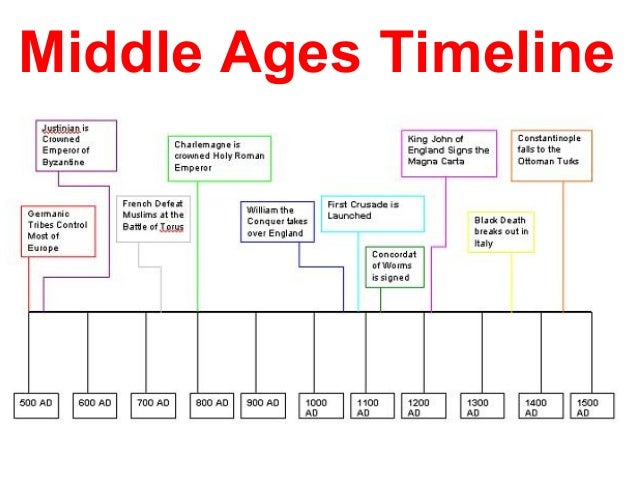
What time period does the phrase Middle Ages refer to?
People use the phrase “Middle Ages” to describe Europe between the fall of Rome in 476 CE and the beginning of the Renaissance in the 14th century. Why was this period called the Middle Ages? The ‘Middle Ages’ are called this because it is the time between the fall of Imperial Rome and the beginning of the Early modern Europe.
What period is referred to as the Middle Ages?
The Middle Ages, also sometimes referred to as the Medieval Period, had its origins in the fall of the Roman Empire and ran from the 5th to the 15th centuries AD, and was succeeded by the Renaissance movement of the 14th century. Because the Middle Age period spans a large segment of human history, historians have split it into three categories: the Early, High, and Late Middle Age periods.
Could they tell the time during the Middle Ages?
During the Middle Ages, people used a combination of water clocks, sun dials, and candle clocks to tell time though none of those could tell time to the minute. While the best water clocks told time to the quarter hour, it wasn’t until the wide use and improvement of mechanical clocks that people could tell time to the minute.
What were the approximate years of the Middle Ages?
Middle Ages, the period in European history from the collapse of Roman civilization in the 5th century ce to the period of the Renaissance (variously interpreted as beginning in the 13th, 14th, or 15th century, depending on the region of Europe and other factors). A brief treatment of the Middle Ages follows. For full treatment, see Europe, history of: The Middle Ages.

What were the 3 periods of the Middle Ages?
The Middle Ages was the period between the 5th and 15th centuries, starting at the collapse of the Roman Empire. This time can be split into three main sections: The Early Middle Ages, High Middle Ages, and Late Middle Ages.
What time period is the Middle Ages Why is it called the middle?
They started around the year 476 CE, when the Western Roman Empire ended, and continued until around the time Christopher Columbus arrived in the New World in 1492. This period of time is called the 'Middle Ages' because it took place between the fall of Imperial Rome and the beginning of early modern Europe.
What are the Middle Ages also known as?
The Middle Ages, the medieval period of European history between the fall of the Roman Empire and the beginning of the Renaissance, are sometimes referred to as the "Dark Ages."
What's the difference between medieval and Middle Ages?
1. The Middle Ages is a noun that is used to refer to the period between the 5th and 15th centuries while the Medieval Ages or “medieval” is an adjective that is used to refer to the people, places, things, and events of that same period. 2.
What was the Middle Ages known for?
It was the era of the Crusades, Gothic art and architecture, the papal monarchy, the birth of the university, the recovery of ancient Greek thought, and the soaring intellectual achievements of St. Thomas Aquinas (c. 1224–74).
What caused the Middle Ages?
It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period.
What is characteristic of the Middle Ages?
The middle ages is characterized by wars, instability and fragmented power structures. The number of castles built in the middle ages isn't known but it is certainly more then 10,000 and possibly more than 100,000. For example, there were around 25,000 medieval castles constructed in Germany alone.
What was life really like in the Middle Ages?
Life was harsh, with a limited diet and little comfort. Women were subordinate to men, in both the peasant and noble classes, and were expected to ensure the smooth running of the household. Children had a 50% survival rate beyond age one, and began to contribute to family life around age twelve.
When did the Middle Ages begin?
The Middle Ages was the period in European history from the collapse of Roman civilization in the 5th century CE to the period of the Renaissance (...
What was the role of Christendom?
After the dissolution of the Roman Empire, the idea arose of Europe as one large church-state, called Christendom. Christendom consisted of two dis...
How long did the Migration Period last?
The Migration Period was a historical period sometimes called the Dark Ages, Late Antiquity, or the Early Middle Ages. The period lasted from the f...
What were the major artistic eras of the Middle Ages?
Romanesque art was the first of two great international artistic eras that flourished in Europe during the Middle Ages. Romanesque architecture eme...
