When was the end of the last glacial period?
The Last Glacial Period (LGP), also known colloquially as the last ice age or simply ice age, occurred from the end of the Eemian to the end of the Younger Dryas, encompassing the period c. 115,000 – c. 11,700 years ago. The LGP is part of a larger sequence of glacial and interglacial periods known as the Quaternary glaciation which started around 2,588,000 years ago and is ongoing.
When is the next glaciation?
The next glaciation. Without human intervention the next glaciation should start in 1500-2500 years. The question that we cannot answer with any degree of certainty is how high CO 2 levels should have to be to prevent glacial inception.
When was the Last Glacial Maximum?
Within the last glacial period, the Last Glacial Maximum was approximately 22,000 years ago.
When was the last Glac?
The last glacial period (the Weichselian) started approximately 115,000 years ago. Interpretations of geological observations suggest several ice-free interstadial periods over large parts of Fennoscandia during the Weichselian (e.g., Svendsen et al., 2004; Helmens and Engels, 2010; Wohlfarth, 2010; Mangerud et al., 2011). When studying past influences of periglacial and glacial conditions on the hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical evolution of a site, boundary conditions derived from ...

How often are glacial periods?
Four fairly regular glacial-interglacial cycles occurred during the past 450,000 years. The shorter interglacial cycles (10,000 to 30,000 years) were about as warm as present and alternated with much longer (70,000 to 90,000 years) glacial cycles substantially colder than present.
What is a glacial period?
Definition of 'glacial period' 1. any period of time during which a large part of the earth's surface was covered with ice, due to the advance of glaciers, as in the late Carboniferous period, and during most of the Pleistocene; glaciation.
Are we in a glacial period?
The most recent glacial period occurred between about 120,000 and 11,500 years ago. Since then, Earth has been in an interglacial period called the Holocene.
What happens during glacial periods?
During a glacial, sea levels drop an average of 100m as water is evaporated and stored in the growing glaciers and ice sheets. During an interglacial, sea levels rise as ice sheets and glaciers melt with the increase in temperature, thus resulting in an increase in volume of the ocean as water is heated.
When was the glacier period?
The glacial periods lasted longer than the interglacial periods. The last glacial period began about 100,000 years ago and lasted until 25,000 years ago. Today we are in a warm interglacial period.
What are the 4 glacial periods?
To geologists, an ice age is defined by the presence of large amounts of land-based ice. Prior to the Quaternary glaciation, land-based ice formed during at least four earlier geologic periods: the Karoo (360–260 Ma), Andean-Saharan (450–420 Ma), Cryogenian (720–635 Ma) and Huronian (2,400–2,100 Ma).
When was the first glacial period?
The Huronian glaciation is the oldest ice age we know about. The Earth was just over 2 billion years old, and home only to unicellular life-forms. The early stages of the Huronian, from 2.4 to 2.3 billion years ago, seem to have been particularly severe, with the entire planet frozen over in the first “snowball Earth”.
What was the last glacial period called?
The Pleistocene epoch is a geological time period that includes the last ice age, when glaciers covered huge parts of the globe.
How long will the next glacial period last?
The amount of heat trapping (greenhouse) gases being emitted into Earth's oceans and atmosphere may delay the next glacial period by an additional 50,000 years.
When did the glacial period end?
The Penultimate Glacial Period (PGP) is the glacial period that occurred before the Last Glacial Period. It began ~194,000 years ago, and ended 135,000 years ago with the beginning of the Eemian interglacial.
How many glacial cycles have occurred in the Quaternary?
Within the Quaternary (about 2.6 Ma to present), there have been a number of glacials and interglacials. At least eight glacial cycles have occurred in the last 740,000 years alone.
How long will the Earth's climate last?
Work by Berger and Loutre suggests that the current warm climate may last another 50,000 years. The amount of heat trapping (greenhouse) gases being emitted into Earth's oceans and atmosphere may delay the next glacial period by an additional 50,000 years.
When did the glacial advance reach its last peak?
The glacial advance reached the Last Glacial Maximum about 26,500 BP. In Europe, the ice sheet reached Northern Germany. In the last 650,000 years, there were, on average, seven cycles of glacial advance and retreat.
