal.
What is retained product of conception?
What are retained products of conception? Retained products of conception (RPOC) refers to tissue that remains in your uterus (womb) after a pregnancy ends. The tissue is usually from the placenta, which is an organ that develops in your uterus during pregnancy.
When does a placenta get retained?
A retained placenta most commonly happens after a vaginal delivery. But RPOC is more common when a pregnancy ends early. It may not cause problems until days, weeks or even months after the pregnancy ends.
What happens if you have a placenta after birth?
Sometimes the entire placenta (also called “afterbirth”) remains in the womb after childbirth. A retained placenta can lead to hemorrhaging (bleeding), severe infection or even death.
How to treat RPOC?
There are several treatments for RPOC, including: Misoprostol: You may receive this drug by mouth or through your vagina. In pregnant women, it helps to induce labor. After an early pregnancy failure or an incomplete abortion, it triggers your body to expel (force out) retained tissue.
Is uterine scarring rare?
Uterine scarring, or Asherman’s syndrome, is rare, but can increase your risk of:
Does RPOC prevent uterus from returning to pre-pregnancy state?
But in some cases, some of the tissue remains in your womb. RPOC prevent your uterus from returning to its pre-pregnancy state.