What socio-economic system is perceived as characteristic of the Middle Ages?
Feudalism designates the social, economic, and political conditions in western Europe during the early Middle Ages, the long stretch of time betwee...
What is the Middle Ages?
People use the phrase “Middle Ages” to describe Europe between the fall of Rome in 476 CE and the beginning of the Renaissance in the 14th century. Many scholars call the era the “medieval period” instead; “Middle Ages,” they say, incorrectly implies that the period is an insignificant blip sandwiched between two much more important epochs.
How did the Middle Ages show devotion to the Church?
The Middle Ages: Art and Architecture. Another way to show devotion to the Church was to build grand cathedrals and other ecclesiastical structures such as monasteries. Cathedrals were the largest buildings in medieval Europe, and they could be found at the center of towns and cities across the continent.
Why did people become flagellants in the Middle Ages?
Understandably terrified about the mysterious disease, some people of the Middle Ages believed the plague was a divine punishment for sin. To obtain forgiveness, some people became “flagellants,” traveling Europe to put on public displays of penance that could include whipping and beating one another.
How did feudal life change?
During the 11th century, however, feudal life began to change. Agricultural innovations such as the heavy plow and three-field crop rotation made farming more efficient and productive, so fewer farm workers were needed–but thanks to the expanded and improved food supply, the population grew. As a result, more and more people were drawn to towns and cities. Meanwhile, the Crusades had expanded trade routes to the East and given Europeans a taste for imported goods such as wine, olive oil and luxurious textiles. As the commercial economy developed, port cities in particular thrived. By 1300, there were some 15 cities in Europe with a population of more than 50,000.
What was the most powerful institution in the medieval period?
After the fall of Rome, no single state or government united the people who lived on the European continent. Instead, the Catholic Church became the most powerful institution of the medieval period. Kings, queens and other leaders derived much of their power from their alliances with and protection of the Church.
What was the Renaissance?
In these cities, a new era was born: the Renaissance. The Renaissance was a time of great intellectual and economic change, but it was not a complete “rebirth”: It had its roots in the world of the Middle Ages.
What was the Islamic world like in 632 CE?
Meanwhile, the Islamic world was growing larger and more powerful. After the prophet Muhammad’s death in 632 CE, Muslim armies conquered large parts of the Middle East, uniting them under the rule of a single caliph. At its height, the medieval Islamic world was more than three times bigger than all of Christendom.
What was the Middle Ages?
The Middle Ages was the period in European history from the collapse of Roman civilization in the 5th century CE to the period of the Renaissance (variously interpreted as beginning in the 13th, 14th, or 15th century, depending on the region of Europe and other factors).
Who introduced the term "middle ages"?
For full treatment, see Europe, history of: The Middle Ages. The term and its conventional meaning were introduced by Italian humanists with invidious intent.
Why did the humanists create the Middle Ages?
In a sense, the humanists invented the Middle Ages in order to distinguish themselves from it. They were making a gesture of their sense of freedom, and yet, at the same time, they were implicitly accepting the medieval conception of history as a series of well-defined ages within a limited framework of time.
What is feudalism in the Middle Ages?
They refer to what those who invented them perceived as the most significant and distinctive characteristics of the early and central Middle Ages. A brief treatment of the Middle Ages follows.
What was the first major artistic era in Europe?
Romanesque art was the first of two great international artistic eras that flourished in Europe during the Middle Ages. Romanesque architecture emerged about 1000 and lasted until about 1150, by which time it had evolved into Gothic. Gothic art was the second of two great international eras that flourished in western and central Europe during the Middle Ages.Gothic art evolved from Romanesque art and lasted from the mid-12th century to as late as the end of the 16th century in some areas.
When did the migration period end?
The Migration period lasted from the fall of Rome to about the year 1000, with a brief hiatus during the flowering of the Carolingian court established by Charlemagne.
Where did Christianity spread?
Christianity spread throughout Europe and the Mediterranean area during the Middle Ages. Click on the boxes in the map key at upper right to see the expansion of Christianity and Islam and the separation between Western and Eastern Christianity in 1054.
When did the Middle Ages begin?
The Early Middle Ages (A.D. 476-1000) The Early Middle Ages, also known as Late Antiquity, began when with the fall of the Roman Empire in the 5th century and ended around the 10th century. It was a transitional period from Classical Antiquity in the ancient Greco-Roman world. Despite being termed the Dark Ages by 18th-century scholars, ...
What was the Middle Ages?
Lasting roughly 1,000 years from the 5th century to the 16th century, the Middle Ages was a pivotal time for religion, politics, science, literature, and human innovation.
What was the population surge in the Middle Ages?