When was the last glacial period?
The last glacial period was the most recent glacial period within the Quaternary glaciation, occurring in the Pleistocene, which began about 110,000 years ago and ended about 15,000 years ago .
What is the difference between glacial and interglacial?
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods. The Last Glacial Period ended about 15,000 years ago.
When was the last glacial period?
The Last Glacial Period ( LGP) occurred from the end of the Eemian to the end of the Younger Dryas, encompassing the period c. 115,000 – c. 11,700 years ago . The LGP is part of a larger sequence of glacial and interglacial periods known as the Quaternary glaciation which started around 2,588,000 years ago and is ongoing.
How are glacial-interglacial cycles paced?
Over the past few million years the glacial-interglacial cycles have been "paced" by periodic variations in the Earth's orbit via Milankovitch cycles . The last glacial period has been intensively studied in North America, northern Eurasia, the Himalaya and other formerly glaciated regions around the world.
What is the name of the glacier that was at its maximum size for only a short period, between 25,000?
Alternative names include: Weichsel glaciation or Vistulian glaciation (referring to the Polish river Vistula or its German name Weichsel). Evidence suggests that the ice sheets were at their maximum size for only a short period, between 25,000 and 13,000 BP. Eight interstadials have been recognized in the Weichselian, including: the Oerel, Glinde, Moershoofd, Hengelo and Denekamp; however correlation with isotope stages is still in process. During the glacial maximum in Scandinavia, only the western parts of Jutland were ice-free, and a large part of what is today the North Sea was dry land connecting Jutland with Britain (see Doggerland ).
Where did glaciation occur?
Outside the main ice sheets, widespread glaciation occurred on the highest mountains of the Alps − Himalaya mountain chain. In contrast to the earlier glacial stages, the Würm glaciation was composed of smaller ice caps and mostly confined to valley glaciers, sending glacial lobes into the Alpine foreland.
Where did glaciation occur in the Southern Hemisphere?
Ice sheets existed in the Andes ( Patagonian Ice Sheet ), where six glacier advances between 33,500 and 13,900 BP in the Chilean Andes have been reported. Antarctica was entirely glaciated, much like today, but unlike today the ice sheet left no uncovered area. In mainland Australia only a very small area in the vicinity of Mount Kosciuszko was glaciated, whereas in Tasmania glaciation was more widespread. An ice sheet formed in New Zealand, covering all of the Southern Alps, where at least three glacial advances can be distinguished. Local ice caps existed in Western New Guinea, Indonesia, where in three ice areas remnants of the Pleistocene glaciers are still preserved today.
Which river was formed during the earlier glacial period?
With the assistance of several very broad glacial lakes, it released floods through the gorge of the Upper Mississippi River, which in turn was formed during an earlier glacial period.
What is the meaning of the word "Würm glaciation"?
Blue: extent in earlier ice ages. The term Würm is derived from a river in the Alpine foreland, approximately marking the maximum glacier advance of this particular glacial period.
What is the oldest glacial period?
The oldest known glacial period is the Huronian. Based on evidence of glacial deposits from the area around Lake Huron in Ontario and elsewhere, it is evident that the Huronian Glaciation lasted from approximately 2,400 to 2,100 Ma. Because rocks of that age are rare, we don’t know much about the intensity or global extent of this glaciation.
How long did the Cryogenian glacier last?
There were two main glacial periods within the Cryogenian, each lasting for about 20 million years: the Sturtian at around 700 Ma and the Marinoan at 650 Ma. There is also evidence of some shorter glaciations both before and after these. The end of the Cryogenian glaciations coincides with the evolution of relatively large ...
What are the three major glaciations of the Phanerozoic?
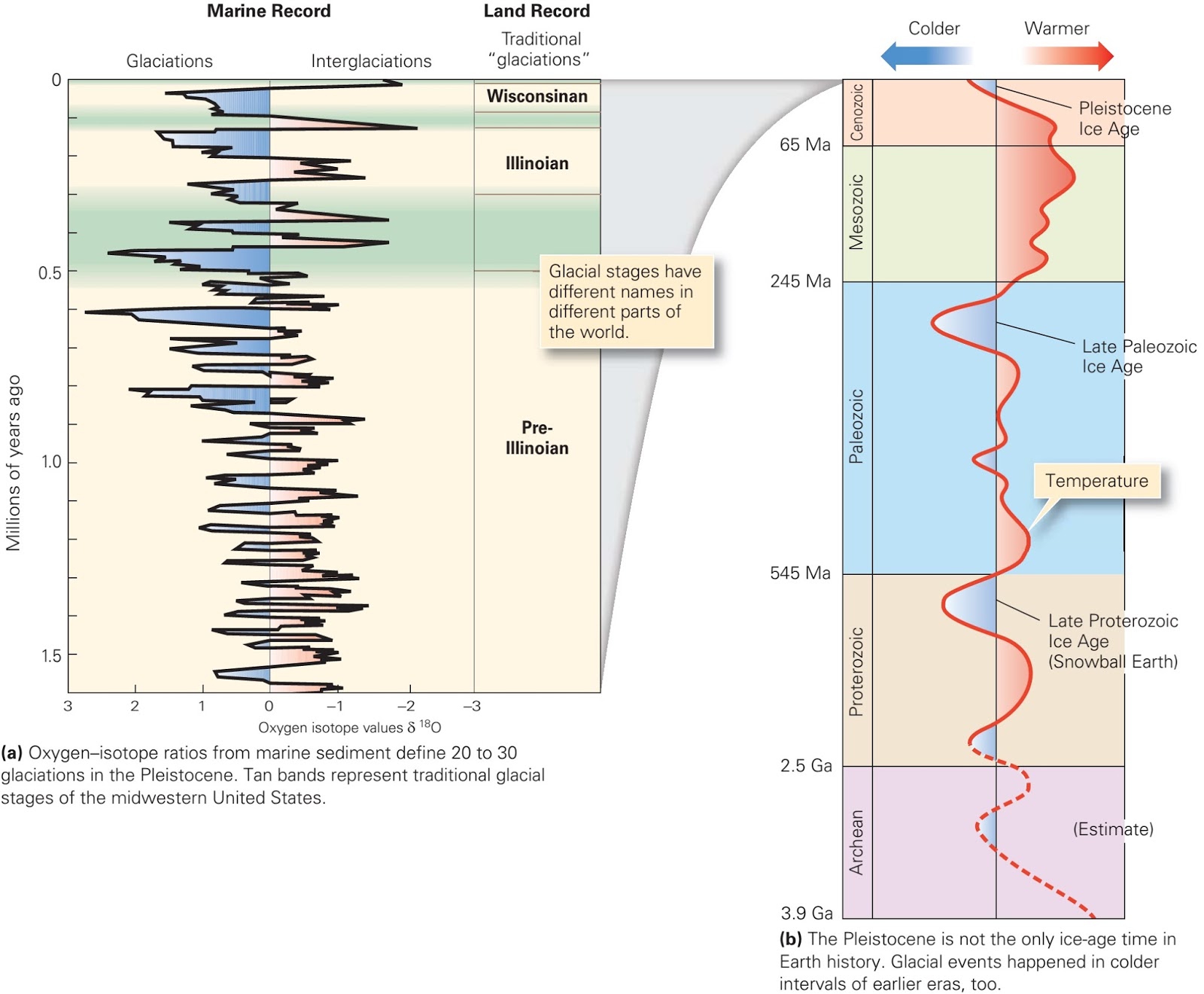
There have been three major glaciations during the Phanerozoic (the past 540 million years), including the Andean/Saharan (recorded in rocks of South America and Africa), the Karoo (named for rocks in southern Africa), and the Cenozoic glaciations . The Karoo was the longest of the Phanerozoic glaciations, persisting for much of the time that the supercontinent Gondwana was situated over the South Pole (~360 to 260 Ma). It covered large parts of Africa, South America, Australia, and Antarctica (see Figure 10.4). As you might recall from Chapter 10, this widespread glaciation, across continents that are now far apart, was an important component of Alfred Wegener’s evidence for continental drift. Unlike the Cryogenian glaciations, the Andean/Saharan, Karoo, and Cenozoic glaciations only affected parts of Earth. During Karoo times, for example, what is now North America was near the equator and remained unglaciated.