The population surge of the High Middle Ages came to a sudden stop with the twin humanitarian crises of the Great Famine (A.D. 1315-1317) and the Black Death (1346-1353). Devastating weather brought poor crops and livestock disease, leading to a famine that killed over 25% of the European population in two years.
Why is the Dark Ages called the Dark Ages?
The primary reason is that there is not much recorded history in this time, so our knowledge of the period is "dark" compared to what we know of ancient Greece and Rome.
What was the purpose of feudalism?
The feudal system was designed to ease the monarch's burden of land ownership by delegating it to European Barons and lords.
What was the Crusades?
The Crusades were a series of holy wars between the Christians and the Muslims during the High Middle Ages. Christianity and the Holy Roman Empire were just starting to take shape as Islam spread, leading to violent clashes over possession of the Holy Land.
What was the Golden Age?
Islam's focus on knowledge led to the Islamic Golden Age (8th-14th centuries), a period of major scientific and economic advances, during this period. Some major Islamic figures during the Early Middle Ages included Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi (A.D. 780-850; "father of algebra"), Ibn Sina (A.D.
What was the Middle Ages?
The Middle Ages were a critically important period for Western Europe. The preceding “Dark Ages,” which lasted for hundreds of years after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, had been a time of chaos and poverty without strong central government to maintain order. During the period, Roman roads and water distribution systems decayed.
When did the Dark Ages begin?
Light began to enter the Dark Ages in the late 700s, when Charlemagne, the son of a powerful warlord controlling vast lands in what is now Germany, France, Austria, Hungary, and the Netherlands, became the leader of the Franks, the largest tribe in Europe. He and his family engaged in decades of military incursions and conquests to acquire ...
What is the Crusader Bible?
One early remarkable example is the illuminated book called the Crusader Bible (Morgan Bible) which was created in Northern France in 1240 and features action scenes complete with battle wounds being inflicted, and detailed realism including specific types of weapons, spurs, armor, and other actual garments.
What was the culture of the 1200s?
Culture grew, and by the 1200s art was no longer the sole realm of the Christian clergy. Artisans formed craft guilds, opened workshops, and sought commissions from the Church, government, the nobility, and the increasingly wealthy merchant class to create frescoes, panel paintings, and illuminated prayer books.
When did the Black Plague happen?
When the Black Plague struck in 1348-1350, much of what had been gained was in danger of being forever lost again when one-third of Europe’s population died. However, wealth became more consolidated in the hands of fewer families, and after recovery from the ravages of the disease there was a return to patronage of the arts—ultimately sewing the seeds for the coming Renaissance.
Who was the Father of Europe?
For all this, Charlemagne (Charles the Great) would be called "the Father of Europe.". One of the most beautiful works of this Carolingian period was a Gospel book created by the monk Godescalc —an extraordinary example of craft, art, calligraphy, and language.
When did the Middle Ages end?
It began with the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and is variously demarcated by historians as ending with the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, merging into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery . Early Middle Ages (also called Dark Ages) High Middle Ages. Late Middle Ages.
Which is the earliest period of the Stone Age?
Paleolithic – is the earliest period of the Stone Age. Lower Paleolithic — time of archaic human species, predates Homo habilies. Middle Paleolithic — coexistence of archaic and anatomically modern human species. Upper Paleolithic — worldwide expansion of anatomically modern humans, the disappearance of archaic humans by extinction ...
What is geologic time scale?
The geologic time scale covers the extent of the existence of Earth, from about 4600 million years ago to the present day. It is marked by Global Boundary Stratotype Sections and Points. Geologic time units are (in order of descending specificity) eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages; and the corresponding chronostratigraphic units, which measure "rock-time", are eonothems, erathems, systems, series, and stages.
What is the period between prehistory and history?
Protohistory – Period between prehistory and history, during which a culture or civilization has not yet developed writing but other cultures have already noted its existence in their own writings; the absolute time scale of "protohistory " varies widely depending on the region, from the late 4th millennium BCE in the Ancient Near East to the present in the case of uncontacted peoples.
What is the Greek and Roman world called?
Classical Antiquity – Broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world. It is the period in which Greek and Roman society flourished and wielded great influence throughout Europe, North Africa and the Middle East.
How many lines are there in a logarithmic timeline?
Logarithmic timeline shows all history on one page in ten lines.
What is the Upper Paleolithic?
Upper Paleolithic — worldwide expansion of anatomically modern humans, the disappearance of archaic humans by extinction or admixture with modern humans; earliest evidence for pictorial art.
How long did the Middle Ages last?
What this means is that it lasted for about a millennium, from the late 5 th century CE to the beginning of the Renaissance in the 15 th century CE.
What were the most important events of the Middle Ages?