What is the most intense glaciation?
Late in the Proterozoic, for reasons that are not fully understood, the climate cooled dramatically and Earth was seized by what appears to be its most intense glaciation. The glaciations of the Cryogenian Period ( cryo is Latin for icy cold) are also known as the “Snowball Earth” glaciations, because it is hypothesized that the entire planet was frozen — even in equatorial regions — with ice on the oceans up to 1 km thick. A visitor to our planet at that time might not have held out much hope for its inhabitability, although life still survived in the oceans. There were two main glacial periods within the Cryogenian, each lasting for about 20 million years: the Sturtian at around 700 Ma and the Marinoan at 650 Ma. There is also evidence of some shorter glaciations both before and after these. The end of the Cryogenian glaciations coincides with the evolution of relatively large and complex life forms on Earth. This started during the Ediacaran Period, and then continued with the so-called explosion of life forms in the Cambrian. Some geologists think that the changing environmental conditions of the Cryogenian are what actually triggered the evolution of large and complex life.
How long has the Pleistocene been around?
The Pleistocene has been characterized by significant temperature variations (through a range of almost 10°C) on time scales of 40,000 to 100,000 years, and corresponding expansion and contraction of ice sheets. These variations are attributed to subtle changes in Earth’s orbital parameters (Milankovitch cycles), which are explained in more detail in Chapter 21. Over the past million years, the glaciation cycles have been approximately 100,000 years; this variability is visible in Figure 16.5.
What was the warmest period of the Mesozoic?
A warm climate persisted into the Cenozoic; in fact there is evidence that the Paleocene (~50 to 60 Ma) was the warmest part of the Phanerozoic since the Cambrian (Figure 16.3).
What is the current interglacial period?
The current interglacial (Holocene) is marked with an H. Point out the previous five interglacial periods.
When did the last glacial period end?
The Earth is currently in such an interglacial period of the Quaternary glaciation, with the last glacial period of the Quaternary having ended approximately 11,700 years ago.
How many ice ages have there been?
There have been five or six major ice ages in the history of Earth over the past 3 billion years. The Late Cenozoic Ice Age began 34 million years ago, its latest phase being the Quaternary glaciation, in progress since 2.58 million years ago. Within ice ages, there exist periods of more severe glacial conditions and more temperate conditions, ...
What is geologic time scale?
Geologic time scale – system that relates geological strata to time. Glacial history of Minnesota. Glacial period – Interval of time within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Ice age – Period of long-term reduction in temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere.
When did the third Ice Age occur?
The third ice age, and possibly most severe, is estimated to have occurred from 720 to 635 Ma (million years) ago, in the Neoproterozoic Era, and it has been suggested that it produced a second " Snowball Earth " i.e. a period during which Earth was completely covered in ice. It has been suggested also that the end of this second cold period was ...
What are the three major ice ages?
Climate history over the past 500 million years, with the last three major ice ages indicated, Andean-Saharan (450 Ma), Karoo (300 Ma) and Late Cenozoic. A less severe cold period or ice age is shown during the Jurassic - Cretaceous (150 Ma). There have been five or six major ice ages in the history ...
How long did the glacial era last?
Before the transition, glacial cycles, consisting of cold ice ages and milder interludes, typically lasted about 40,000 years—but those weaker cycles gave way to longer-lasting icy eras with cycles lasting roughly 100,000 years.
What are the secondary fluctuations of glacial periods?
These are known as interstadial and stadial periods, which occur when glaciers retreat and advance, respectively . Despite the occurrence of interstadials and stadials, the researchers evaluated the overall strength of interglacials.
How many interglacial periods have there been?
Researchers identified 11 different interglacial periods over the past 800,000 years, but the interglacial period we are experiencing now may last an exceptionally long time.
How long before the interglacial ends?
The earth's orbit around the sun has to be a certain shape before this interglacial is capable of ending ending (which is in about 5 to 15 thousand years. Also, greenhouse gasses will not save you from the return of the glacial period.
How long do interglacials last?
Although most interglacials typically last about 10,000 to 30,000 years, the researchers suggest that the current epoch—the Holocene—may last much longer because of the increased levels of atmospheric greenhouse gases resulting from human activity.
Can CO2 prevent another ice age?
As considered in this paper, published research supports the view that a moderate increase in the atmospheric CO2 level could prevent the initiation of another ice age. The amount of C02 resulting from the use of the world's fossil fuel reserves should be sufficient to provide this protection for thousands of years.
How long did the glacial period last?
The periods alternated every 41,000 years until 1 million years ago when the glacial periods changed to a cycle of 100,000 years. These cooled down temperatures possibly resulted in the evolution of homo-sapiens.
How long has the Earth been in a glacial period?
Surprisingly, the earth is currently experiencing a glacial period. This one started about 2.58 million years ago and is still going on, this time with significantly milder temperatures. Antarctica first froze over about 14 million years ago due to the creation of the Himalayan mountains. The higher they grew, the more weathering they were exposed to which decreased carbon dioxide levels. This time, the glacial and interglacial periods were controlled by the orbiting of the earth and the levels of sun that reached the surface. The periods alternated every 41,000 years until 1 million years ago when the glacial periods changed to a cycle of 100,000 years. These cooled down temperatures possibly resulted in the evolution of homo-sapiens. Human brains became larger and when the ice caps moved closer to the poles, humans began to cultivate agriculture which led to today’s modern civilization.
What are the two things that glaciers do?
Glaciers carve out the surface of the Earth, leaving behind valleys and lakes. Once temperatures increase, glaciers melt and fill those valleys and lakes with water. It is believed that these eras are brought on by solar radiation and shifts in plate tectonics. A glaciation period is marked by glacial and interglacial periods.
What is the oldest ice age?
Huronian. Researchers have identified five separate ice ages. The oldest of these is the Huronian glaciation which occurred 2.4 to 2.1 billion years ago! During this time, the only living organisms on earth were unicellular. Temperatures were so low that the entire globe was covered in ice and snow.
How did the Ice Age affect Earth?
In the past, ice ages have triggered mass extinction events on Earth and threaten to do the same in the future as well. An ice age is a moment in time when global temperatures can reach drastically cold levels. The decreased temperatures prevent snow from melting which creates a layer of ice under all of the accumulating snow.
Why do glaciers move?
This phenomenon causes the whole ice mass to move; in other words, a glacier is created. Glaciers carve out the surface of the Earth, leaving behind valleys and lakes.
What happened after the Cryogenian period?
After the Cryogenian period, earth experienced the Andean-Saharan glaciation. This happened about 450 to 420 million years ago and brought with it the first major extinction. Glaciers first formed in what is now Africa and eastern Brazil and slowly covered present-day South America. During this period, trilobites, brachiopods, and cephalopods made up animal life. They were all lost to this ice age.
How long does a woman's period last?
Your period, also known as menstruation, typically lasts anywhere from two to eight days. Many women experience symptoms during their period. Certain symptoms like cramping or mood changes can begin before the actual period.
How long does it take for your period to stop?
These symptoms include: Your period becomes irregular after it’s been steady and predictable for a long time. Your periods suddenly stop for 90 days or more and you aren’t pregnant. You think you may be pregnant. Your period lasts for more than eight days. You bleed much more heavily than usual.
How does a woman's body work during her period?
Overview. Menstruation typically works on a monthly cycle. It’s the process a woman’s body goes through as it prepares for possible pregnancy. During this process, an egg will be released from the ovaries. If that egg isn’t fertilized, the lining of the uterus is shed through the vagina during a woman’s menstrual period.
What causes irregular menstrual cycles?
Other factors that can make you irregular, or cause changes to your menstrual cycle, include: 1 extreme weight loss 2 excessive exercising 3 infections to the reproductive organs, like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) 4 conditions like polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) 5 increased stress 6 changes in diet
What is the follicular phase?
The follicular phase. The follicular phase starts on the first day of menstruation and ends when ovulation begins. During this stage, the ovaries produce follicles, which then house eggs. This stimulates the thickening of the uterus’s lining. There’s an increase in estrogen during this time.
What are the symptoms of a woman's period?
Many women experience symptoms during their period. Certain symptoms like cramping or mood changes can begin before the actual period. This is often called premenstrual syndrome, or PMS. Most women’s menstrual symptoms resolve after the period is over.