The Middle Ages also introduced the world to some pretty horrific events such as the Black Death which killed several millions of people; the Hundred Years War; the Crusades; and the Wars of the Roses. The period was also a time rife with the feudal system of government and economics that saw peasants (or serfs) toil and break their backs in exchange for the protection given by their lords. Therefore unless one was a knight, a nobleman or even the king himself, life was pretty much difficult compared to the centuries that came after the Middle Ages.
Why were guilds formed?
They were formed with the sole purpose of protecting the interests of their members. It also gave them a united front against powerful lords or nobles. With regard to merchant guilds, it’s been said those guilds dictated a bulk part of the local economy. In typical fashion of the Middle Ages, women were not allowed to become members of the guilds.
What did the rich wear in the Middle Ages?
The rich lords and noblemen put on tunic, breaches and cloak. The women on the other hand, wore unusually long skirts ( kirtle) as a sign of modesty. Other important clothes for them were the apron and a cloak.
What were the three classes of medieval society?
Middle Ages – Definition, Summary and Timeline | Image: Medieval French manuscript showing the three classes of medieval society – the clergy, the knights, and the peasants (or serfs) | Li Livres dou Sante, 13th century. Here is a quick summary of what the Middle Ages were all about in Europe.
What were the common themes of the Middle Ages?
Common chivalry themes include being courageous, honor, integrity, and service to the weak and vulnerable.
How long did the Hundred Years War last?
1337: France and England lock horns in a bitter conflict called the Hundred Years War, which lasts for 116 years.
What era followed the Middle Ages?
The Early Modern Era, which immediately followed the Middle Ages, saw a resurgence of the values and philosophies from the Classical era. When you think of Leonardo da Vinci, William Shakespeare, Johann Sebastian Bach, and Christopher Columbus, you’re thinking of the Early Modern Era.
What is the Middle Ages?
The Middle Ages (A.D. 476 -A.D. 1450 ) The Middle Ages is also known as the Medieval or Post-Classical era. Historians refer to the early part of this period as the Dark Ages due to the loss of recorded history after the fall of the Roman Empire in A.D. 476.
How many eras are there in the Prehistoric era?
The Prehistoric era can be divided into three shorter eras based on the advancements that occurred in those time periods. They include: The Stone Age (2.5 million B.C. to 3000 B.C.) - documents the human migration from Africa and first use of tools by Neanderthals, Denisovans and early humans.
What was the name of the period that saw the Black Plague, the beginning of European exploration and the invention of the?
Late Middle Ages (A.D. 1250 to A.D. 1450) - a period that saw the Black Plague, the beginning of European exploration and the invention of the printing press
What were the major civilizations of the Classical Era?
These empires included: Ancient Greece (600 B.C. to A.D. 600) - foundation of democracy, philosophy, mathematics , drama, and poetry.
What are the five eras of history?
They use these resources to divide human existence into five main historical eras: Prehistory, Classical, Middle Ages, Early Modern, and Modern eras. Keep reading to learn the main civilizations, technological achievements, ...
How long did the Middle Ages last?
The Middle Ages was an unstable period that lasted for nearly a millennium. Historians often group the era into three distinct periods: the Early Middle Ages, the High Middle Ages and the Late Middle Ages.
Why are the Middle Ages called the Dark Ages?
Another reason why the Middle Ages are often called the Dark Ages is because, compared with other eras, historians don't know as much about this time. In some ways, this period of time has been lost to history.
When did the Dark Ages start?
Many textbooks list the Dark Ages as extending from 500-1500 AD, although it should be noted these are approximations. The term 'Dark Ages' was coined by an Italian scholar named Francesco Petrarch.
Why are the Middle Ages so dark?
Some scholars perceive Europe as having been plunged into darkness when the Roman Empire fell in around 500 AD. The Middle Ages are often said to be dark because of a supposed lack of scientific and cultural advancement.
Why are historians rethinking the Dark Ages?
That said, historians are increasingly rethinking the Dark Ages. Many no longer use the term because new scholarship is showing that this era may not have been as dark as had previously been thought.
What was the Dark Ages?
Traditionally, the Dark Ages was thought to be a time when little cultural development and scientific discovery happened. Learn more about the Dark Ages or the Middle Ages, and explore the controversy that surrounds the historical timeline of the era. Updated: 09/16/2021
What was the Catholic Church's position in the Dark Ages?
The Catholic Church was extremely institutionalized and often opposed the scientific and cultural advancements the Greeks and Romans had pioneered. The Dark Ages were a difficult time in which to live: famine and disease were common.
What is the term for the period between the fall of Rome and the beginning of the Italian Renaissance?
Dark Ages: Another term for the middle ages; the period of time between the fall of Rome and the beginning of the Italian Renaissance. Feudalism: A system of labor that hindered upward social mobility. Bubonic Plague: A plague that devastated Europe in the late 1340s and early 1350s. Learning Outcomes.