How long does it take for a woman's period to stabilize?
Their periods will often shorten and stabilize between one and three years after menstruation begins. Irregular periods include periods that are lighter, heavier, arrive unpredictably, or last longer or shorter than the average.

Overview
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods. The Last Glacial Period ended about 15,000 years ago. The Holocene is the current interglacial. A time with no glaciers on Earth is considered a greenhouse climate state.
Quaternary Period
Within the Quaternary, which started about 2.6 million years before present, there have been a number of glacials and interglacials. At least eight glacial cycles have occurred in the last 740,000 years alone.
Penultimate Glacial Period
The Penultimate Glacial Period (PGP) is the glacial period that occurred before the Last Glacial Period. It began about 194,000 years ago and ended 135,000 years ago, with the beginning of the Eemian interglacial.
Last Glacial Period
The last glacial period was the most recent glacial period within the Quaternary glaciation. It occurred in the Pleistocene, which began about 110,000 years ago and ended about 15,000 years ago. The glaciations that occurred during the glacial period covered many areas of the Northern Hemisphere and have different names, depending on their geographic distributions: Wisconsin (in North America), Devensian (in Great Britain), Midlandian (in Ireland), Würm (in the Alps), Weichsel …
Next glacial period
Since orbital variations are predictable, computer models that relate orbital variations to climate can predict future climate possibilities. Work by Berger and Loutre suggests that the current warm climate may last another 50,000 years. The amount of heat trapping (greenhouse) gases being emitted into the Earth's oceans and its atmosphere may delay the next glacial period by an additional 50,000 years.
Summary
The Last Glacial Period (LGP), also known colloquially as the last ice age or simply ice age, occurred from the end of the Eemian to the end of the Younger Dryas, encompassing the period c. 115,000 – c. 11,700 years ago. The LGP is part of a larger sequence of glacial and interglacial periods known as the Quaternary glaciation which started around 2,588,000 years ago and is ongoin…
Named local glaciations
During the last glacial period, Antarctica was blanketed by a massive ice sheet, much as it is today; however, the ice covered all land areas and extended into the ocean onto the middle and outer continental shelf. Counterintuitively though, according to ice modeling done in 2002, ice over central East Antarctica was generally thinner than it is today.
Origin and definition
The LGP is often colloquially referred to as the "last ice age", though the term ice age is not strictly defined, and on a longer geological perspective, the last few million years could be termed a single ice age given the continual presence of ice sheets near both poles. Glacials are somewhat better defined, as colder phases during which glaciers advance, separated by relatively warm interglacials. The end of the last glacial period, which was about 10,000 years ago, is often calle…
Overview
Canada was nearly completely covered by ice, as was the northern part of the United States, both blanketed by the huge Laurentide Ice Sheet. Alaska remained mostly ice free due to arid climate conditions. Local glaciations existed in the Rocky Mountains and the Cordilleran ice sheet and as ice fields and ice caps in the Sierra Nevada in northern California. In northern Eurasia, the Scandinavian ice s…
Deglaciation
Scientists from the Center for Arctic Gas Hydrate, Environment and Climate at the University of Tromsø, published a study in June 2017 describing over a hundred ocean sediment craters, some 3,000 m wide and up to 300 m deep, formed by explosive eruptions of methane from destabilized methane hydrates, following ice-sheet retreat during the LGP, around 12,000 years ago. These are…
Further reading
• Bowen, D.Q. (1978). Quaternary geology: a stratigraphic framework for multidisciplinary work. Oxford UK: Pergamon Press. ISBN 978-0-08-020409-3.
• Ehlers, J.; Gibbard, P. L., eds. (2004). Quaternary Glaciations: Extent and Chronology 2: Part II North America. Amsterdam: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-444-51462-2.
External links
• Pielou, E. C. After the Ice Age: The Return of Life to Glaciated North America (University of Chicago Press: 1992)
• National Atlas of the USA: Wisconsin Glaciation in North America: Present state of knowledge
• Ray, N.; Adams, J.M. (2001). "A GIS-based Vegetation Map of the World at the Last Glacial Maximum (25,000–15,000 BP)" (PDF). Internet Archaeology. 11.